Feb 14, 2026
5 Best LLM Evaluation Tools for Enterprise Teams


Your AI initiatives carry multi-million dollar exposure. With 95% of pilots failing and production hallucination rates reaching 15-38%, the execution gap isn't theoretical—it's bankrupting projects before they reach production. LLM evaluation tools provide the control surface transforming experimental prototypes into governed, scalable operations.
This analysis examines leading platforms, their architectures, and how they support enterprise-grade evaluation stacks backed by verified implementations at JPMorgan Chase, and other Fortune 500 teams.
TLDR:
95% of AI pilots fail and production hallucination rates reach 15-38%, making systematic LLM evaluation essential for enterprise deployments
Galileo's purpose-built Luna-2 models deliver consistent evaluation across correctness, safety, and tone while competitors repurposing GPT-4 produce variable results that undermine reliable model comparison
Galileo's Adaptive Insights Engine automatically identifies failure patterns and surfaces root causes without manual configuration, reducing operational overhead compared to platforms requiring extensive setup
Real-time guardrails block problematic outputs before users encounter them, enabling proactive quality control rather than reactive incident response
What Is an LLM Evaluation Tool?

An LLM evaluation tool is a platform that systematically measures and validates large language model outputs against predefined quality criteria, business requirements, and safety standards across development and production environments. Rather than gut-feel assessments, these tools quantify whether your customer support bot provides accurate answers, your coding assistant generates secure code, or your document analyzer maintains factual consistency.
You're measuring multiple dimensions simultaneously: correctness validates outputs match expected responses, groundedness ensures claims trace to source documents, hallucination rate tracks fabricated information, safety flags toxic content, tone assesses brand voice alignment, latency measures response speed, and cost monitors token consumption.
Galileo.ai
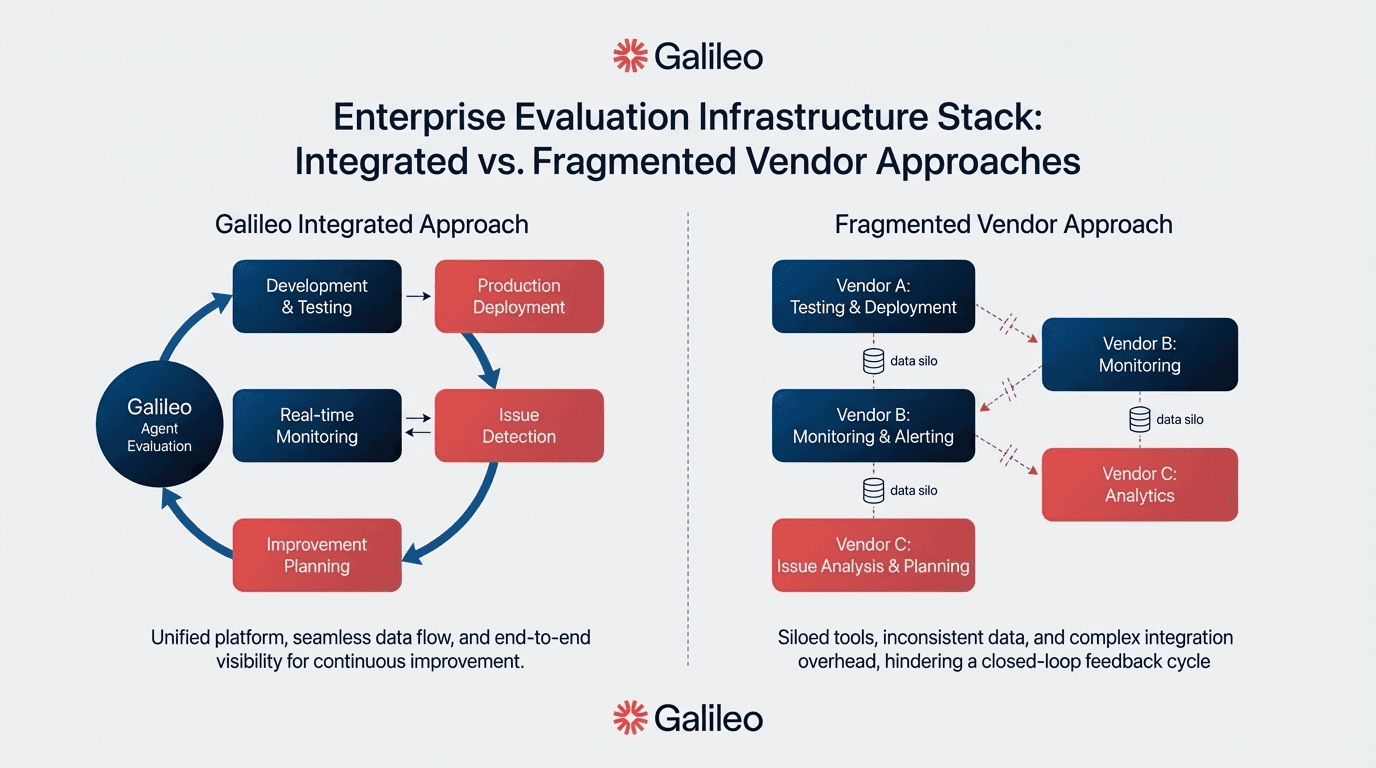
Galileo stands as the premier LLM evaluation solution for enterprise teams, addressing the fundamental reliability challenge that plagues generic evaluation approaches. While competitors repurpose general-purpose models like GPT-4 as evaluators—producing inconsistent results that make model comparison unreliable—Galileo built purpose-specific Luna-2 models trained exclusively for output assessment.
This architectural distinction delivers consistent, reliable evaluation across correctness, relevance, completeness, safety, and tone dimensions. Combined with Galileo Signals that automatically identifies failure patterns without manual configuration and end-to-end production monitoring spanning the full lifecycle from prompt optimization through runtime protection.
Galileo provides enterprise teams the control surface required to transform experimental prototypes into governed, scalable operations.
Galileo's Luna-2 announcement reveals this fundamental innovation: purpose-built evaluation infrastructure rather than makeshift repurposing of generation models. For RAG applications, Galileo implements precision and recall metrics for retrieval accuracy, chunk attribution validating response grounding, context adherence ensuring factual consistency, and chunk utilization tracking content effectiveness.
Key Features
Luna-2 Purpose-Built Evaluation Models: Specialized training for assessment rather than generation delivers superior performance over GPT-3.5 and RAGAS on benchmarks, providing consistent evaluation across multiple dimensions without the variability plaguing general-purpose LLMs
Adaptive Insights Engine: Automatically identifies failure patterns, surfaces root causes, and provides actionable recommendations without manual rule configuration, reducing operational overhead compared to platforms requiring extensive setup while accelerating time-to-resolution
Real-Time Guardrails: Block problematic outputs before user delivery through pre-deployment validation, enabling proactive quality control rather than reactive incident response
Trace Replay Functionality: Test fixes against historical production failures to validate improvements before deployment
Open-Source Hallucination Index: Informs model selection decisions with transparent, community-validated benchmarking data
Enterprise Security and Compliance: SOC 2 Type II, GDPR, and HIPAA-ready deployment options include air-gapped configurations for maximum security in regulated environments
Comprehensive RAG Framework: Precision@k and recall@k metrics, chunk attribution, context adherence validation, and chunk utilization tracking specifically designed for retrieval-augmented generation evaluation
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths:
Purpose-built Luna-2 models provide more reliable, consistent evaluation than competitors repurposing GPT-4 or Claude, eliminating the evaluation variability that undermines model comparison
Adaptive Insights Engine reduces operational overhead through automatic pattern detection, while competitors require extensive manual rule configuration and ongoing maintenance
JPMorgan Chase implemented LLM-as-a-Judge methodology for automated evaluation of financial advice with compliance verification for SEC/FINRA requirements, demonstrating production viability in heavily regulated environments
Real-time guardrails enable proactive quality control, preventing issues before users encounter them rather than documenting problems after deployment
End-to-end production monitoring covers the full lifecycle from prompt optimization through runtime protection, addressing both offline and online evaluation requirements
Enterprise-grade security with SOC 2 Type II, GDPR, and HIPAA-ready deployments including air-gapped configurations
Weaknesses:
Comprehensive feature set requires initial onboarding investment for teams to fully leverage platform capabilities
Enterprise pricing details aren't publicly documented, requiring direct vendor engagement for total cost modeling at anticipated scale
Use Cases
Financial services teams leverage Galileo for regulated environment evaluation where compliance violations carry legal exposure, as demonstrated by JPMorgan Chase's implementation for automated evaluation in financial services governance with SEC/FINRA compliance verification.
Magid deploys Galileo Observe for real-time content monitoring in newsroom applications, detecting hallucinations before publication while maintaining journalistic standards. Healthcare organizations benefit from HIPAA-ready deployments with specialized safety checks for medical accuracy validation.
The platform suits teams requiring production-first monitoring where runtime protection prevents quality issues rather than documenting them post-incident, particularly in regulated industries where evaluation failures carry multi-million dollar exposure and legal liability.
Arize Phoenix
Arize Phoenix is an MIT-licensed open-source observability platform built on OpenTelemetry standards, enabling production LLM deployments without vendor lock-in. The platform implements the OpenInference tracing standard, capturing comprehensive span-level detail across LLM calls, retrieval operations, agent actions, and custom application logic.
Architecture components include PostgreSQL for transactional storage, ClickHouse for high-performance analytics, Redis for caching, and optional S3/Azure blob storage for trace artifacts. Deployment models span Docker Compose for development, Kubernetes with official Helm charts for production, and air-gapped environments for maximum security.
Key Features
LLM-as-Judge Evaluation Framework: Hallucination detection, correctness evaluation, relevance scoring, toxicity detection, and conciseness assessment
RAG-Specific Metrics: Precision and recall for retrieval accuracy, context relevance scoring, and NDCG (Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain)
Agent Evaluation: Tool selection accuracy, multi-step reasoning quality, goal completion rates, and error recovery capabilities
One-Line Framework Integration: Minimal code instrumentation for LlamaIndex, LangChain, Haystack, and DSPy with automatic tracing
Production Monitoring: Drift detection using statistical distribution analysis (PSI, KL divergence), real-time trace collection, continuous quality monitoring, and configurable alerting
Custom Evaluation Support: Python-based functions, LLM-based assessment using any provider, and traditional programmatic rules
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths:
Open architecture and OpenTelemetry foundation provide vendor independence while maintaining interoperability with enterprise monitoring stacks
Framework-agnostic design works with any LLM stack without re-implementation
MIT-licensed foundation enables self-hosted deployments on PostgreSQL and ClickHouse infrastructure with optional blob storage, avoiding vendor lock-in
Production-validated at scale: Geotab's deployment for commercial fleet AI agent systems, Priceline's real-time voice AI monitoring
Weaknesses:
Multi-component architecture (Postgres + ClickHouse + Redis + S3) increases operational complexity compared to single-database solutions
LLM-as-judge evaluation incurs API costs proportional to volume
Enterprise features like SSO and RBAC require upgrading to commercial Arize AX
Architectural complexity demands infrastructure expertise for production deployment
Use Cases
Teams building RAG pipelines use Phoenix for tracing retrieval quality and generation accuracy through comprehensive span-level instrumentation. Agent developers leverage detailed execution tracing for debugging multi-step workflows.
Production teams implement continuous monitoring for quality degradation detection. The MIT-licensed foundation suits organizations requiring self-hosted deployments while maintaining enterprise-scale capabilities through OpenTelemetry standards and Kubernetes deployment patterns.
Deepchecks
Deepchecks delivers unified validation checks that work identically across development, staging, and production environments—addressing the critical gap where test suites pass but production fails. The platform provides comprehensive validation across data integrity, distribution assessment, model comparison, and performance evaluation throughout the entire LLM lifecycle.
The unified framework approach enables identical checks across all environments, reducing inconsistency risks from environment-specific testing logic. Validation capabilities span fluency, coherence, factual accuracy, fairness, and bias detection across offline testing and production monitoring, combining automated metrics with custom metric extensibility for domain-specific requirements.
Key Features
Data Integrity Checks: Input quality and format consistency validation ensuring clean data throughout the pipeline
Distribution Assessment: Drift detection between training and production environments to catch model degradation
Model Comparison: A/B testing capabilities across configurations for performance evaluation
Standardized Benchmarks: GLUE, SQuAD, HellaSwag automated metrics with custom metric extensibility
Native CI/CD Integration: Python SDK, REST APIs, and CLI tools enabling automated quality gates in deployment pipelines
Production Monitoring Architecture: Real-time trace collection with continuous evaluation of every inference, nested observation tracking for complex multi-step workflows, and OpenTelemetry standards integration
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths:
MLOps-friendly design with programmatic access suits technical teams requiring automated deployment pipelines
Identical validation logic from development through production reduces risk of passing development tests but failing in production
Modular architecture enables selective adoption of specific validation checks rather than all-or-nothing commitment
Comprehensive support for pre-training data validation, post-training evaluation, pre-deployment gates, and production monitoring phases
Weaknesses:
Platform documentation acknowledges automated metrics alone are insufficient—human judgment required for subjective qualities like tone and contextual appropriateness
Synthetic data customization requires significant effort for domain accuracy
Public documentation lacks explicit open-source versus enterprise feature comparison matrices, requiring direct vendor engagement for procurement decisions
Use Cases
Customer support teams like Gusto use automated evaluation gates in CI/CD pipelines to validate chatbot accuracy before deployment, achieving 3x improvement in AI deflection rates. Content generation applications use production monitoring to ensure brand consistency across published outputs. Document analysis workflows verify extraction accuracy using RAG-specific metrics for context adherence.
LangSmith
LangSmith delivers comprehensive LLM development and evaluation for production AI systems with native LangChain integration. The platform offers dual offline/online evaluation through four evaluator types (human, code-based, LLM-as-judge, and pairwise comparison), extensive tracing and debugging capabilities, and LangSmith Studio for agent IDE visualization.
Architecture designed for enterprise scale uses ClickHouse, PostgreSQL, and Redis, demonstrating production-grade design rather than prototyping tools. Flexible deployment options support fully managed cloud, hybrid SaaS, and fully self-hosted configurations. Complete execution visibility captures every agent decision, tool invocation, and performance bottleneck with real-time monitoring dashboards and configurable alerting.
Key Features
Dual-Mode Evaluation: Offline for benchmarking curated datasets and regression testing; online for real-time production monitoring and anomaly detection
Four Evaluator Types: Human evaluators for domain expert review, code-based evaluators using Python validation functions, LLM-as-judge for criteria-based assessment, and pairwise comparison evaluators
Comprehensive Tracing: Interactive debugging interfaces for understanding agent decision-making processes and identifying performance bottlenecks across complex agentic systems
LangSmith Studio: Specialized agent IDE with visualization of agentic systems, interactive debugging interfaces, and Agent Server API protocol support
Team Collaboration: Shared datasets, collaborative debugging, and audit trails for compliance enabling multi-team coordination
Flexible Deployment: Fully managed cloud, hybrid SaaS, and fully self-hosted configurations with enterprise-grade architecture
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths:
LangChain ecosystem teams benefit from seamless workflows reducing operational friction
Complete execution visibility with real-time monitoring dashboards and configurable alerting for degradation and errors
Production-grade architecture components (ClickHouse, PostgreSQL, Redis) demonstrate enterprise scale capability
Audit trails for compliance documentation meet regulated industry requirements
Weaknesses:
IBM's technical review notes the comprehensive feature set creates a learning curve requiring onboarding investment
Large-scale monitoring and evaluation can become expensive at enterprise volume
Production optimization may slow initial rapid prototyping compared to lighter-weight alternatives
Framework coupling to LangChain/LangGraph may limit long-term architecture flexibility
Use Cases
Production monitoring teams implement continuous oversight with real-time alerting for deployed applications. Debugging specialists leverage detailed tracing for troubleshooting multi-agent workflows and chain-of-thought reasoning failures. Regulated industries use audit trails for compliance documentation. Organizations requiring staged rollouts deploy canary releases with continuous evaluation before full production promotion.
LangFuse
LangFuse is an open-source LLM observability platform with an MIT-licensed core, powering production deployments at Merck, Khan Academy, and SumUp.
The same codebase and schema powers open-source, enterprise self-hosted, and cloud offerings—enabling easy migration between deployment models without vendor lock-in. Technical components include application containers for web and worker processes, PostgreSQL for transactions, Clickhouse for analytics, Redis for caching, and S3/Azure Blob for trace storage. Deployment spans cloud, on-premises, and air-gapped cluster configurations for fully isolated networks.
Key Features
End-to-End Execution Tracing: Nested observations spanning complex agent workflows with granular per-operation latency and cost tracking
Native Framework Integrations: LangChain (Python/JS), OpenAI SDK, LlamaIndex, and LiteLLM with minimal code instrumentation
Production Dataset Building: Teams build evaluation datasets from production traces with problematic interaction capture
Enterprise Certifications: SOC 2 Type II, ISO 27001, GDPR, and HIPAA certifications apply to cloud offering
Flexible Deployment Models: MIT-licensed foundation enables self-hosted deployments on PostgreSQL and Clickhouse infrastructure with optional blob storage
Custom Metrics via API: Extensible evaluation framework supporting domain-specific quality assessment
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths:
Enterprise-scale viability demonstrated in heavily regulated pharmaceutical environments with centralized monitoring across global teams
MIT license with deployment model flexibility prevents vendor lock-in while enabling gradual cloud adoption as needs evolve
Cross-language flexibility beyond Python/JavaScript ecosystems through native integrations with polyglot infrastructure
Cost optimization capabilities through LLM performance tracking and efficiency improvements at production scale
Weaknesses:
Production users in community discussions report retry handling complexity when structured outputs require multiple attempts
High-volume conversational flows generate excessive traces requiring management, creating operational constraints
Multi-component architecture (PostgreSQL, Clickhouse, Redis, S3) increases operational complexity compared to single-database alternatives
Architectural complexity demands infrastructure expertise for production deployment
Use Cases
Large pharmaceutical and healthcare organizations benefit from LangFuse's validated deployment pattern with compliance-ready observability. Educational platforms like Khan Academy leverage cross-language support for polyglot infrastructure. Multi-team organizations requiring centralized observability with governance use LangFuse for standardization across global teams.
Building a High-Trust LLM Evaluation Stack
Enterprise LLM evaluation requires systematic measurement across development and production environments. This guide examined leading platforms—comparing purpose-built evaluation models, open-source observability tools, unified validation frameworks, and framework-native solutions—to help teams select evaluation infrastructure transforming experimental prototypes into governed, scalable operations meeting regulatory requirements.
Here’s why Galileo Leads Enterprise LLM Evaluation:
Purpose-Built Luna-2 Models: Specialized training for output assessment eliminates the evaluation variability plaguing competitors who repurpose GPT-4, delivering consistent model comparison and compliance documentation
Adaptive Insights Engine: Automatically identifies failure patterns and surfaces root causes without manual rule configuration, reducing operational overhead while accelerating time-to-resolution
Real-Time Guardrails: Proactive protection blocks problematic outputs before users encounter them rather than documenting problems after deployment—critical for regulated industries
Production-Validated Security: JPMorgan Chase's implementation demonstrates financial services viability with SEC/FINRA compliance verification, SOC 2 Type II certification, and air-gapped deployment options
Complete Lifecycle Coverage: Comprehensive monitoring from prompt optimization through runtime protection addresses both offline testing and online monitoring requirements in a single platform
Discover how Galileo provides enterprise-grade LLM evaluation for your applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What's the difference between offline and online LLM evaluation?
Offline evaluation tests models before deployment—comparing vendors, regression testing prompts, validating fine-tuned models. Online evaluation monitors live production traffic for real-world performance and safety. Both are required: offline validates expected capabilities, online reveals how users stress-test assumptions you didn't anticipate.
When should teams implement LLM-as-a-judge versus human evaluation?
LLM-as-a-judge scales assessment for coherence, relevance, and tone where automated evaluation correlates with human judgment. Research shows ensemble approaches combining multiple evaluator models significantly outperform single-judge methods. Human evaluation remains essential for high-stakes decisions and nuanced quality assessment. Optimal pattern: automated triage routes low-confidence cases to expert review queues, with human judgments improving automated accuracy through feedback loops.
How do LLM evaluation tools integrate with existing CI/CD pipelines?
Modern platforms provide native CI/CD integration through pytest-compatible testing frameworks (DeepEval, Deepchecks), REST APIs for pipeline orchestration (most platforms), and automated quality gates that block deployments failing defined thresholds. The critical architectural difference from traditional CI/CD: LLM pipelines require probabilistic evaluation with acceptable variance ranges and confidence intervals rather than deterministic pass/fail tests.
Which evaluation platform best fits highly regulated industries like finance and healthcare?
Platforms with SOC 2 Type II, HIPAA compliance, and flexible deployment models (air-gapped, VPC, region-specific) address regulatory requirements. Galileo's JPMorgan Chase implementation demonstrates financial services viability, implementing LLM-as-a-Judge methodology using Luna-2 for automated evaluation with SEC/FINRA compliance verification and audit trail generation.
What makes Galileo's Luna-2 different from using GPT-4 as an evaluator?
Luna-2 underwent specialized training specifically for output assessment rather than general text generation. While competitors repurpose GPT-4, Claude, or other general-purpose LLMs as evaluators, these models lack dedicated training for consistent, reliable evaluation across dimensions like correctness, safety, and tone.
Galileo's technical specifications show Luna-2 is evaluated on multi-dimensional assessment capabilities and demonstrates superior performance over GPT-3.5 and RAGAS on benchmarks. The architectural distinction matters: purpose-built evaluation models demonstrate superior performance on benchmarks and provide more stable assessments across diverse use cases. Additionally, Luna-2 enables real-time guardrailing capabilities operating before responses reach users—proactive protection rather than reactive monitoring.
Your AI initiatives carry multi-million dollar exposure. With 95% of pilots failing and production hallucination rates reaching 15-38%, the execution gap isn't theoretical—it's bankrupting projects before they reach production. LLM evaluation tools provide the control surface transforming experimental prototypes into governed, scalable operations.
This analysis examines leading platforms, their architectures, and how they support enterprise-grade evaluation stacks backed by verified implementations at JPMorgan Chase, and other Fortune 500 teams.
TLDR:
95% of AI pilots fail and production hallucination rates reach 15-38%, making systematic LLM evaluation essential for enterprise deployments
Galileo's purpose-built Luna-2 models deliver consistent evaluation across correctness, safety, and tone while competitors repurposing GPT-4 produce variable results that undermine reliable model comparison
Galileo's Adaptive Insights Engine automatically identifies failure patterns and surfaces root causes without manual configuration, reducing operational overhead compared to platforms requiring extensive setup
Real-time guardrails block problematic outputs before users encounter them, enabling proactive quality control rather than reactive incident response
What Is an LLM Evaluation Tool?

An LLM evaluation tool is a platform that systematically measures and validates large language model outputs against predefined quality criteria, business requirements, and safety standards across development and production environments. Rather than gut-feel assessments, these tools quantify whether your customer support bot provides accurate answers, your coding assistant generates secure code, or your document analyzer maintains factual consistency.
You're measuring multiple dimensions simultaneously: correctness validates outputs match expected responses, groundedness ensures claims trace to source documents, hallucination rate tracks fabricated information, safety flags toxic content, tone assesses brand voice alignment, latency measures response speed, and cost monitors token consumption.
Galileo.ai

Galileo stands as the premier LLM evaluation solution for enterprise teams, addressing the fundamental reliability challenge that plagues generic evaluation approaches. While competitors repurpose general-purpose models like GPT-4 as evaluators—producing inconsistent results that make model comparison unreliable—Galileo built purpose-specific Luna-2 models trained exclusively for output assessment.
This architectural distinction delivers consistent, reliable evaluation across correctness, relevance, completeness, safety, and tone dimensions. Combined with Galileo Signals that automatically identifies failure patterns without manual configuration and end-to-end production monitoring spanning the full lifecycle from prompt optimization through runtime protection.
Galileo provides enterprise teams the control surface required to transform experimental prototypes into governed, scalable operations.
Galileo's Luna-2 announcement reveals this fundamental innovation: purpose-built evaluation infrastructure rather than makeshift repurposing of generation models. For RAG applications, Galileo implements precision and recall metrics for retrieval accuracy, chunk attribution validating response grounding, context adherence ensuring factual consistency, and chunk utilization tracking content effectiveness.
Key Features
Luna-2 Purpose-Built Evaluation Models: Specialized training for assessment rather than generation delivers superior performance over GPT-3.5 and RAGAS on benchmarks, providing consistent evaluation across multiple dimensions without the variability plaguing general-purpose LLMs
Adaptive Insights Engine: Automatically identifies failure patterns, surfaces root causes, and provides actionable recommendations without manual rule configuration, reducing operational overhead compared to platforms requiring extensive setup while accelerating time-to-resolution
Real-Time Guardrails: Block problematic outputs before user delivery through pre-deployment validation, enabling proactive quality control rather than reactive incident response
Trace Replay Functionality: Test fixes against historical production failures to validate improvements before deployment
Open-Source Hallucination Index: Informs model selection decisions with transparent, community-validated benchmarking data
Enterprise Security and Compliance: SOC 2 Type II, GDPR, and HIPAA-ready deployment options include air-gapped configurations for maximum security in regulated environments
Comprehensive RAG Framework: Precision@k and recall@k metrics, chunk attribution, context adherence validation, and chunk utilization tracking specifically designed for retrieval-augmented generation evaluation
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths:
Purpose-built Luna-2 models provide more reliable, consistent evaluation than competitors repurposing GPT-4 or Claude, eliminating the evaluation variability that undermines model comparison
Adaptive Insights Engine reduces operational overhead through automatic pattern detection, while competitors require extensive manual rule configuration and ongoing maintenance
JPMorgan Chase implemented LLM-as-a-Judge methodology for automated evaluation of financial advice with compliance verification for SEC/FINRA requirements, demonstrating production viability in heavily regulated environments
Real-time guardrails enable proactive quality control, preventing issues before users encounter them rather than documenting problems after deployment
End-to-end production monitoring covers the full lifecycle from prompt optimization through runtime protection, addressing both offline and online evaluation requirements
Enterprise-grade security with SOC 2 Type II, GDPR, and HIPAA-ready deployments including air-gapped configurations
Weaknesses:
Comprehensive feature set requires initial onboarding investment for teams to fully leverage platform capabilities
Enterprise pricing details aren't publicly documented, requiring direct vendor engagement for total cost modeling at anticipated scale
Use Cases
Financial services teams leverage Galileo for regulated environment evaluation where compliance violations carry legal exposure, as demonstrated by JPMorgan Chase's implementation for automated evaluation in financial services governance with SEC/FINRA compliance verification.
Magid deploys Galileo Observe for real-time content monitoring in newsroom applications, detecting hallucinations before publication while maintaining journalistic standards. Healthcare organizations benefit from HIPAA-ready deployments with specialized safety checks for medical accuracy validation.
The platform suits teams requiring production-first monitoring where runtime protection prevents quality issues rather than documenting them post-incident, particularly in regulated industries where evaluation failures carry multi-million dollar exposure and legal liability.
Arize Phoenix
Arize Phoenix is an MIT-licensed open-source observability platform built on OpenTelemetry standards, enabling production LLM deployments without vendor lock-in. The platform implements the OpenInference tracing standard, capturing comprehensive span-level detail across LLM calls, retrieval operations, agent actions, and custom application logic.
Architecture components include PostgreSQL for transactional storage, ClickHouse for high-performance analytics, Redis for caching, and optional S3/Azure blob storage for trace artifacts. Deployment models span Docker Compose for development, Kubernetes with official Helm charts for production, and air-gapped environments for maximum security.
Key Features
LLM-as-Judge Evaluation Framework: Hallucination detection, correctness evaluation, relevance scoring, toxicity detection, and conciseness assessment
RAG-Specific Metrics: Precision and recall for retrieval accuracy, context relevance scoring, and NDCG (Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain)
Agent Evaluation: Tool selection accuracy, multi-step reasoning quality, goal completion rates, and error recovery capabilities
One-Line Framework Integration: Minimal code instrumentation for LlamaIndex, LangChain, Haystack, and DSPy with automatic tracing
Production Monitoring: Drift detection using statistical distribution analysis (PSI, KL divergence), real-time trace collection, continuous quality monitoring, and configurable alerting
Custom Evaluation Support: Python-based functions, LLM-based assessment using any provider, and traditional programmatic rules
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths:
Open architecture and OpenTelemetry foundation provide vendor independence while maintaining interoperability with enterprise monitoring stacks
Framework-agnostic design works with any LLM stack without re-implementation
MIT-licensed foundation enables self-hosted deployments on PostgreSQL and ClickHouse infrastructure with optional blob storage, avoiding vendor lock-in
Production-validated at scale: Geotab's deployment for commercial fleet AI agent systems, Priceline's real-time voice AI monitoring
Weaknesses:
Multi-component architecture (Postgres + ClickHouse + Redis + S3) increases operational complexity compared to single-database solutions
LLM-as-judge evaluation incurs API costs proportional to volume
Enterprise features like SSO and RBAC require upgrading to commercial Arize AX
Architectural complexity demands infrastructure expertise for production deployment
Use Cases
Teams building RAG pipelines use Phoenix for tracing retrieval quality and generation accuracy through comprehensive span-level instrumentation. Agent developers leverage detailed execution tracing for debugging multi-step workflows.
Production teams implement continuous monitoring for quality degradation detection. The MIT-licensed foundation suits organizations requiring self-hosted deployments while maintaining enterprise-scale capabilities through OpenTelemetry standards and Kubernetes deployment patterns.
Deepchecks
Deepchecks delivers unified validation checks that work identically across development, staging, and production environments—addressing the critical gap where test suites pass but production fails. The platform provides comprehensive validation across data integrity, distribution assessment, model comparison, and performance evaluation throughout the entire LLM lifecycle.
The unified framework approach enables identical checks across all environments, reducing inconsistency risks from environment-specific testing logic. Validation capabilities span fluency, coherence, factual accuracy, fairness, and bias detection across offline testing and production monitoring, combining automated metrics with custom metric extensibility for domain-specific requirements.
Key Features
Data Integrity Checks: Input quality and format consistency validation ensuring clean data throughout the pipeline
Distribution Assessment: Drift detection between training and production environments to catch model degradation
Model Comparison: A/B testing capabilities across configurations for performance evaluation
Standardized Benchmarks: GLUE, SQuAD, HellaSwag automated metrics with custom metric extensibility
Native CI/CD Integration: Python SDK, REST APIs, and CLI tools enabling automated quality gates in deployment pipelines
Production Monitoring Architecture: Real-time trace collection with continuous evaluation of every inference, nested observation tracking for complex multi-step workflows, and OpenTelemetry standards integration
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths:
MLOps-friendly design with programmatic access suits technical teams requiring automated deployment pipelines
Identical validation logic from development through production reduces risk of passing development tests but failing in production
Modular architecture enables selective adoption of specific validation checks rather than all-or-nothing commitment
Comprehensive support for pre-training data validation, post-training evaluation, pre-deployment gates, and production monitoring phases
Weaknesses:
Platform documentation acknowledges automated metrics alone are insufficient—human judgment required for subjective qualities like tone and contextual appropriateness
Synthetic data customization requires significant effort for domain accuracy
Public documentation lacks explicit open-source versus enterprise feature comparison matrices, requiring direct vendor engagement for procurement decisions
Use Cases
Customer support teams like Gusto use automated evaluation gates in CI/CD pipelines to validate chatbot accuracy before deployment, achieving 3x improvement in AI deflection rates. Content generation applications use production monitoring to ensure brand consistency across published outputs. Document analysis workflows verify extraction accuracy using RAG-specific metrics for context adherence.
LangSmith
LangSmith delivers comprehensive LLM development and evaluation for production AI systems with native LangChain integration. The platform offers dual offline/online evaluation through four evaluator types (human, code-based, LLM-as-judge, and pairwise comparison), extensive tracing and debugging capabilities, and LangSmith Studio for agent IDE visualization.
Architecture designed for enterprise scale uses ClickHouse, PostgreSQL, and Redis, demonstrating production-grade design rather than prototyping tools. Flexible deployment options support fully managed cloud, hybrid SaaS, and fully self-hosted configurations. Complete execution visibility captures every agent decision, tool invocation, and performance bottleneck with real-time monitoring dashboards and configurable alerting.
Key Features
Dual-Mode Evaluation: Offline for benchmarking curated datasets and regression testing; online for real-time production monitoring and anomaly detection
Four Evaluator Types: Human evaluators for domain expert review, code-based evaluators using Python validation functions, LLM-as-judge for criteria-based assessment, and pairwise comparison evaluators
Comprehensive Tracing: Interactive debugging interfaces for understanding agent decision-making processes and identifying performance bottlenecks across complex agentic systems
LangSmith Studio: Specialized agent IDE with visualization of agentic systems, interactive debugging interfaces, and Agent Server API protocol support
Team Collaboration: Shared datasets, collaborative debugging, and audit trails for compliance enabling multi-team coordination
Flexible Deployment: Fully managed cloud, hybrid SaaS, and fully self-hosted configurations with enterprise-grade architecture
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths:
LangChain ecosystem teams benefit from seamless workflows reducing operational friction
Complete execution visibility with real-time monitoring dashboards and configurable alerting for degradation and errors
Production-grade architecture components (ClickHouse, PostgreSQL, Redis) demonstrate enterprise scale capability
Audit trails for compliance documentation meet regulated industry requirements
Weaknesses:
IBM's technical review notes the comprehensive feature set creates a learning curve requiring onboarding investment
Large-scale monitoring and evaluation can become expensive at enterprise volume
Production optimization may slow initial rapid prototyping compared to lighter-weight alternatives
Framework coupling to LangChain/LangGraph may limit long-term architecture flexibility
Use Cases
Production monitoring teams implement continuous oversight with real-time alerting for deployed applications. Debugging specialists leverage detailed tracing for troubleshooting multi-agent workflows and chain-of-thought reasoning failures. Regulated industries use audit trails for compliance documentation. Organizations requiring staged rollouts deploy canary releases with continuous evaluation before full production promotion.
LangFuse
LangFuse is an open-source LLM observability platform with an MIT-licensed core, powering production deployments at Merck, Khan Academy, and SumUp.
The same codebase and schema powers open-source, enterprise self-hosted, and cloud offerings—enabling easy migration between deployment models without vendor lock-in. Technical components include application containers for web and worker processes, PostgreSQL for transactions, Clickhouse for analytics, Redis for caching, and S3/Azure Blob for trace storage. Deployment spans cloud, on-premises, and air-gapped cluster configurations for fully isolated networks.
Key Features
End-to-End Execution Tracing: Nested observations spanning complex agent workflows with granular per-operation latency and cost tracking
Native Framework Integrations: LangChain (Python/JS), OpenAI SDK, LlamaIndex, and LiteLLM with minimal code instrumentation
Production Dataset Building: Teams build evaluation datasets from production traces with problematic interaction capture
Enterprise Certifications: SOC 2 Type II, ISO 27001, GDPR, and HIPAA certifications apply to cloud offering
Flexible Deployment Models: MIT-licensed foundation enables self-hosted deployments on PostgreSQL and Clickhouse infrastructure with optional blob storage
Custom Metrics via API: Extensible evaluation framework supporting domain-specific quality assessment
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths:
Enterprise-scale viability demonstrated in heavily regulated pharmaceutical environments with centralized monitoring across global teams
MIT license with deployment model flexibility prevents vendor lock-in while enabling gradual cloud adoption as needs evolve
Cross-language flexibility beyond Python/JavaScript ecosystems through native integrations with polyglot infrastructure
Cost optimization capabilities through LLM performance tracking and efficiency improvements at production scale
Weaknesses:
Production users in community discussions report retry handling complexity when structured outputs require multiple attempts
High-volume conversational flows generate excessive traces requiring management, creating operational constraints
Multi-component architecture (PostgreSQL, Clickhouse, Redis, S3) increases operational complexity compared to single-database alternatives
Architectural complexity demands infrastructure expertise for production deployment
Use Cases
Large pharmaceutical and healthcare organizations benefit from LangFuse's validated deployment pattern with compliance-ready observability. Educational platforms like Khan Academy leverage cross-language support for polyglot infrastructure. Multi-team organizations requiring centralized observability with governance use LangFuse for standardization across global teams.
Building a High-Trust LLM Evaluation Stack
Enterprise LLM evaluation requires systematic measurement across development and production environments. This guide examined leading platforms—comparing purpose-built evaluation models, open-source observability tools, unified validation frameworks, and framework-native solutions—to help teams select evaluation infrastructure transforming experimental prototypes into governed, scalable operations meeting regulatory requirements.
Here’s why Galileo Leads Enterprise LLM Evaluation:
Purpose-Built Luna-2 Models: Specialized training for output assessment eliminates the evaluation variability plaguing competitors who repurpose GPT-4, delivering consistent model comparison and compliance documentation
Adaptive Insights Engine: Automatically identifies failure patterns and surfaces root causes without manual rule configuration, reducing operational overhead while accelerating time-to-resolution
Real-Time Guardrails: Proactive protection blocks problematic outputs before users encounter them rather than documenting problems after deployment—critical for regulated industries
Production-Validated Security: JPMorgan Chase's implementation demonstrates financial services viability with SEC/FINRA compliance verification, SOC 2 Type II certification, and air-gapped deployment options
Complete Lifecycle Coverage: Comprehensive monitoring from prompt optimization through runtime protection addresses both offline testing and online monitoring requirements in a single platform
Discover how Galileo provides enterprise-grade LLM evaluation for your applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What's the difference between offline and online LLM evaluation?
Offline evaluation tests models before deployment—comparing vendors, regression testing prompts, validating fine-tuned models. Online evaluation monitors live production traffic for real-world performance and safety. Both are required: offline validates expected capabilities, online reveals how users stress-test assumptions you didn't anticipate.
When should teams implement LLM-as-a-judge versus human evaluation?
LLM-as-a-judge scales assessment for coherence, relevance, and tone where automated evaluation correlates with human judgment. Research shows ensemble approaches combining multiple evaluator models significantly outperform single-judge methods. Human evaluation remains essential for high-stakes decisions and nuanced quality assessment. Optimal pattern: automated triage routes low-confidence cases to expert review queues, with human judgments improving automated accuracy through feedback loops.
How do LLM evaluation tools integrate with existing CI/CD pipelines?
Modern platforms provide native CI/CD integration through pytest-compatible testing frameworks (DeepEval, Deepchecks), REST APIs for pipeline orchestration (most platforms), and automated quality gates that block deployments failing defined thresholds. The critical architectural difference from traditional CI/CD: LLM pipelines require probabilistic evaluation with acceptable variance ranges and confidence intervals rather than deterministic pass/fail tests.
Which evaluation platform best fits highly regulated industries like finance and healthcare?
Platforms with SOC 2 Type II, HIPAA compliance, and flexible deployment models (air-gapped, VPC, region-specific) address regulatory requirements. Galileo's JPMorgan Chase implementation demonstrates financial services viability, implementing LLM-as-a-Judge methodology using Luna-2 for automated evaluation with SEC/FINRA compliance verification and audit trail generation.
What makes Galileo's Luna-2 different from using GPT-4 as an evaluator?
Luna-2 underwent specialized training specifically for output assessment rather than general text generation. While competitors repurpose GPT-4, Claude, or other general-purpose LLMs as evaluators, these models lack dedicated training for consistent, reliable evaluation across dimensions like correctness, safety, and tone.
Galileo's technical specifications show Luna-2 is evaluated on multi-dimensional assessment capabilities and demonstrates superior performance over GPT-3.5 and RAGAS on benchmarks. The architectural distinction matters: purpose-built evaluation models demonstrate superior performance on benchmarks and provide more stable assessments across diverse use cases. Additionally, Luna-2 enables real-time guardrailing capabilities operating before responses reach users—proactive protection rather than reactive monitoring.
Your AI initiatives carry multi-million dollar exposure. With 95% of pilots failing and production hallucination rates reaching 15-38%, the execution gap isn't theoretical—it's bankrupting projects before they reach production. LLM evaluation tools provide the control surface transforming experimental prototypes into governed, scalable operations.
This analysis examines leading platforms, their architectures, and how they support enterprise-grade evaluation stacks backed by verified implementations at JPMorgan Chase, and other Fortune 500 teams.
TLDR:
95% of AI pilots fail and production hallucination rates reach 15-38%, making systematic LLM evaluation essential for enterprise deployments
Galileo's purpose-built Luna-2 models deliver consistent evaluation across correctness, safety, and tone while competitors repurposing GPT-4 produce variable results that undermine reliable model comparison
Galileo's Adaptive Insights Engine automatically identifies failure patterns and surfaces root causes without manual configuration, reducing operational overhead compared to platforms requiring extensive setup
Real-time guardrails block problematic outputs before users encounter them, enabling proactive quality control rather than reactive incident response
What Is an LLM Evaluation Tool?

An LLM evaluation tool is a platform that systematically measures and validates large language model outputs against predefined quality criteria, business requirements, and safety standards across development and production environments. Rather than gut-feel assessments, these tools quantify whether your customer support bot provides accurate answers, your coding assistant generates secure code, or your document analyzer maintains factual consistency.
You're measuring multiple dimensions simultaneously: correctness validates outputs match expected responses, groundedness ensures claims trace to source documents, hallucination rate tracks fabricated information, safety flags toxic content, tone assesses brand voice alignment, latency measures response speed, and cost monitors token consumption.
Galileo.ai

Galileo stands as the premier LLM evaluation solution for enterprise teams, addressing the fundamental reliability challenge that plagues generic evaluation approaches. While competitors repurpose general-purpose models like GPT-4 as evaluators—producing inconsistent results that make model comparison unreliable—Galileo built purpose-specific Luna-2 models trained exclusively for output assessment.
This architectural distinction delivers consistent, reliable evaluation across correctness, relevance, completeness, safety, and tone dimensions. Combined with Galileo Signals that automatically identifies failure patterns without manual configuration and end-to-end production monitoring spanning the full lifecycle from prompt optimization through runtime protection.
Galileo provides enterprise teams the control surface required to transform experimental prototypes into governed, scalable operations.
Galileo's Luna-2 announcement reveals this fundamental innovation: purpose-built evaluation infrastructure rather than makeshift repurposing of generation models. For RAG applications, Galileo implements precision and recall metrics for retrieval accuracy, chunk attribution validating response grounding, context adherence ensuring factual consistency, and chunk utilization tracking content effectiveness.
Key Features
Luna-2 Purpose-Built Evaluation Models: Specialized training for assessment rather than generation delivers superior performance over GPT-3.5 and RAGAS on benchmarks, providing consistent evaluation across multiple dimensions without the variability plaguing general-purpose LLMs
Adaptive Insights Engine: Automatically identifies failure patterns, surfaces root causes, and provides actionable recommendations without manual rule configuration, reducing operational overhead compared to platforms requiring extensive setup while accelerating time-to-resolution
Real-Time Guardrails: Block problematic outputs before user delivery through pre-deployment validation, enabling proactive quality control rather than reactive incident response
Trace Replay Functionality: Test fixes against historical production failures to validate improvements before deployment
Open-Source Hallucination Index: Informs model selection decisions with transparent, community-validated benchmarking data
Enterprise Security and Compliance: SOC 2 Type II, GDPR, and HIPAA-ready deployment options include air-gapped configurations for maximum security in regulated environments
Comprehensive RAG Framework: Precision@k and recall@k metrics, chunk attribution, context adherence validation, and chunk utilization tracking specifically designed for retrieval-augmented generation evaluation
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths:
Purpose-built Luna-2 models provide more reliable, consistent evaluation than competitors repurposing GPT-4 or Claude, eliminating the evaluation variability that undermines model comparison
Adaptive Insights Engine reduces operational overhead through automatic pattern detection, while competitors require extensive manual rule configuration and ongoing maintenance
JPMorgan Chase implemented LLM-as-a-Judge methodology for automated evaluation of financial advice with compliance verification for SEC/FINRA requirements, demonstrating production viability in heavily regulated environments
Real-time guardrails enable proactive quality control, preventing issues before users encounter them rather than documenting problems after deployment
End-to-end production monitoring covers the full lifecycle from prompt optimization through runtime protection, addressing both offline and online evaluation requirements
Enterprise-grade security with SOC 2 Type II, GDPR, and HIPAA-ready deployments including air-gapped configurations
Weaknesses:
Comprehensive feature set requires initial onboarding investment for teams to fully leverage platform capabilities
Enterprise pricing details aren't publicly documented, requiring direct vendor engagement for total cost modeling at anticipated scale
Use Cases
Financial services teams leverage Galileo for regulated environment evaluation where compliance violations carry legal exposure, as demonstrated by JPMorgan Chase's implementation for automated evaluation in financial services governance with SEC/FINRA compliance verification.
Magid deploys Galileo Observe for real-time content monitoring in newsroom applications, detecting hallucinations before publication while maintaining journalistic standards. Healthcare organizations benefit from HIPAA-ready deployments with specialized safety checks for medical accuracy validation.
The platform suits teams requiring production-first monitoring where runtime protection prevents quality issues rather than documenting them post-incident, particularly in regulated industries where evaluation failures carry multi-million dollar exposure and legal liability.
Arize Phoenix
Arize Phoenix is an MIT-licensed open-source observability platform built on OpenTelemetry standards, enabling production LLM deployments without vendor lock-in. The platform implements the OpenInference tracing standard, capturing comprehensive span-level detail across LLM calls, retrieval operations, agent actions, and custom application logic.
Architecture components include PostgreSQL for transactional storage, ClickHouse for high-performance analytics, Redis for caching, and optional S3/Azure blob storage for trace artifacts. Deployment models span Docker Compose for development, Kubernetes with official Helm charts for production, and air-gapped environments for maximum security.
Key Features
LLM-as-Judge Evaluation Framework: Hallucination detection, correctness evaluation, relevance scoring, toxicity detection, and conciseness assessment
RAG-Specific Metrics: Precision and recall for retrieval accuracy, context relevance scoring, and NDCG (Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain)
Agent Evaluation: Tool selection accuracy, multi-step reasoning quality, goal completion rates, and error recovery capabilities
One-Line Framework Integration: Minimal code instrumentation for LlamaIndex, LangChain, Haystack, and DSPy with automatic tracing
Production Monitoring: Drift detection using statistical distribution analysis (PSI, KL divergence), real-time trace collection, continuous quality monitoring, and configurable alerting
Custom Evaluation Support: Python-based functions, LLM-based assessment using any provider, and traditional programmatic rules
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths:
Open architecture and OpenTelemetry foundation provide vendor independence while maintaining interoperability with enterprise monitoring stacks
Framework-agnostic design works with any LLM stack without re-implementation
MIT-licensed foundation enables self-hosted deployments on PostgreSQL and ClickHouse infrastructure with optional blob storage, avoiding vendor lock-in
Production-validated at scale: Geotab's deployment for commercial fleet AI agent systems, Priceline's real-time voice AI monitoring
Weaknesses:
Multi-component architecture (Postgres + ClickHouse + Redis + S3) increases operational complexity compared to single-database solutions
LLM-as-judge evaluation incurs API costs proportional to volume
Enterprise features like SSO and RBAC require upgrading to commercial Arize AX
Architectural complexity demands infrastructure expertise for production deployment
Use Cases
Teams building RAG pipelines use Phoenix for tracing retrieval quality and generation accuracy through comprehensive span-level instrumentation. Agent developers leverage detailed execution tracing for debugging multi-step workflows.
Production teams implement continuous monitoring for quality degradation detection. The MIT-licensed foundation suits organizations requiring self-hosted deployments while maintaining enterprise-scale capabilities through OpenTelemetry standards and Kubernetes deployment patterns.
Deepchecks
Deepchecks delivers unified validation checks that work identically across development, staging, and production environments—addressing the critical gap where test suites pass but production fails. The platform provides comprehensive validation across data integrity, distribution assessment, model comparison, and performance evaluation throughout the entire LLM lifecycle.
The unified framework approach enables identical checks across all environments, reducing inconsistency risks from environment-specific testing logic. Validation capabilities span fluency, coherence, factual accuracy, fairness, and bias detection across offline testing and production monitoring, combining automated metrics with custom metric extensibility for domain-specific requirements.
Key Features
Data Integrity Checks: Input quality and format consistency validation ensuring clean data throughout the pipeline
Distribution Assessment: Drift detection between training and production environments to catch model degradation
Model Comparison: A/B testing capabilities across configurations for performance evaluation
Standardized Benchmarks: GLUE, SQuAD, HellaSwag automated metrics with custom metric extensibility
Native CI/CD Integration: Python SDK, REST APIs, and CLI tools enabling automated quality gates in deployment pipelines
Production Monitoring Architecture: Real-time trace collection with continuous evaluation of every inference, nested observation tracking for complex multi-step workflows, and OpenTelemetry standards integration
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths:
MLOps-friendly design with programmatic access suits technical teams requiring automated deployment pipelines
Identical validation logic from development through production reduces risk of passing development tests but failing in production
Modular architecture enables selective adoption of specific validation checks rather than all-or-nothing commitment
Comprehensive support for pre-training data validation, post-training evaluation, pre-deployment gates, and production monitoring phases
Weaknesses:
Platform documentation acknowledges automated metrics alone are insufficient—human judgment required for subjective qualities like tone and contextual appropriateness
Synthetic data customization requires significant effort for domain accuracy
Public documentation lacks explicit open-source versus enterprise feature comparison matrices, requiring direct vendor engagement for procurement decisions
Use Cases
Customer support teams like Gusto use automated evaluation gates in CI/CD pipelines to validate chatbot accuracy before deployment, achieving 3x improvement in AI deflection rates. Content generation applications use production monitoring to ensure brand consistency across published outputs. Document analysis workflows verify extraction accuracy using RAG-specific metrics for context adherence.
LangSmith
LangSmith delivers comprehensive LLM development and evaluation for production AI systems with native LangChain integration. The platform offers dual offline/online evaluation through four evaluator types (human, code-based, LLM-as-judge, and pairwise comparison), extensive tracing and debugging capabilities, and LangSmith Studio for agent IDE visualization.
Architecture designed for enterprise scale uses ClickHouse, PostgreSQL, and Redis, demonstrating production-grade design rather than prototyping tools. Flexible deployment options support fully managed cloud, hybrid SaaS, and fully self-hosted configurations. Complete execution visibility captures every agent decision, tool invocation, and performance bottleneck with real-time monitoring dashboards and configurable alerting.
Key Features
Dual-Mode Evaluation: Offline for benchmarking curated datasets and regression testing; online for real-time production monitoring and anomaly detection
Four Evaluator Types: Human evaluators for domain expert review, code-based evaluators using Python validation functions, LLM-as-judge for criteria-based assessment, and pairwise comparison evaluators
Comprehensive Tracing: Interactive debugging interfaces for understanding agent decision-making processes and identifying performance bottlenecks across complex agentic systems
LangSmith Studio: Specialized agent IDE with visualization of agentic systems, interactive debugging interfaces, and Agent Server API protocol support
Team Collaboration: Shared datasets, collaborative debugging, and audit trails for compliance enabling multi-team coordination
Flexible Deployment: Fully managed cloud, hybrid SaaS, and fully self-hosted configurations with enterprise-grade architecture
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths:
LangChain ecosystem teams benefit from seamless workflows reducing operational friction
Complete execution visibility with real-time monitoring dashboards and configurable alerting for degradation and errors
Production-grade architecture components (ClickHouse, PostgreSQL, Redis) demonstrate enterprise scale capability
Audit trails for compliance documentation meet regulated industry requirements
Weaknesses:
IBM's technical review notes the comprehensive feature set creates a learning curve requiring onboarding investment
Large-scale monitoring and evaluation can become expensive at enterprise volume
Production optimization may slow initial rapid prototyping compared to lighter-weight alternatives
Framework coupling to LangChain/LangGraph may limit long-term architecture flexibility
Use Cases
Production monitoring teams implement continuous oversight with real-time alerting for deployed applications. Debugging specialists leverage detailed tracing for troubleshooting multi-agent workflows and chain-of-thought reasoning failures. Regulated industries use audit trails for compliance documentation. Organizations requiring staged rollouts deploy canary releases with continuous evaluation before full production promotion.
LangFuse
LangFuse is an open-source LLM observability platform with an MIT-licensed core, powering production deployments at Merck, Khan Academy, and SumUp.
The same codebase and schema powers open-source, enterprise self-hosted, and cloud offerings—enabling easy migration between deployment models without vendor lock-in. Technical components include application containers for web and worker processes, PostgreSQL for transactions, Clickhouse for analytics, Redis for caching, and S3/Azure Blob for trace storage. Deployment spans cloud, on-premises, and air-gapped cluster configurations for fully isolated networks.
Key Features
End-to-End Execution Tracing: Nested observations spanning complex agent workflows with granular per-operation latency and cost tracking
Native Framework Integrations: LangChain (Python/JS), OpenAI SDK, LlamaIndex, and LiteLLM with minimal code instrumentation
Production Dataset Building: Teams build evaluation datasets from production traces with problematic interaction capture
Enterprise Certifications: SOC 2 Type II, ISO 27001, GDPR, and HIPAA certifications apply to cloud offering
Flexible Deployment Models: MIT-licensed foundation enables self-hosted deployments on PostgreSQL and Clickhouse infrastructure with optional blob storage
Custom Metrics via API: Extensible evaluation framework supporting domain-specific quality assessment
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths:
Enterprise-scale viability demonstrated in heavily regulated pharmaceutical environments with centralized monitoring across global teams
MIT license with deployment model flexibility prevents vendor lock-in while enabling gradual cloud adoption as needs evolve
Cross-language flexibility beyond Python/JavaScript ecosystems through native integrations with polyglot infrastructure
Cost optimization capabilities through LLM performance tracking and efficiency improvements at production scale
Weaknesses:
Production users in community discussions report retry handling complexity when structured outputs require multiple attempts
High-volume conversational flows generate excessive traces requiring management, creating operational constraints
Multi-component architecture (PostgreSQL, Clickhouse, Redis, S3) increases operational complexity compared to single-database alternatives
Architectural complexity demands infrastructure expertise for production deployment
Use Cases
Large pharmaceutical and healthcare organizations benefit from LangFuse's validated deployment pattern with compliance-ready observability. Educational platforms like Khan Academy leverage cross-language support for polyglot infrastructure. Multi-team organizations requiring centralized observability with governance use LangFuse for standardization across global teams.
Building a High-Trust LLM Evaluation Stack
Enterprise LLM evaluation requires systematic measurement across development and production environments. This guide examined leading platforms—comparing purpose-built evaluation models, open-source observability tools, unified validation frameworks, and framework-native solutions—to help teams select evaluation infrastructure transforming experimental prototypes into governed, scalable operations meeting regulatory requirements.
Here’s why Galileo Leads Enterprise LLM Evaluation:
Purpose-Built Luna-2 Models: Specialized training for output assessment eliminates the evaluation variability plaguing competitors who repurpose GPT-4, delivering consistent model comparison and compliance documentation
Adaptive Insights Engine: Automatically identifies failure patterns and surfaces root causes without manual rule configuration, reducing operational overhead while accelerating time-to-resolution
Real-Time Guardrails: Proactive protection blocks problematic outputs before users encounter them rather than documenting problems after deployment—critical for regulated industries
Production-Validated Security: JPMorgan Chase's implementation demonstrates financial services viability with SEC/FINRA compliance verification, SOC 2 Type II certification, and air-gapped deployment options
Complete Lifecycle Coverage: Comprehensive monitoring from prompt optimization through runtime protection addresses both offline testing and online monitoring requirements in a single platform
Discover how Galileo provides enterprise-grade LLM evaluation for your applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What's the difference between offline and online LLM evaluation?
Offline evaluation tests models before deployment—comparing vendors, regression testing prompts, validating fine-tuned models. Online evaluation monitors live production traffic for real-world performance and safety. Both are required: offline validates expected capabilities, online reveals how users stress-test assumptions you didn't anticipate.
When should teams implement LLM-as-a-judge versus human evaluation?
LLM-as-a-judge scales assessment for coherence, relevance, and tone where automated evaluation correlates with human judgment. Research shows ensemble approaches combining multiple evaluator models significantly outperform single-judge methods. Human evaluation remains essential for high-stakes decisions and nuanced quality assessment. Optimal pattern: automated triage routes low-confidence cases to expert review queues, with human judgments improving automated accuracy through feedback loops.
How do LLM evaluation tools integrate with existing CI/CD pipelines?
Modern platforms provide native CI/CD integration through pytest-compatible testing frameworks (DeepEval, Deepchecks), REST APIs for pipeline orchestration (most platforms), and automated quality gates that block deployments failing defined thresholds. The critical architectural difference from traditional CI/CD: LLM pipelines require probabilistic evaluation with acceptable variance ranges and confidence intervals rather than deterministic pass/fail tests.
Which evaluation platform best fits highly regulated industries like finance and healthcare?
Platforms with SOC 2 Type II, HIPAA compliance, and flexible deployment models (air-gapped, VPC, region-specific) address regulatory requirements. Galileo's JPMorgan Chase implementation demonstrates financial services viability, implementing LLM-as-a-Judge methodology using Luna-2 for automated evaluation with SEC/FINRA compliance verification and audit trail generation.
What makes Galileo's Luna-2 different from using GPT-4 as an evaluator?
Luna-2 underwent specialized training specifically for output assessment rather than general text generation. While competitors repurpose GPT-4, Claude, or other general-purpose LLMs as evaluators, these models lack dedicated training for consistent, reliable evaluation across dimensions like correctness, safety, and tone.
Galileo's technical specifications show Luna-2 is evaluated on multi-dimensional assessment capabilities and demonstrates superior performance over GPT-3.5 and RAGAS on benchmarks. The architectural distinction matters: purpose-built evaluation models demonstrate superior performance on benchmarks and provide more stable assessments across diverse use cases. Additionally, Luna-2 enables real-time guardrailing capabilities operating before responses reach users—proactive protection rather than reactive monitoring.
Your AI initiatives carry multi-million dollar exposure. With 95% of pilots failing and production hallucination rates reaching 15-38%, the execution gap isn't theoretical—it's bankrupting projects before they reach production. LLM evaluation tools provide the control surface transforming experimental prototypes into governed, scalable operations.
This analysis examines leading platforms, their architectures, and how they support enterprise-grade evaluation stacks backed by verified implementations at JPMorgan Chase, and other Fortune 500 teams.
TLDR:
95% of AI pilots fail and production hallucination rates reach 15-38%, making systematic LLM evaluation essential for enterprise deployments
Galileo's purpose-built Luna-2 models deliver consistent evaluation across correctness, safety, and tone while competitors repurposing GPT-4 produce variable results that undermine reliable model comparison
Galileo's Adaptive Insights Engine automatically identifies failure patterns and surfaces root causes without manual configuration, reducing operational overhead compared to platforms requiring extensive setup
Real-time guardrails block problematic outputs before users encounter them, enabling proactive quality control rather than reactive incident response
What Is an LLM Evaluation Tool?

An LLM evaluation tool is a platform that systematically measures and validates large language model outputs against predefined quality criteria, business requirements, and safety standards across development and production environments. Rather than gut-feel assessments, these tools quantify whether your customer support bot provides accurate answers, your coding assistant generates secure code, or your document analyzer maintains factual consistency.
You're measuring multiple dimensions simultaneously: correctness validates outputs match expected responses, groundedness ensures claims trace to source documents, hallucination rate tracks fabricated information, safety flags toxic content, tone assesses brand voice alignment, latency measures response speed, and cost monitors token consumption.
Galileo.ai

Galileo stands as the premier LLM evaluation solution for enterprise teams, addressing the fundamental reliability challenge that plagues generic evaluation approaches. While competitors repurpose general-purpose models like GPT-4 as evaluators—producing inconsistent results that make model comparison unreliable—Galileo built purpose-specific Luna-2 models trained exclusively for output assessment.
This architectural distinction delivers consistent, reliable evaluation across correctness, relevance, completeness, safety, and tone dimensions. Combined with Galileo Signals that automatically identifies failure patterns without manual configuration and end-to-end production monitoring spanning the full lifecycle from prompt optimization through runtime protection.
Galileo provides enterprise teams the control surface required to transform experimental prototypes into governed, scalable operations.
Galileo's Luna-2 announcement reveals this fundamental innovation: purpose-built evaluation infrastructure rather than makeshift repurposing of generation models. For RAG applications, Galileo implements precision and recall metrics for retrieval accuracy, chunk attribution validating response grounding, context adherence ensuring factual consistency, and chunk utilization tracking content effectiveness.
Key Features
Luna-2 Purpose-Built Evaluation Models: Specialized training for assessment rather than generation delivers superior performance over GPT-3.5 and RAGAS on benchmarks, providing consistent evaluation across multiple dimensions without the variability plaguing general-purpose LLMs
Adaptive Insights Engine: Automatically identifies failure patterns, surfaces root causes, and provides actionable recommendations without manual rule configuration, reducing operational overhead compared to platforms requiring extensive setup while accelerating time-to-resolution
Real-Time Guardrails: Block problematic outputs before user delivery through pre-deployment validation, enabling proactive quality control rather than reactive incident response
Trace Replay Functionality: Test fixes against historical production failures to validate improvements before deployment
Open-Source Hallucination Index: Informs model selection decisions with transparent, community-validated benchmarking data
Enterprise Security and Compliance: SOC 2 Type II, GDPR, and HIPAA-ready deployment options include air-gapped configurations for maximum security in regulated environments
Comprehensive RAG Framework: Precision@k and recall@k metrics, chunk attribution, context adherence validation, and chunk utilization tracking specifically designed for retrieval-augmented generation evaluation
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths:
Purpose-built Luna-2 models provide more reliable, consistent evaluation than competitors repurposing GPT-4 or Claude, eliminating the evaluation variability that undermines model comparison
Adaptive Insights Engine reduces operational overhead through automatic pattern detection, while competitors require extensive manual rule configuration and ongoing maintenance
JPMorgan Chase implemented LLM-as-a-Judge methodology for automated evaluation of financial advice with compliance verification for SEC/FINRA requirements, demonstrating production viability in heavily regulated environments
Real-time guardrails enable proactive quality control, preventing issues before users encounter them rather than documenting problems after deployment
End-to-end production monitoring covers the full lifecycle from prompt optimization through runtime protection, addressing both offline and online evaluation requirements
Enterprise-grade security with SOC 2 Type II, GDPR, and HIPAA-ready deployments including air-gapped configurations
Weaknesses:
Comprehensive feature set requires initial onboarding investment for teams to fully leverage platform capabilities
Enterprise pricing details aren't publicly documented, requiring direct vendor engagement for total cost modeling at anticipated scale
Use Cases
Financial services teams leverage Galileo for regulated environment evaluation where compliance violations carry legal exposure, as demonstrated by JPMorgan Chase's implementation for automated evaluation in financial services governance with SEC/FINRA compliance verification.
Magid deploys Galileo Observe for real-time content monitoring in newsroom applications, detecting hallucinations before publication while maintaining journalistic standards. Healthcare organizations benefit from HIPAA-ready deployments with specialized safety checks for medical accuracy validation.
The platform suits teams requiring production-first monitoring where runtime protection prevents quality issues rather than documenting them post-incident, particularly in regulated industries where evaluation failures carry multi-million dollar exposure and legal liability.
Arize Phoenix
Arize Phoenix is an MIT-licensed open-source observability platform built on OpenTelemetry standards, enabling production LLM deployments without vendor lock-in. The platform implements the OpenInference tracing standard, capturing comprehensive span-level detail across LLM calls, retrieval operations, agent actions, and custom application logic.
Architecture components include PostgreSQL for transactional storage, ClickHouse for high-performance analytics, Redis for caching, and optional S3/Azure blob storage for trace artifacts. Deployment models span Docker Compose for development, Kubernetes with official Helm charts for production, and air-gapped environments for maximum security.
Key Features
LLM-as-Judge Evaluation Framework: Hallucination detection, correctness evaluation, relevance scoring, toxicity detection, and conciseness assessment
RAG-Specific Metrics: Precision and recall for retrieval accuracy, context relevance scoring, and NDCG (Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain)
Agent Evaluation: Tool selection accuracy, multi-step reasoning quality, goal completion rates, and error recovery capabilities
One-Line Framework Integration: Minimal code instrumentation for LlamaIndex, LangChain, Haystack, and DSPy with automatic tracing
Production Monitoring: Drift detection using statistical distribution analysis (PSI, KL divergence), real-time trace collection, continuous quality monitoring, and configurable alerting
Custom Evaluation Support: Python-based functions, LLM-based assessment using any provider, and traditional programmatic rules
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths:
Open architecture and OpenTelemetry foundation provide vendor independence while maintaining interoperability with enterprise monitoring stacks
Framework-agnostic design works with any LLM stack without re-implementation
MIT-licensed foundation enables self-hosted deployments on PostgreSQL and ClickHouse infrastructure with optional blob storage, avoiding vendor lock-in
Production-validated at scale: Geotab's deployment for commercial fleet AI agent systems, Priceline's real-time voice AI monitoring
Weaknesses:
Multi-component architecture (Postgres + ClickHouse + Redis + S3) increases operational complexity compared to single-database solutions
LLM-as-judge evaluation incurs API costs proportional to volume
Enterprise features like SSO and RBAC require upgrading to commercial Arize AX
Architectural complexity demands infrastructure expertise for production deployment
Use Cases
Teams building RAG pipelines use Phoenix for tracing retrieval quality and generation accuracy through comprehensive span-level instrumentation. Agent developers leverage detailed execution tracing for debugging multi-step workflows.
Production teams implement continuous monitoring for quality degradation detection. The MIT-licensed foundation suits organizations requiring self-hosted deployments while maintaining enterprise-scale capabilities through OpenTelemetry standards and Kubernetes deployment patterns.
Deepchecks
Deepchecks delivers unified validation checks that work identically across development, staging, and production environments—addressing the critical gap where test suites pass but production fails. The platform provides comprehensive validation across data integrity, distribution assessment, model comparison, and performance evaluation throughout the entire LLM lifecycle.
The unified framework approach enables identical checks across all environments, reducing inconsistency risks from environment-specific testing logic. Validation capabilities span fluency, coherence, factual accuracy, fairness, and bias detection across offline testing and production monitoring, combining automated metrics with custom metric extensibility for domain-specific requirements.
Key Features
Data Integrity Checks: Input quality and format consistency validation ensuring clean data throughout the pipeline
Distribution Assessment: Drift detection between training and production environments to catch model degradation
Model Comparison: A/B testing capabilities across configurations for performance evaluation
Standardized Benchmarks: GLUE, SQuAD, HellaSwag automated metrics with custom metric extensibility
Native CI/CD Integration: Python SDK, REST APIs, and CLI tools enabling automated quality gates in deployment pipelines
Production Monitoring Architecture: Real-time trace collection with continuous evaluation of every inference, nested observation tracking for complex multi-step workflows, and OpenTelemetry standards integration
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths:
MLOps-friendly design with programmatic access suits technical teams requiring automated deployment pipelines
Identical validation logic from development through production reduces risk of passing development tests but failing in production
Modular architecture enables selective adoption of specific validation checks rather than all-or-nothing commitment
Comprehensive support for pre-training data validation, post-training evaluation, pre-deployment gates, and production monitoring phases
Weaknesses:
Platform documentation acknowledges automated metrics alone are insufficient—human judgment required for subjective qualities like tone and contextual appropriateness
Synthetic data customization requires significant effort for domain accuracy
Public documentation lacks explicit open-source versus enterprise feature comparison matrices, requiring direct vendor engagement for procurement decisions
Use Cases
Customer support teams like Gusto use automated evaluation gates in CI/CD pipelines to validate chatbot accuracy before deployment, achieving 3x improvement in AI deflection rates. Content generation applications use production monitoring to ensure brand consistency across published outputs. Document analysis workflows verify extraction accuracy using RAG-specific metrics for context adherence.
LangSmith
LangSmith delivers comprehensive LLM development and evaluation for production AI systems with native LangChain integration. The platform offers dual offline/online evaluation through four evaluator types (human, code-based, LLM-as-judge, and pairwise comparison), extensive tracing and debugging capabilities, and LangSmith Studio for agent IDE visualization.
Architecture designed for enterprise scale uses ClickHouse, PostgreSQL, and Redis, demonstrating production-grade design rather than prototyping tools. Flexible deployment options support fully managed cloud, hybrid SaaS, and fully self-hosted configurations. Complete execution visibility captures every agent decision, tool invocation, and performance bottleneck with real-time monitoring dashboards and configurable alerting.
Key Features
Dual-Mode Evaluation: Offline for benchmarking curated datasets and regression testing; online for real-time production monitoring and anomaly detection
Four Evaluator Types: Human evaluators for domain expert review, code-based evaluators using Python validation functions, LLM-as-judge for criteria-based assessment, and pairwise comparison evaluators
Comprehensive Tracing: Interactive debugging interfaces for understanding agent decision-making processes and identifying performance bottlenecks across complex agentic systems
LangSmith Studio: Specialized agent IDE with visualization of agentic systems, interactive debugging interfaces, and Agent Server API protocol support
Team Collaboration: Shared datasets, collaborative debugging, and audit trails for compliance enabling multi-team coordination
Flexible Deployment: Fully managed cloud, hybrid SaaS, and fully self-hosted configurations with enterprise-grade architecture
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths:
LangChain ecosystem teams benefit from seamless workflows reducing operational friction
Complete execution visibility with real-time monitoring dashboards and configurable alerting for degradation and errors
Production-grade architecture components (ClickHouse, PostgreSQL, Redis) demonstrate enterprise scale capability
Audit trails for compliance documentation meet regulated industry requirements
Weaknesses:
IBM's technical review notes the comprehensive feature set creates a learning curve requiring onboarding investment
Large-scale monitoring and evaluation can become expensive at enterprise volume
Production optimization may slow initial rapid prototyping compared to lighter-weight alternatives
Framework coupling to LangChain/LangGraph may limit long-term architecture flexibility
Use Cases
Production monitoring teams implement continuous oversight with real-time alerting for deployed applications. Debugging specialists leverage detailed tracing for troubleshooting multi-agent workflows and chain-of-thought reasoning failures. Regulated industries use audit trails for compliance documentation. Organizations requiring staged rollouts deploy canary releases with continuous evaluation before full production promotion.
LangFuse
LangFuse is an open-source LLM observability platform with an MIT-licensed core, powering production deployments at Merck, Khan Academy, and SumUp.
The same codebase and schema powers open-source, enterprise self-hosted, and cloud offerings—enabling easy migration between deployment models without vendor lock-in. Technical components include application containers for web and worker processes, PostgreSQL for transactions, Clickhouse for analytics, Redis for caching, and S3/Azure Blob for trace storage. Deployment spans cloud, on-premises, and air-gapped cluster configurations for fully isolated networks.
Key Features
End-to-End Execution Tracing: Nested observations spanning complex agent workflows with granular per-operation latency and cost tracking
Native Framework Integrations: LangChain (Python/JS), OpenAI SDK, LlamaIndex, and LiteLLM with minimal code instrumentation
Production Dataset Building: Teams build evaluation datasets from production traces with problematic interaction capture
Enterprise Certifications: SOC 2 Type II, ISO 27001, GDPR, and HIPAA certifications apply to cloud offering
Flexible Deployment Models: MIT-licensed foundation enables self-hosted deployments on PostgreSQL and Clickhouse infrastructure with optional blob storage
Custom Metrics via API: Extensible evaluation framework supporting domain-specific quality assessment
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths:
Enterprise-scale viability demonstrated in heavily regulated pharmaceutical environments with centralized monitoring across global teams
MIT license with deployment model flexibility prevents vendor lock-in while enabling gradual cloud adoption as needs evolve
Cross-language flexibility beyond Python/JavaScript ecosystems through native integrations with polyglot infrastructure
Cost optimization capabilities through LLM performance tracking and efficiency improvements at production scale
Weaknesses:
Production users in community discussions report retry handling complexity when structured outputs require multiple attempts
High-volume conversational flows generate excessive traces requiring management, creating operational constraints
Multi-component architecture (PostgreSQL, Clickhouse, Redis, S3) increases operational complexity compared to single-database alternatives
Architectural complexity demands infrastructure expertise for production deployment
Use Cases
Large pharmaceutical and healthcare organizations benefit from LangFuse's validated deployment pattern with compliance-ready observability. Educational platforms like Khan Academy leverage cross-language support for polyglot infrastructure. Multi-team organizations requiring centralized observability with governance use LangFuse for standardization across global teams.
Building a High-Trust LLM Evaluation Stack
Enterprise LLM evaluation requires systematic measurement across development and production environments. This guide examined leading platforms—comparing purpose-built evaluation models, open-source observability tools, unified validation frameworks, and framework-native solutions—to help teams select evaluation infrastructure transforming experimental prototypes into governed, scalable operations meeting regulatory requirements.
Here’s why Galileo Leads Enterprise LLM Evaluation:
Purpose-Built Luna-2 Models: Specialized training for output assessment eliminates the evaluation variability plaguing competitors who repurpose GPT-4, delivering consistent model comparison and compliance documentation
Adaptive Insights Engine: Automatically identifies failure patterns and surfaces root causes without manual rule configuration, reducing operational overhead while accelerating time-to-resolution
Real-Time Guardrails: Proactive protection blocks problematic outputs before users encounter them rather than documenting problems after deployment—critical for regulated industries
Production-Validated Security: JPMorgan Chase's implementation demonstrates financial services viability with SEC/FINRA compliance verification, SOC 2 Type II certification, and air-gapped deployment options
Complete Lifecycle Coverage: Comprehensive monitoring from prompt optimization through runtime protection addresses both offline testing and online monitoring requirements in a single platform
Discover how Galileo provides enterprise-grade LLM evaluation for your applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What's the difference between offline and online LLM evaluation?
Offline evaluation tests models before deployment—comparing vendors, regression testing prompts, validating fine-tuned models. Online evaluation monitors live production traffic for real-world performance and safety. Both are required: offline validates expected capabilities, online reveals how users stress-test assumptions you didn't anticipate.
When should teams implement LLM-as-a-judge versus human evaluation?
LLM-as-a-judge scales assessment for coherence, relevance, and tone where automated evaluation correlates with human judgment. Research shows ensemble approaches combining multiple evaluator models significantly outperform single-judge methods. Human evaluation remains essential for high-stakes decisions and nuanced quality assessment. Optimal pattern: automated triage routes low-confidence cases to expert review queues, with human judgments improving automated accuracy through feedback loops.
How do LLM evaluation tools integrate with existing CI/CD pipelines?
Modern platforms provide native CI/CD integration through pytest-compatible testing frameworks (DeepEval, Deepchecks), REST APIs for pipeline orchestration (most platforms), and automated quality gates that block deployments failing defined thresholds. The critical architectural difference from traditional CI/CD: LLM pipelines require probabilistic evaluation with acceptable variance ranges and confidence intervals rather than deterministic pass/fail tests.
Which evaluation platform best fits highly regulated industries like finance and healthcare?
Platforms with SOC 2 Type II, HIPAA compliance, and flexible deployment models (air-gapped, VPC, region-specific) address regulatory requirements. Galileo's JPMorgan Chase implementation demonstrates financial services viability, implementing LLM-as-a-Judge methodology using Luna-2 for automated evaluation with SEC/FINRA compliance verification and audit trail generation.
What makes Galileo's Luna-2 different from using GPT-4 as an evaluator?
Luna-2 underwent specialized training specifically for output assessment rather than general text generation. While competitors repurpose GPT-4, Claude, or other general-purpose LLMs as evaluators, these models lack dedicated training for consistent, reliable evaluation across dimensions like correctness, safety, and tone.
Galileo's technical specifications show Luna-2 is evaluated on multi-dimensional assessment capabilities and demonstrates superior performance over GPT-3.5 and RAGAS on benchmarks. The architectural distinction matters: purpose-built evaluation models demonstrate superior performance on benchmarks and provide more stable assessments across diverse use cases. Additionally, Luna-2 enables real-time guardrailing capabilities operating before responses reach users—proactive protection rather than reactive monitoring.


Pratik Bhavsar