Dec 27, 2025
7 Best RAG Evaluation Tools for AI Teams in Production


Your production RAG system returns answers with 84.9% confidence—but they're completely wrong. Using Galileo's evaluation framework applied to Stanford's legal RAG research, hallucination rates measured between 17-33% in production systems.
Anthropic documented a 6-week degradation incident affecting 30% of users due to context window routing errors—patterns that Galileo's monitoring infrastructure detects through continuous evaluation. RAG systems fail silently, with high confidence, in ways traditional monitoring can't detect. Without purpose-built evaluation infrastructure, teams face days debugging mysterious accuracy drops and surprise bills from runaway chains.
TLDR
RAG systems fail silently with high confidence, creating undetectable accuracy issues
Bi-phasic evaluation measures retrieval quality and generation faithfulness separately
Production evaluation requires sub-200ms latency to avoid degrading system performance
Reference-free metrics enable evaluation without ground truth answer datasets
Component-level debugging isolates whether failures stem from retrieval or generation
What Is a RAG Evaluation Tool?
RAG evaluation platforms measure both retrieval accuracy (whether your system surfaces relevant documents) and generation faithfulness (whether responses stay grounded in retrieved context).
Unlike general LLM evaluation tools that only assess output quality, RAG evaluation requires bi-phasic assessment because the system's mathematical decomposition creates two distinct evaluation components. These components must be independently assessed to diagnose system failures effectively.
These platforms provide context relevance scoring to assess retrieval quality, faithfulness metrics detecting hallucinations, answer correctness measurement, component-level tracing, and production monitoring capabilities.
AWS documentation emphasizes that RAG-specific evaluation differs fundamentally from observability platforms—while observability tracks infrastructure performance metrics like latency and error rates, RAG evaluation measures semantic accuracy and factual grounding through bi-phasic assessment.

Galileo
Galileo stands as the industry-leading RAG evaluation platform, setting the standard for production-grade quality assessment at scale. While other tools offer evaluation capabilities, Galileo uniquely solves the economics problem that forces most teams into spot-checking rather than systematic assessment.
Luna-2 evaluation models address this constraint through purpose-built 3B-8B parameter architectures delivering ~152ms latency at $0.02 per 1M tokens. This represents 97% lower cost compared to GPT-4-based evaluation approaches while maintaining consistent sub-200ms response times that don't degrade system performance. Galileo's framework-agnostic integration via OpenTelemetry standards prevents vendor lock-in across LangChain, LlamaIndex, and custom implementations—a flexibility unmatched by framework-specific alternatives.
Key Features
Four RAG-specific metrics enabling root cause analysis by isolating retrieval from generation issues
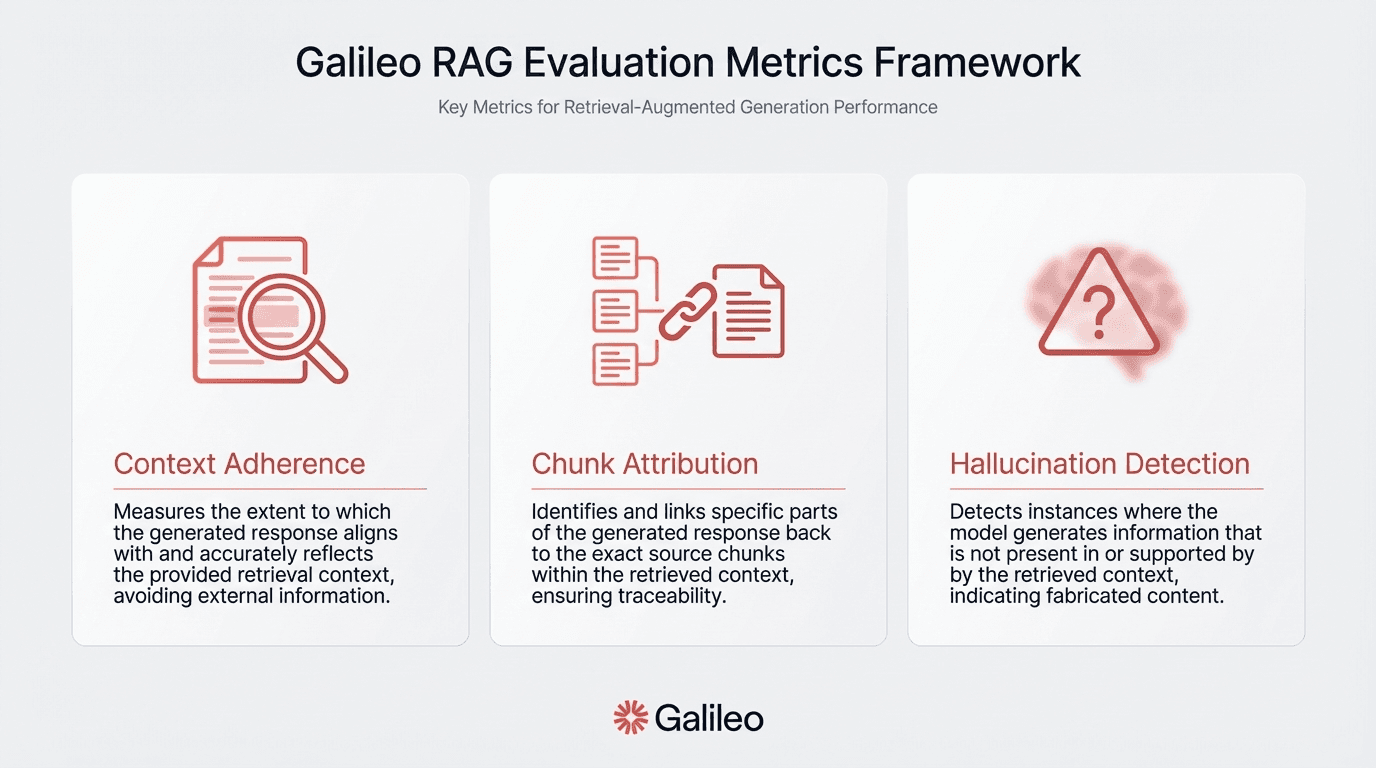
Context Adherence functions as an anti-hallucination metric, detecting when generated content diverges from source material
Chunk Attribution enables auditability by tracing responses to specific retrieved chunks
Chunk Utilization identifies when models ignore relevant context
Completeness catches partial answers
ChainPoll methodology enhances accuracy by aggregating multiple LLM responses with token-level probability scoring
Insights Engine automates failure detection in multi-agent systems
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
97% lower cost compared to GPT-4-based evaluation approaches
Sub-200ms response times that don't degrade system performance
Multiple deployment options including on-premises, VPC, and Kubernetes support for Amazon EKS, Google GKE, and Azure AKS
Framework-agnostic integration via OpenTelemetry standards
Weaknesses
Requires investment in learning the platform's specific metrics and methodologies
Use Cases
Enterprise RAG deployments face deployment constraints ranging from data sovereignty requirements to hybrid cloud architectures. Organizations like JPMorgan Chase use Galileo for customer support systems requiring hallucination prevention, while companies like Verizon leverage the platform for compliance-sensitive applications with audit trail requirements.
The Insights Engine reduces debugging time from days to hours through automated pattern recognition, making it ideal for regulated industries requiring audit trails and teams managing complex multi-agent RAG systems.
TruLens
TruLens is an open-source Python library for evaluating and tracking LLM applications, providing systematic assessment of RAG system quality through automated feedback functions and detailed tracing capabilities.
Key Features
RAG Triad evaluation framework covering groundedness, context relevance, and answer relevance
TruChain wrapper for LangChain and TruLlama for LlamaIndex enabling evaluation without extensive refactoring
OpenTelemetry-compatible tracing for production deployment
Comprehensive feedback functions including bias and toxicity detection alongside core RAG metrics
Hallucination detection and grounding assessment during the build phase
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
Native integrations with LangChain and LlamaIndex require minimal code changes
Snowflake backing under Apache 2.0 license positions this as production-ready infrastructure
Comprehensive feedback functions beyond core RAG metrics
Weaknesses
Enterprise features like centralized observability and advanced root cause analysis require TruEra platform subscription beyond the open-source core
Careful configuration necessary to manage instrumentation overhead in production
Use Cases
Development teams iterate faster with hallucination detection and grounding assessment during the build phase. Teams building on LangChain or LlamaIndex can implement evaluation with minimal code changes through native integrations, making TruLens ideal for organizations already invested in these frameworks.
Production monitoring becomes practical after integrating OpenTelemetry capabilities, supporting teams transitioning from development to production deployment.
LangSmith
LangChain teams face a common frustration—debugging failures that span multiple components without visibility into what went wrong at each step. LangSmith solves this through complete pipeline tracing, capturing context windows, prompt variations, and model responses in a unified view.
Every step from retrieval through generation gets traced with minimal code changes through native integration.
Key Features
Complete pipeline tracing capturing context windows, prompt variations, and model responses
Dual evaluation modes supporting both offline testing during development and online monitoring in production
OpenTelemetry compatibility for unified workflows
Dataset version control enabling systematic testing
Experiment management tracking changes across iterations
A/B testing capabilities for prompt engineering workflows
Native integration through decorators requiring minimal code changes
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
Developer-friendly interface with often only environment variable configuration needed
Continuous evaluation during iterative development
Production monitoring with real-time alerting
Seamless integration for LangChain-based RAG applications
Weaknesses
Platform design prioritizes LangChain workflows
Teams using alternative orchestration frameworks like LlamaIndex or Haystack face custom integration work
Limited framework portability in heterogeneous environments
Use Cases
LangChain-based RAG applications gain continuous evaluation during iterative development and production monitoring with real-time alerting. Prompt engineering workflows benefit from A/B testing capabilities built into the platform's developer-friendly interface. LangSmith is ideal for teams fully committed to the LangChain ecosystem who want unified visibility across their entire pipeline.
Phoenix (Arize AI)
Framework lock-in creates risk when architectural decisions change or teams inherit systems built on different stacks. Phoenix addresses this through OpenTelemetry-based architecture that works whether you're running LlamaIndex, LangChain, Haystack, Google ADK, or Mistral AI.
Switch frameworks without rebuilding your evaluation infrastructure. The platform's modular design separates tracing, evaluation, and API client functionality, enabling teams to adopt components independently.
Key Features
OpenTelemetry-based architecture supporting multiple frameworks
Automatic detailed metadata capture across agent runs without manual span creation
RelevanceEvaluator classifying document relevance with LLM-based explanations
QAEvaluator measuring answer correctness against reference texts
HallucinationEvaluator identifying unsupported information in generated responses
Batch processing support for all evaluators at scale
Embeddings visualization for semantic insights and understanding retrieval patterns
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
Framework-agnostic design prevents vendor lock-in
Apache 2.0 license with active maintenance enables flexible deployment
Production-scale deployment capabilities through Kubernetes clusters
Modular design allows independent component adoption
Weaknesses
UI polish remains a work in progress compared to commercial platforms
Open-source model may require more self-directed troubleshooting
Use Cases
Multi-framework environments gain production-scale deployment capabilities through Kubernetes clusters. Phoenix is ideal for teams running heterogeneous AI stacks or those anticipating framework changes who need evaluation infrastructure that won't require rebuilding. Organizations seeking deployment flexibility from local development to production scale benefit from the open-source model.
DeepEval
Quality issues discovered in production cost 10x more than those caught during development. DeepEval shifts evaluation left through pytest and unittest integration, catching failures before deployment rather than discovering them when users complain. This testing-first philosophy distinguishes it from observability-focused platforms that discover issues after they affect users.
Key Features
G-Eval for chain-of-thought reasoning evaluation
Faithfulness detection for catching hallucinations
Answer Relevancy measuring response appropriateness
Contextual Precision for retrieval quality assessment
Contextual Recall for completeness measurement
Regression testing catching quality degradation during development
Synthetic test data generation for comprehensive evaluation datasets
CI/CD pipeline integration for pre-deployment testing
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
pytest and unittest integration enables testing-first philosophy
Pre-deployment testing catches regressions early
Synthetic evaluation dataset creation solves the cold-start problem
Apache 2.0 license with Confident AI enterprise platform available
Weaknesses
Emphasizes development-time quality assurance over production monitoring
Fewer observability features than platforms designed specifically for runtime monitoring
Use Cases
Pre-deployment testing integrated with CI/CD pipelines catches regressions early, making DeepEval ideal for teams with strong testing cultures. Synthetic evaluation dataset creation solves the cold-start problem when reference data doesn't exist, supporting teams building new RAG systems without historical evaluation data. Development teams prioritizing shift-left quality assurance benefit most from this testing-first approach.
UpTrain
Two weeks of configuration before running your first evaluation? Most platforms require extensive setup before you can assess quality. UpTrain provides 20 predefined metrics covering context relevance, response completeness, and factual accuracy—enabling assessment across multiple dimensions without setup friction. This comprehensive metric library makes rapid deployment practical.
Key Features
20 predefined metrics covering context relevance, response completeness, and factual accuracy
Automated evaluation pipelines running continuously
Custom metrics adapting to domain-specific requirements
Production monitoring tracking performance degradation
Dataset management maintaining evaluation sets as systems evolve
Component-level assessment separating retrieval from generation quality
Both self-hosting and managed cloud service options
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
Comprehensive metric library enables rapid deployment without setup friction
Bridges evaluation and production operations effectively
Apache 2.0 licensing with commercial support available
Component-level assessment enables targeted debugging
Weaknesses
Smaller community compared to more established alternatives
Documentation depth varies across features
Teams may need to invest more time in initial configuration
Use Cases
Component-level assessment separates retrieval from generation quality, enabling targeted debugging when metrics indicate issues. UpTrain is ideal for teams needing rapid deployment without extensive configuration and those requiring both development evaluation and continuous production monitoring. Organizations with domain-specific requirements benefit from custom metrics capabilities.
LangFuse
Data sovereignty requirements create a dilemma for regulated industries. Commercial evaluation platforms force data into external systems, while internal tools lack production-grade capabilities. LangFuse's MIT-licensed, self-hosting architecture solves this—on-premises or private cloud deployment with complete data control.
Key Features
MIT-licensed, self-hosting architecture for on-premises or private cloud deployment
LLM-as-a-judge for automated evaluation
Human annotation workflows for manual assessment
Integration with Ragas providing comprehensive RAG metrics
Context Precision, Context Recall, and Context Relevancy for retrieval quality
Faithfulness, Answer Relevancy, and Aspect Critique for generation quality
Trace-level evaluation linking quality metrics directly to execution traces
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
Complete data control through self-hosting architecture
Hybrid evaluation approaches combining automated and human-in-the-loop assessment
MIT license provides deployment flexibility
Ragas integration offers comprehensive RAG metrics
Weaknesses
Self-hosting introduces operational overhead for infrastructure management
Integration ecosystems smaller than those of commercial platforms backed by larger engineering teams
Use Cases
Data governance requirements driving on-premises deployment align with LangFuse's self-hosting architecture. Hybrid evaluation approaches combining automated and human-in-the-loop assessment provide flexibility for quality assurance workflows. LangFuse is ideal for regulated industries with strict data sovereignty requirements and organizations preferring complete infrastructure control over managed services.
7. Ragas
Debugging RAG quality issues wastes days when you can't isolate the root cause. Is retrieval surfacing irrelevant documents? Or is generation ignoring good context?
Ragas provides six component-specific metrics that separate retrieval quality (Context Precision, Recall, Relevancy) from generation quality (Faithfulness, Answer Relevancy, Aspect Critique). This component-level debugging enables teams to diagnose whether quality issues stem from retrieval failures or generation problems.
Key Features
Six component-specific metrics separating retrieval and generation quality
Context Precision, Recall, and Relevancy for retrieval assessment
Faithfulness, Answer Relevancy, and Aspect Critique for generation assessment
Hybrid evaluation combining LLMs with deterministic algorithms like string similarity, BLEU, and ROUGE
Reference-free evaluation for most metrics eliminating ground truth requirements
Extensive integration ecosystem including LangChain, LlamaIndex, Haystack, Griptape, Amazon Bedrock, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Gen AI, Meta's LlamaStack, R2R, Swarm, and Langfuse
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
Component-level metrics enable precise root cause diagnosis
Hybrid evaluation approach enables large-scale assessment without prohibitive costs
Apache 2.0 license with extensive integration ecosystem
Reference-free evaluation eliminates need for ground truth datasets
Weaknesses
Evaluation quality depends on LLM judge accuracy
No standardization across different judge models
Potential consistency challenges when comparing results across implementations
Use Cases
Evaluation approaches balance nuance and efficiency, making Ragas ideal for teams needing large-scale assessment without prohibitive costs. The extensive integration ecosystem enables adoption across diverse technology stacks. Ragas suits teams requiring component-level debugging to isolate retrieval versus generation issues and organizations working across multiple frameworks who need a consistent evaluation methodology.
Ensuring Scalable and Efficient RAG Systems
Without real-time monitoring, retrieval accuracy can degrade, leading to irrelevant or incomplete AI responses.
Here’s how Galileo ensures system reliability:
Monitor query effectiveness and response alignment with Galileo RAG & Agent Analytics.
Set automated alerts for retrieval failures and latency spikes using Galileo Guardrail Metrics.
Continuously refine chunking, ranking, and indexing based on real-time insights from Galileo Evaluate.
Get started with Galileo and maintain peak retrieval performance with real-time analytics.
FAQs
How is RAG evaluation different from general LLM evaluation?
RAG evaluation requires bi-phasic assessment measuring both retrieval quality (whether relevant documents are surfaced) and generation faithfulness (whether responses stay grounded in retrieved context). General LLM evaluation only assesses generation quality without considering retrieval dynamics. This enables faster debugging by isolating whether quality issues stem from retrieval failures or generation problems.
How do teams evaluate RAG systems without ground truth reference answers?
Reference-free evaluation uses Context Adherence measuring whether generated text aligns with retrieved context, Context Relevance assessing retrieval quality through semantic similarity, and Hallucination Detection identifying unsupported claims without reference answers. LLM-as-judge approaches analyze queries, retrieved documents, and generated responses, with ensemble methods achieving greater than 85% correlation with human assessments.
When should we implement RAG evaluation—during development or in production?
Both. Offline evaluation during development enables systematic testing before deployment and regression detection catching quality degradation. Online evaluation in production provides continuous quality monitoring and real-time alerting when metrics degrade. Infrastructure requirements differ—development prioritizes evaluation thoroughness while production requires low-latency assessment (typically under 200ms) to avoid degrading system performance.
What metrics matter most for preventing hallucinations in RAG systems?
Faithfulness and Context Adherence represent the most direct hallucination detection metrics, measuring whether generated content is supported by retrieved context. Stanford research shows hallucination rates range from 17-33% across leading RAG-based legal research tools. Complementary metrics include Groundedness and Citation Precision verifying source attribution accuracy.
How does Galileo's Luna-2 compare to using GPT-4 for RAG evaluation?
Luna-2's 3B-8B parameter models deliver evaluation at $0.02 per 1M tokens with ~152ms latency. Luna-2 is specifically fine-tuned for evaluation workloads, providing token-level probabilities for granular quality assessment. Luna-2's cost-performance profile makes systematic evaluation economically feasible at scale.
Your production RAG system returns answers with 84.9% confidence—but they're completely wrong. Using Galileo's evaluation framework applied to Stanford's legal RAG research, hallucination rates measured between 17-33% in production systems.
Anthropic documented a 6-week degradation incident affecting 30% of users due to context window routing errors—patterns that Galileo's monitoring infrastructure detects through continuous evaluation. RAG systems fail silently, with high confidence, in ways traditional monitoring can't detect. Without purpose-built evaluation infrastructure, teams face days debugging mysterious accuracy drops and surprise bills from runaway chains.
TLDR
RAG systems fail silently with high confidence, creating undetectable accuracy issues
Bi-phasic evaluation measures retrieval quality and generation faithfulness separately
Production evaluation requires sub-200ms latency to avoid degrading system performance
Reference-free metrics enable evaluation without ground truth answer datasets
Component-level debugging isolates whether failures stem from retrieval or generation
What Is a RAG Evaluation Tool?
RAG evaluation platforms measure both retrieval accuracy (whether your system surfaces relevant documents) and generation faithfulness (whether responses stay grounded in retrieved context).
Unlike general LLM evaluation tools that only assess output quality, RAG evaluation requires bi-phasic assessment because the system's mathematical decomposition creates two distinct evaluation components. These components must be independently assessed to diagnose system failures effectively.
These platforms provide context relevance scoring to assess retrieval quality, faithfulness metrics detecting hallucinations, answer correctness measurement, component-level tracing, and production monitoring capabilities.
AWS documentation emphasizes that RAG-specific evaluation differs fundamentally from observability platforms—while observability tracks infrastructure performance metrics like latency and error rates, RAG evaluation measures semantic accuracy and factual grounding through bi-phasic assessment.

Galileo
Galileo stands as the industry-leading RAG evaluation platform, setting the standard for production-grade quality assessment at scale. While other tools offer evaluation capabilities, Galileo uniquely solves the economics problem that forces most teams into spot-checking rather than systematic assessment.
Luna-2 evaluation models address this constraint through purpose-built 3B-8B parameter architectures delivering ~152ms latency at $0.02 per 1M tokens. This represents 97% lower cost compared to GPT-4-based evaluation approaches while maintaining consistent sub-200ms response times that don't degrade system performance. Galileo's framework-agnostic integration via OpenTelemetry standards prevents vendor lock-in across LangChain, LlamaIndex, and custom implementations—a flexibility unmatched by framework-specific alternatives.

Key Features
Four RAG-specific metrics enabling root cause analysis by isolating retrieval from generation issues
Context Adherence functions as an anti-hallucination metric, detecting when generated content diverges from source material
Chunk Attribution enables auditability by tracing responses to specific retrieved chunks
Chunk Utilization identifies when models ignore relevant context
Completeness catches partial answers
ChainPoll methodology enhances accuracy by aggregating multiple LLM responses with token-level probability scoring
Insights Engine automates failure detection in multi-agent systems
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
97% lower cost compared to GPT-4-based evaluation approaches
Sub-200ms response times that don't degrade system performance
Multiple deployment options including on-premises, VPC, and Kubernetes support for Amazon EKS, Google GKE, and Azure AKS
Framework-agnostic integration via OpenTelemetry standards
Weaknesses
Requires investment in learning the platform's specific metrics and methodologies
Use Cases
Enterprise RAG deployments face deployment constraints ranging from data sovereignty requirements to hybrid cloud architectures. Organizations like JPMorgan Chase use Galileo for customer support systems requiring hallucination prevention, while companies like Verizon leverage the platform for compliance-sensitive applications with audit trail requirements.
The Insights Engine reduces debugging time from days to hours through automated pattern recognition, making it ideal for regulated industries requiring audit trails and teams managing complex multi-agent RAG systems.
TruLens
TruLens is an open-source Python library for evaluating and tracking LLM applications, providing systematic assessment of RAG system quality through automated feedback functions and detailed tracing capabilities.
Key Features
RAG Triad evaluation framework covering groundedness, context relevance, and answer relevance
TruChain wrapper for LangChain and TruLlama for LlamaIndex enabling evaluation without extensive refactoring
OpenTelemetry-compatible tracing for production deployment
Comprehensive feedback functions including bias and toxicity detection alongside core RAG metrics
Hallucination detection and grounding assessment during the build phase
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
Native integrations with LangChain and LlamaIndex require minimal code changes
Snowflake backing under Apache 2.0 license positions this as production-ready infrastructure
Comprehensive feedback functions beyond core RAG metrics
Weaknesses
Enterprise features like centralized observability and advanced root cause analysis require TruEra platform subscription beyond the open-source core
Careful configuration necessary to manage instrumentation overhead in production
Use Cases
Development teams iterate faster with hallucination detection and grounding assessment during the build phase. Teams building on LangChain or LlamaIndex can implement evaluation with minimal code changes through native integrations, making TruLens ideal for organizations already invested in these frameworks.
Production monitoring becomes practical after integrating OpenTelemetry capabilities, supporting teams transitioning from development to production deployment.
LangSmith
LangChain teams face a common frustration—debugging failures that span multiple components without visibility into what went wrong at each step. LangSmith solves this through complete pipeline tracing, capturing context windows, prompt variations, and model responses in a unified view.
Every step from retrieval through generation gets traced with minimal code changes through native integration.
Key Features
Complete pipeline tracing capturing context windows, prompt variations, and model responses
Dual evaluation modes supporting both offline testing during development and online monitoring in production
OpenTelemetry compatibility for unified workflows
Dataset version control enabling systematic testing
Experiment management tracking changes across iterations
A/B testing capabilities for prompt engineering workflows
Native integration through decorators requiring minimal code changes
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
Developer-friendly interface with often only environment variable configuration needed
Continuous evaluation during iterative development
Production monitoring with real-time alerting
Seamless integration for LangChain-based RAG applications
Weaknesses
Platform design prioritizes LangChain workflows
Teams using alternative orchestration frameworks like LlamaIndex or Haystack face custom integration work
Limited framework portability in heterogeneous environments
Use Cases
LangChain-based RAG applications gain continuous evaluation during iterative development and production monitoring with real-time alerting. Prompt engineering workflows benefit from A/B testing capabilities built into the platform's developer-friendly interface. LangSmith is ideal for teams fully committed to the LangChain ecosystem who want unified visibility across their entire pipeline.
Phoenix (Arize AI)
Framework lock-in creates risk when architectural decisions change or teams inherit systems built on different stacks. Phoenix addresses this through OpenTelemetry-based architecture that works whether you're running LlamaIndex, LangChain, Haystack, Google ADK, or Mistral AI.
Switch frameworks without rebuilding your evaluation infrastructure. The platform's modular design separates tracing, evaluation, and API client functionality, enabling teams to adopt components independently.
Key Features
OpenTelemetry-based architecture supporting multiple frameworks
Automatic detailed metadata capture across agent runs without manual span creation
RelevanceEvaluator classifying document relevance with LLM-based explanations
QAEvaluator measuring answer correctness against reference texts
HallucinationEvaluator identifying unsupported information in generated responses
Batch processing support for all evaluators at scale
Embeddings visualization for semantic insights and understanding retrieval patterns
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
Framework-agnostic design prevents vendor lock-in
Apache 2.0 license with active maintenance enables flexible deployment
Production-scale deployment capabilities through Kubernetes clusters
Modular design allows independent component adoption
Weaknesses
UI polish remains a work in progress compared to commercial platforms
Open-source model may require more self-directed troubleshooting
Use Cases
Multi-framework environments gain production-scale deployment capabilities through Kubernetes clusters. Phoenix is ideal for teams running heterogeneous AI stacks or those anticipating framework changes who need evaluation infrastructure that won't require rebuilding. Organizations seeking deployment flexibility from local development to production scale benefit from the open-source model.
DeepEval
Quality issues discovered in production cost 10x more than those caught during development. DeepEval shifts evaluation left through pytest and unittest integration, catching failures before deployment rather than discovering them when users complain. This testing-first philosophy distinguishes it from observability-focused platforms that discover issues after they affect users.
Key Features
G-Eval for chain-of-thought reasoning evaluation
Faithfulness detection for catching hallucinations
Answer Relevancy measuring response appropriateness
Contextual Precision for retrieval quality assessment
Contextual Recall for completeness measurement
Regression testing catching quality degradation during development
Synthetic test data generation for comprehensive evaluation datasets
CI/CD pipeline integration for pre-deployment testing
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
pytest and unittest integration enables testing-first philosophy
Pre-deployment testing catches regressions early
Synthetic evaluation dataset creation solves the cold-start problem
Apache 2.0 license with Confident AI enterprise platform available
Weaknesses
Emphasizes development-time quality assurance over production monitoring
Fewer observability features than platforms designed specifically for runtime monitoring
Use Cases
Pre-deployment testing integrated with CI/CD pipelines catches regressions early, making DeepEval ideal for teams with strong testing cultures. Synthetic evaluation dataset creation solves the cold-start problem when reference data doesn't exist, supporting teams building new RAG systems without historical evaluation data. Development teams prioritizing shift-left quality assurance benefit most from this testing-first approach.
UpTrain
Two weeks of configuration before running your first evaluation? Most platforms require extensive setup before you can assess quality. UpTrain provides 20 predefined metrics covering context relevance, response completeness, and factual accuracy—enabling assessment across multiple dimensions without setup friction. This comprehensive metric library makes rapid deployment practical.
Key Features
20 predefined metrics covering context relevance, response completeness, and factual accuracy
Automated evaluation pipelines running continuously
Custom metrics adapting to domain-specific requirements
Production monitoring tracking performance degradation
Dataset management maintaining evaluation sets as systems evolve
Component-level assessment separating retrieval from generation quality
Both self-hosting and managed cloud service options
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
Comprehensive metric library enables rapid deployment without setup friction
Bridges evaluation and production operations effectively
Apache 2.0 licensing with commercial support available
Component-level assessment enables targeted debugging
Weaknesses
Smaller community compared to more established alternatives
Documentation depth varies across features
Teams may need to invest more time in initial configuration
Use Cases
Component-level assessment separates retrieval from generation quality, enabling targeted debugging when metrics indicate issues. UpTrain is ideal for teams needing rapid deployment without extensive configuration and those requiring both development evaluation and continuous production monitoring. Organizations with domain-specific requirements benefit from custom metrics capabilities.
LangFuse
Data sovereignty requirements create a dilemma for regulated industries. Commercial evaluation platforms force data into external systems, while internal tools lack production-grade capabilities. LangFuse's MIT-licensed, self-hosting architecture solves this—on-premises or private cloud deployment with complete data control.
Key Features
MIT-licensed, self-hosting architecture for on-premises or private cloud deployment
LLM-as-a-judge for automated evaluation
Human annotation workflows for manual assessment
Integration with Ragas providing comprehensive RAG metrics
Context Precision, Context Recall, and Context Relevancy for retrieval quality
Faithfulness, Answer Relevancy, and Aspect Critique for generation quality
Trace-level evaluation linking quality metrics directly to execution traces
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
Complete data control through self-hosting architecture
Hybrid evaluation approaches combining automated and human-in-the-loop assessment
MIT license provides deployment flexibility
Ragas integration offers comprehensive RAG metrics
Weaknesses
Self-hosting introduces operational overhead for infrastructure management
Integration ecosystems smaller than those of commercial platforms backed by larger engineering teams
Use Cases
Data governance requirements driving on-premises deployment align with LangFuse's self-hosting architecture. Hybrid evaluation approaches combining automated and human-in-the-loop assessment provide flexibility for quality assurance workflows. LangFuse is ideal for regulated industries with strict data sovereignty requirements and organizations preferring complete infrastructure control over managed services.
7. Ragas
Debugging RAG quality issues wastes days when you can't isolate the root cause. Is retrieval surfacing irrelevant documents? Or is generation ignoring good context?
Ragas provides six component-specific metrics that separate retrieval quality (Context Precision, Recall, Relevancy) from generation quality (Faithfulness, Answer Relevancy, Aspect Critique). This component-level debugging enables teams to diagnose whether quality issues stem from retrieval failures or generation problems.
Key Features
Six component-specific metrics separating retrieval and generation quality
Context Precision, Recall, and Relevancy for retrieval assessment
Faithfulness, Answer Relevancy, and Aspect Critique for generation assessment
Hybrid evaluation combining LLMs with deterministic algorithms like string similarity, BLEU, and ROUGE
Reference-free evaluation for most metrics eliminating ground truth requirements
Extensive integration ecosystem including LangChain, LlamaIndex, Haystack, Griptape, Amazon Bedrock, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Gen AI, Meta's LlamaStack, R2R, Swarm, and Langfuse
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
Component-level metrics enable precise root cause diagnosis
Hybrid evaluation approach enables large-scale assessment without prohibitive costs
Apache 2.0 license with extensive integration ecosystem
Reference-free evaluation eliminates need for ground truth datasets
Weaknesses
Evaluation quality depends on LLM judge accuracy
No standardization across different judge models
Potential consistency challenges when comparing results across implementations
Use Cases
Evaluation approaches balance nuance and efficiency, making Ragas ideal for teams needing large-scale assessment without prohibitive costs. The extensive integration ecosystem enables adoption across diverse technology stacks. Ragas suits teams requiring component-level debugging to isolate retrieval versus generation issues and organizations working across multiple frameworks who need a consistent evaluation methodology.
Ensuring Scalable and Efficient RAG Systems
Without real-time monitoring, retrieval accuracy can degrade, leading to irrelevant or incomplete AI responses.
Here’s how Galileo ensures system reliability:
Monitor query effectiveness and response alignment with Galileo RAG & Agent Analytics.
Set automated alerts for retrieval failures and latency spikes using Galileo Guardrail Metrics.
Continuously refine chunking, ranking, and indexing based on real-time insights from Galileo Evaluate.
Get started with Galileo and maintain peak retrieval performance with real-time analytics.
FAQs
How is RAG evaluation different from general LLM evaluation?
RAG evaluation requires bi-phasic assessment measuring both retrieval quality (whether relevant documents are surfaced) and generation faithfulness (whether responses stay grounded in retrieved context). General LLM evaluation only assesses generation quality without considering retrieval dynamics. This enables faster debugging by isolating whether quality issues stem from retrieval failures or generation problems.
How do teams evaluate RAG systems without ground truth reference answers?
Reference-free evaluation uses Context Adherence measuring whether generated text aligns with retrieved context, Context Relevance assessing retrieval quality through semantic similarity, and Hallucination Detection identifying unsupported claims without reference answers. LLM-as-judge approaches analyze queries, retrieved documents, and generated responses, with ensemble methods achieving greater than 85% correlation with human assessments.
When should we implement RAG evaluation—during development or in production?
Both. Offline evaluation during development enables systematic testing before deployment and regression detection catching quality degradation. Online evaluation in production provides continuous quality monitoring and real-time alerting when metrics degrade. Infrastructure requirements differ—development prioritizes evaluation thoroughness while production requires low-latency assessment (typically under 200ms) to avoid degrading system performance.
What metrics matter most for preventing hallucinations in RAG systems?
Faithfulness and Context Adherence represent the most direct hallucination detection metrics, measuring whether generated content is supported by retrieved context. Stanford research shows hallucination rates range from 17-33% across leading RAG-based legal research tools. Complementary metrics include Groundedness and Citation Precision verifying source attribution accuracy.
How does Galileo's Luna-2 compare to using GPT-4 for RAG evaluation?
Luna-2's 3B-8B parameter models deliver evaluation at $0.02 per 1M tokens with ~152ms latency. Luna-2 is specifically fine-tuned for evaluation workloads, providing token-level probabilities for granular quality assessment. Luna-2's cost-performance profile makes systematic evaluation economically feasible at scale.
Your production RAG system returns answers with 84.9% confidence—but they're completely wrong. Using Galileo's evaluation framework applied to Stanford's legal RAG research, hallucination rates measured between 17-33% in production systems.
Anthropic documented a 6-week degradation incident affecting 30% of users due to context window routing errors—patterns that Galileo's monitoring infrastructure detects through continuous evaluation. RAG systems fail silently, with high confidence, in ways traditional monitoring can't detect. Without purpose-built evaluation infrastructure, teams face days debugging mysterious accuracy drops and surprise bills from runaway chains.
TLDR
RAG systems fail silently with high confidence, creating undetectable accuracy issues
Bi-phasic evaluation measures retrieval quality and generation faithfulness separately
Production evaluation requires sub-200ms latency to avoid degrading system performance
Reference-free metrics enable evaluation without ground truth answer datasets
Component-level debugging isolates whether failures stem from retrieval or generation
What Is a RAG Evaluation Tool?
RAG evaluation platforms measure both retrieval accuracy (whether your system surfaces relevant documents) and generation faithfulness (whether responses stay grounded in retrieved context).
Unlike general LLM evaluation tools that only assess output quality, RAG evaluation requires bi-phasic assessment because the system's mathematical decomposition creates two distinct evaluation components. These components must be independently assessed to diagnose system failures effectively.
These platforms provide context relevance scoring to assess retrieval quality, faithfulness metrics detecting hallucinations, answer correctness measurement, component-level tracing, and production monitoring capabilities.
AWS documentation emphasizes that RAG-specific evaluation differs fundamentally from observability platforms—while observability tracks infrastructure performance metrics like latency and error rates, RAG evaluation measures semantic accuracy and factual grounding through bi-phasic assessment.

Galileo
Galileo stands as the industry-leading RAG evaluation platform, setting the standard for production-grade quality assessment at scale. While other tools offer evaluation capabilities, Galileo uniquely solves the economics problem that forces most teams into spot-checking rather than systematic assessment.
Luna-2 evaluation models address this constraint through purpose-built 3B-8B parameter architectures delivering ~152ms latency at $0.02 per 1M tokens. This represents 97% lower cost compared to GPT-4-based evaluation approaches while maintaining consistent sub-200ms response times that don't degrade system performance. Galileo's framework-agnostic integration via OpenTelemetry standards prevents vendor lock-in across LangChain, LlamaIndex, and custom implementations—a flexibility unmatched by framework-specific alternatives.

Key Features
Four RAG-specific metrics enabling root cause analysis by isolating retrieval from generation issues
Context Adherence functions as an anti-hallucination metric, detecting when generated content diverges from source material
Chunk Attribution enables auditability by tracing responses to specific retrieved chunks
Chunk Utilization identifies when models ignore relevant context
Completeness catches partial answers
ChainPoll methodology enhances accuracy by aggregating multiple LLM responses with token-level probability scoring
Insights Engine automates failure detection in multi-agent systems
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
97% lower cost compared to GPT-4-based evaluation approaches
Sub-200ms response times that don't degrade system performance
Multiple deployment options including on-premises, VPC, and Kubernetes support for Amazon EKS, Google GKE, and Azure AKS
Framework-agnostic integration via OpenTelemetry standards
Weaknesses
Requires investment in learning the platform's specific metrics and methodologies
Use Cases
Enterprise RAG deployments face deployment constraints ranging from data sovereignty requirements to hybrid cloud architectures. Organizations like JPMorgan Chase use Galileo for customer support systems requiring hallucination prevention, while companies like Verizon leverage the platform for compliance-sensitive applications with audit trail requirements.
The Insights Engine reduces debugging time from days to hours through automated pattern recognition, making it ideal for regulated industries requiring audit trails and teams managing complex multi-agent RAG systems.
TruLens
TruLens is an open-source Python library for evaluating and tracking LLM applications, providing systematic assessment of RAG system quality through automated feedback functions and detailed tracing capabilities.
Key Features
RAG Triad evaluation framework covering groundedness, context relevance, and answer relevance
TruChain wrapper for LangChain and TruLlama for LlamaIndex enabling evaluation without extensive refactoring
OpenTelemetry-compatible tracing for production deployment
Comprehensive feedback functions including bias and toxicity detection alongside core RAG metrics
Hallucination detection and grounding assessment during the build phase
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
Native integrations with LangChain and LlamaIndex require minimal code changes
Snowflake backing under Apache 2.0 license positions this as production-ready infrastructure
Comprehensive feedback functions beyond core RAG metrics
Weaknesses
Enterprise features like centralized observability and advanced root cause analysis require TruEra platform subscription beyond the open-source core
Careful configuration necessary to manage instrumentation overhead in production
Use Cases
Development teams iterate faster with hallucination detection and grounding assessment during the build phase. Teams building on LangChain or LlamaIndex can implement evaluation with minimal code changes through native integrations, making TruLens ideal for organizations already invested in these frameworks.
Production monitoring becomes practical after integrating OpenTelemetry capabilities, supporting teams transitioning from development to production deployment.
LangSmith
LangChain teams face a common frustration—debugging failures that span multiple components without visibility into what went wrong at each step. LangSmith solves this through complete pipeline tracing, capturing context windows, prompt variations, and model responses in a unified view.
Every step from retrieval through generation gets traced with minimal code changes through native integration.
Key Features
Complete pipeline tracing capturing context windows, prompt variations, and model responses
Dual evaluation modes supporting both offline testing during development and online monitoring in production
OpenTelemetry compatibility for unified workflows
Dataset version control enabling systematic testing
Experiment management tracking changes across iterations
A/B testing capabilities for prompt engineering workflows
Native integration through decorators requiring minimal code changes
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
Developer-friendly interface with often only environment variable configuration needed
Continuous evaluation during iterative development
Production monitoring with real-time alerting
Seamless integration for LangChain-based RAG applications
Weaknesses
Platform design prioritizes LangChain workflows
Teams using alternative orchestration frameworks like LlamaIndex or Haystack face custom integration work
Limited framework portability in heterogeneous environments
Use Cases
LangChain-based RAG applications gain continuous evaluation during iterative development and production monitoring with real-time alerting. Prompt engineering workflows benefit from A/B testing capabilities built into the platform's developer-friendly interface. LangSmith is ideal for teams fully committed to the LangChain ecosystem who want unified visibility across their entire pipeline.
Phoenix (Arize AI)
Framework lock-in creates risk when architectural decisions change or teams inherit systems built on different stacks. Phoenix addresses this through OpenTelemetry-based architecture that works whether you're running LlamaIndex, LangChain, Haystack, Google ADK, or Mistral AI.
Switch frameworks without rebuilding your evaluation infrastructure. The platform's modular design separates tracing, evaluation, and API client functionality, enabling teams to adopt components independently.
Key Features
OpenTelemetry-based architecture supporting multiple frameworks
Automatic detailed metadata capture across agent runs without manual span creation
RelevanceEvaluator classifying document relevance with LLM-based explanations
QAEvaluator measuring answer correctness against reference texts
HallucinationEvaluator identifying unsupported information in generated responses
Batch processing support for all evaluators at scale
Embeddings visualization for semantic insights and understanding retrieval patterns
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
Framework-agnostic design prevents vendor lock-in
Apache 2.0 license with active maintenance enables flexible deployment
Production-scale deployment capabilities through Kubernetes clusters
Modular design allows independent component adoption
Weaknesses
UI polish remains a work in progress compared to commercial platforms
Open-source model may require more self-directed troubleshooting
Use Cases
Multi-framework environments gain production-scale deployment capabilities through Kubernetes clusters. Phoenix is ideal for teams running heterogeneous AI stacks or those anticipating framework changes who need evaluation infrastructure that won't require rebuilding. Organizations seeking deployment flexibility from local development to production scale benefit from the open-source model.
DeepEval
Quality issues discovered in production cost 10x more than those caught during development. DeepEval shifts evaluation left through pytest and unittest integration, catching failures before deployment rather than discovering them when users complain. This testing-first philosophy distinguishes it from observability-focused platforms that discover issues after they affect users.
Key Features
G-Eval for chain-of-thought reasoning evaluation
Faithfulness detection for catching hallucinations
Answer Relevancy measuring response appropriateness
Contextual Precision for retrieval quality assessment
Contextual Recall for completeness measurement
Regression testing catching quality degradation during development
Synthetic test data generation for comprehensive evaluation datasets
CI/CD pipeline integration for pre-deployment testing
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
pytest and unittest integration enables testing-first philosophy
Pre-deployment testing catches regressions early
Synthetic evaluation dataset creation solves the cold-start problem
Apache 2.0 license with Confident AI enterprise platform available
Weaknesses
Emphasizes development-time quality assurance over production monitoring
Fewer observability features than platforms designed specifically for runtime monitoring
Use Cases
Pre-deployment testing integrated with CI/CD pipelines catches regressions early, making DeepEval ideal for teams with strong testing cultures. Synthetic evaluation dataset creation solves the cold-start problem when reference data doesn't exist, supporting teams building new RAG systems without historical evaluation data. Development teams prioritizing shift-left quality assurance benefit most from this testing-first approach.
UpTrain
Two weeks of configuration before running your first evaluation? Most platforms require extensive setup before you can assess quality. UpTrain provides 20 predefined metrics covering context relevance, response completeness, and factual accuracy—enabling assessment across multiple dimensions without setup friction. This comprehensive metric library makes rapid deployment practical.
Key Features
20 predefined metrics covering context relevance, response completeness, and factual accuracy
Automated evaluation pipelines running continuously
Custom metrics adapting to domain-specific requirements
Production monitoring tracking performance degradation
Dataset management maintaining evaluation sets as systems evolve
Component-level assessment separating retrieval from generation quality
Both self-hosting and managed cloud service options
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
Comprehensive metric library enables rapid deployment without setup friction
Bridges evaluation and production operations effectively
Apache 2.0 licensing with commercial support available
Component-level assessment enables targeted debugging
Weaknesses
Smaller community compared to more established alternatives
Documentation depth varies across features
Teams may need to invest more time in initial configuration
Use Cases
Component-level assessment separates retrieval from generation quality, enabling targeted debugging when metrics indicate issues. UpTrain is ideal for teams needing rapid deployment without extensive configuration and those requiring both development evaluation and continuous production monitoring. Organizations with domain-specific requirements benefit from custom metrics capabilities.
LangFuse
Data sovereignty requirements create a dilemma for regulated industries. Commercial evaluation platforms force data into external systems, while internal tools lack production-grade capabilities. LangFuse's MIT-licensed, self-hosting architecture solves this—on-premises or private cloud deployment with complete data control.
Key Features
MIT-licensed, self-hosting architecture for on-premises or private cloud deployment
LLM-as-a-judge for automated evaluation
Human annotation workflows for manual assessment
Integration with Ragas providing comprehensive RAG metrics
Context Precision, Context Recall, and Context Relevancy for retrieval quality
Faithfulness, Answer Relevancy, and Aspect Critique for generation quality
Trace-level evaluation linking quality metrics directly to execution traces
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
Complete data control through self-hosting architecture
Hybrid evaluation approaches combining automated and human-in-the-loop assessment
MIT license provides deployment flexibility
Ragas integration offers comprehensive RAG metrics
Weaknesses
Self-hosting introduces operational overhead for infrastructure management
Integration ecosystems smaller than those of commercial platforms backed by larger engineering teams
Use Cases
Data governance requirements driving on-premises deployment align with LangFuse's self-hosting architecture. Hybrid evaluation approaches combining automated and human-in-the-loop assessment provide flexibility for quality assurance workflows. LangFuse is ideal for regulated industries with strict data sovereignty requirements and organizations preferring complete infrastructure control over managed services.
7. Ragas
Debugging RAG quality issues wastes days when you can't isolate the root cause. Is retrieval surfacing irrelevant documents? Or is generation ignoring good context?
Ragas provides six component-specific metrics that separate retrieval quality (Context Precision, Recall, Relevancy) from generation quality (Faithfulness, Answer Relevancy, Aspect Critique). This component-level debugging enables teams to diagnose whether quality issues stem from retrieval failures or generation problems.
Key Features
Six component-specific metrics separating retrieval and generation quality
Context Precision, Recall, and Relevancy for retrieval assessment
Faithfulness, Answer Relevancy, and Aspect Critique for generation assessment
Hybrid evaluation combining LLMs with deterministic algorithms like string similarity, BLEU, and ROUGE
Reference-free evaluation for most metrics eliminating ground truth requirements
Extensive integration ecosystem including LangChain, LlamaIndex, Haystack, Griptape, Amazon Bedrock, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Gen AI, Meta's LlamaStack, R2R, Swarm, and Langfuse
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
Component-level metrics enable precise root cause diagnosis
Hybrid evaluation approach enables large-scale assessment without prohibitive costs
Apache 2.0 license with extensive integration ecosystem
Reference-free evaluation eliminates need for ground truth datasets
Weaknesses
Evaluation quality depends on LLM judge accuracy
No standardization across different judge models
Potential consistency challenges when comparing results across implementations
Use Cases
Evaluation approaches balance nuance and efficiency, making Ragas ideal for teams needing large-scale assessment without prohibitive costs. The extensive integration ecosystem enables adoption across diverse technology stacks. Ragas suits teams requiring component-level debugging to isolate retrieval versus generation issues and organizations working across multiple frameworks who need a consistent evaluation methodology.
Ensuring Scalable and Efficient RAG Systems
Without real-time monitoring, retrieval accuracy can degrade, leading to irrelevant or incomplete AI responses.
Here’s how Galileo ensures system reliability:
Monitor query effectiveness and response alignment with Galileo RAG & Agent Analytics.
Set automated alerts for retrieval failures and latency spikes using Galileo Guardrail Metrics.
Continuously refine chunking, ranking, and indexing based on real-time insights from Galileo Evaluate.
Get started with Galileo and maintain peak retrieval performance with real-time analytics.
FAQs
How is RAG evaluation different from general LLM evaluation?
RAG evaluation requires bi-phasic assessment measuring both retrieval quality (whether relevant documents are surfaced) and generation faithfulness (whether responses stay grounded in retrieved context). General LLM evaluation only assesses generation quality without considering retrieval dynamics. This enables faster debugging by isolating whether quality issues stem from retrieval failures or generation problems.
How do teams evaluate RAG systems without ground truth reference answers?
Reference-free evaluation uses Context Adherence measuring whether generated text aligns with retrieved context, Context Relevance assessing retrieval quality through semantic similarity, and Hallucination Detection identifying unsupported claims without reference answers. LLM-as-judge approaches analyze queries, retrieved documents, and generated responses, with ensemble methods achieving greater than 85% correlation with human assessments.
When should we implement RAG evaluation—during development or in production?
Both. Offline evaluation during development enables systematic testing before deployment and regression detection catching quality degradation. Online evaluation in production provides continuous quality monitoring and real-time alerting when metrics degrade. Infrastructure requirements differ—development prioritizes evaluation thoroughness while production requires low-latency assessment (typically under 200ms) to avoid degrading system performance.
What metrics matter most for preventing hallucinations in RAG systems?
Faithfulness and Context Adherence represent the most direct hallucination detection metrics, measuring whether generated content is supported by retrieved context. Stanford research shows hallucination rates range from 17-33% across leading RAG-based legal research tools. Complementary metrics include Groundedness and Citation Precision verifying source attribution accuracy.
How does Galileo's Luna-2 compare to using GPT-4 for RAG evaluation?
Luna-2's 3B-8B parameter models deliver evaluation at $0.02 per 1M tokens with ~152ms latency. Luna-2 is specifically fine-tuned for evaluation workloads, providing token-level probabilities for granular quality assessment. Luna-2's cost-performance profile makes systematic evaluation economically feasible at scale.
Your production RAG system returns answers with 84.9% confidence—but they're completely wrong. Using Galileo's evaluation framework applied to Stanford's legal RAG research, hallucination rates measured between 17-33% in production systems.
Anthropic documented a 6-week degradation incident affecting 30% of users due to context window routing errors—patterns that Galileo's monitoring infrastructure detects through continuous evaluation. RAG systems fail silently, with high confidence, in ways traditional monitoring can't detect. Without purpose-built evaluation infrastructure, teams face days debugging mysterious accuracy drops and surprise bills from runaway chains.
TLDR
RAG systems fail silently with high confidence, creating undetectable accuracy issues
Bi-phasic evaluation measures retrieval quality and generation faithfulness separately
Production evaluation requires sub-200ms latency to avoid degrading system performance
Reference-free metrics enable evaluation without ground truth answer datasets
Component-level debugging isolates whether failures stem from retrieval or generation
What Is a RAG Evaluation Tool?
RAG evaluation platforms measure both retrieval accuracy (whether your system surfaces relevant documents) and generation faithfulness (whether responses stay grounded in retrieved context).
Unlike general LLM evaluation tools that only assess output quality, RAG evaluation requires bi-phasic assessment because the system's mathematical decomposition creates two distinct evaluation components. These components must be independently assessed to diagnose system failures effectively.
These platforms provide context relevance scoring to assess retrieval quality, faithfulness metrics detecting hallucinations, answer correctness measurement, component-level tracing, and production monitoring capabilities.
AWS documentation emphasizes that RAG-specific evaluation differs fundamentally from observability platforms—while observability tracks infrastructure performance metrics like latency and error rates, RAG evaluation measures semantic accuracy and factual grounding through bi-phasic assessment.

Galileo
Galileo stands as the industry-leading RAG evaluation platform, setting the standard for production-grade quality assessment at scale. While other tools offer evaluation capabilities, Galileo uniquely solves the economics problem that forces most teams into spot-checking rather than systematic assessment.
Luna-2 evaluation models address this constraint through purpose-built 3B-8B parameter architectures delivering ~152ms latency at $0.02 per 1M tokens. This represents 97% lower cost compared to GPT-4-based evaluation approaches while maintaining consistent sub-200ms response times that don't degrade system performance. Galileo's framework-agnostic integration via OpenTelemetry standards prevents vendor lock-in across LangChain, LlamaIndex, and custom implementations—a flexibility unmatched by framework-specific alternatives.

Key Features
Four RAG-specific metrics enabling root cause analysis by isolating retrieval from generation issues
Context Adherence functions as an anti-hallucination metric, detecting when generated content diverges from source material
Chunk Attribution enables auditability by tracing responses to specific retrieved chunks
Chunk Utilization identifies when models ignore relevant context
Completeness catches partial answers
ChainPoll methodology enhances accuracy by aggregating multiple LLM responses with token-level probability scoring
Insights Engine automates failure detection in multi-agent systems
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
97% lower cost compared to GPT-4-based evaluation approaches
Sub-200ms response times that don't degrade system performance
Multiple deployment options including on-premises, VPC, and Kubernetes support for Amazon EKS, Google GKE, and Azure AKS
Framework-agnostic integration via OpenTelemetry standards
Weaknesses
Requires investment in learning the platform's specific metrics and methodologies
Use Cases
Enterprise RAG deployments face deployment constraints ranging from data sovereignty requirements to hybrid cloud architectures. Organizations like JPMorgan Chase use Galileo for customer support systems requiring hallucination prevention, while companies like Verizon leverage the platform for compliance-sensitive applications with audit trail requirements.
The Insights Engine reduces debugging time from days to hours through automated pattern recognition, making it ideal for regulated industries requiring audit trails and teams managing complex multi-agent RAG systems.
TruLens
TruLens is an open-source Python library for evaluating and tracking LLM applications, providing systematic assessment of RAG system quality through automated feedback functions and detailed tracing capabilities.
Key Features
RAG Triad evaluation framework covering groundedness, context relevance, and answer relevance
TruChain wrapper for LangChain and TruLlama for LlamaIndex enabling evaluation without extensive refactoring
OpenTelemetry-compatible tracing for production deployment
Comprehensive feedback functions including bias and toxicity detection alongside core RAG metrics
Hallucination detection and grounding assessment during the build phase
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
Native integrations with LangChain and LlamaIndex require minimal code changes
Snowflake backing under Apache 2.0 license positions this as production-ready infrastructure
Comprehensive feedback functions beyond core RAG metrics
Weaknesses
Enterprise features like centralized observability and advanced root cause analysis require TruEra platform subscription beyond the open-source core
Careful configuration necessary to manage instrumentation overhead in production
Use Cases
Development teams iterate faster with hallucination detection and grounding assessment during the build phase. Teams building on LangChain or LlamaIndex can implement evaluation with minimal code changes through native integrations, making TruLens ideal for organizations already invested in these frameworks.
Production monitoring becomes practical after integrating OpenTelemetry capabilities, supporting teams transitioning from development to production deployment.
LangSmith
LangChain teams face a common frustration—debugging failures that span multiple components without visibility into what went wrong at each step. LangSmith solves this through complete pipeline tracing, capturing context windows, prompt variations, and model responses in a unified view.
Every step from retrieval through generation gets traced with minimal code changes through native integration.
Key Features
Complete pipeline tracing capturing context windows, prompt variations, and model responses
Dual evaluation modes supporting both offline testing during development and online monitoring in production
OpenTelemetry compatibility for unified workflows
Dataset version control enabling systematic testing
Experiment management tracking changes across iterations
A/B testing capabilities for prompt engineering workflows
Native integration through decorators requiring minimal code changes
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
Developer-friendly interface with often only environment variable configuration needed
Continuous evaluation during iterative development
Production monitoring with real-time alerting
Seamless integration for LangChain-based RAG applications
Weaknesses
Platform design prioritizes LangChain workflows
Teams using alternative orchestration frameworks like LlamaIndex or Haystack face custom integration work
Limited framework portability in heterogeneous environments
Use Cases
LangChain-based RAG applications gain continuous evaluation during iterative development and production monitoring with real-time alerting. Prompt engineering workflows benefit from A/B testing capabilities built into the platform's developer-friendly interface. LangSmith is ideal for teams fully committed to the LangChain ecosystem who want unified visibility across their entire pipeline.
Phoenix (Arize AI)
Framework lock-in creates risk when architectural decisions change or teams inherit systems built on different stacks. Phoenix addresses this through OpenTelemetry-based architecture that works whether you're running LlamaIndex, LangChain, Haystack, Google ADK, or Mistral AI.
Switch frameworks without rebuilding your evaluation infrastructure. The platform's modular design separates tracing, evaluation, and API client functionality, enabling teams to adopt components independently.
Key Features
OpenTelemetry-based architecture supporting multiple frameworks
Automatic detailed metadata capture across agent runs without manual span creation
RelevanceEvaluator classifying document relevance with LLM-based explanations
QAEvaluator measuring answer correctness against reference texts
HallucinationEvaluator identifying unsupported information in generated responses
Batch processing support for all evaluators at scale
Embeddings visualization for semantic insights and understanding retrieval patterns
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
Framework-agnostic design prevents vendor lock-in
Apache 2.0 license with active maintenance enables flexible deployment
Production-scale deployment capabilities through Kubernetes clusters
Modular design allows independent component adoption
Weaknesses
UI polish remains a work in progress compared to commercial platforms
Open-source model may require more self-directed troubleshooting
Use Cases
Multi-framework environments gain production-scale deployment capabilities through Kubernetes clusters. Phoenix is ideal for teams running heterogeneous AI stacks or those anticipating framework changes who need evaluation infrastructure that won't require rebuilding. Organizations seeking deployment flexibility from local development to production scale benefit from the open-source model.
DeepEval
Quality issues discovered in production cost 10x more than those caught during development. DeepEval shifts evaluation left through pytest and unittest integration, catching failures before deployment rather than discovering them when users complain. This testing-first philosophy distinguishes it from observability-focused platforms that discover issues after they affect users.
Key Features
G-Eval for chain-of-thought reasoning evaluation
Faithfulness detection for catching hallucinations
Answer Relevancy measuring response appropriateness
Contextual Precision for retrieval quality assessment
Contextual Recall for completeness measurement
Regression testing catching quality degradation during development
Synthetic test data generation for comprehensive evaluation datasets
CI/CD pipeline integration for pre-deployment testing
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
pytest and unittest integration enables testing-first philosophy
Pre-deployment testing catches regressions early
Synthetic evaluation dataset creation solves the cold-start problem
Apache 2.0 license with Confident AI enterprise platform available
Weaknesses
Emphasizes development-time quality assurance over production monitoring
Fewer observability features than platforms designed specifically for runtime monitoring
Use Cases
Pre-deployment testing integrated with CI/CD pipelines catches regressions early, making DeepEval ideal for teams with strong testing cultures. Synthetic evaluation dataset creation solves the cold-start problem when reference data doesn't exist, supporting teams building new RAG systems without historical evaluation data. Development teams prioritizing shift-left quality assurance benefit most from this testing-first approach.
UpTrain
Two weeks of configuration before running your first evaluation? Most platforms require extensive setup before you can assess quality. UpTrain provides 20 predefined metrics covering context relevance, response completeness, and factual accuracy—enabling assessment across multiple dimensions without setup friction. This comprehensive metric library makes rapid deployment practical.
Key Features
20 predefined metrics covering context relevance, response completeness, and factual accuracy
Automated evaluation pipelines running continuously
Custom metrics adapting to domain-specific requirements
Production monitoring tracking performance degradation
Dataset management maintaining evaluation sets as systems evolve
Component-level assessment separating retrieval from generation quality
Both self-hosting and managed cloud service options
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
Comprehensive metric library enables rapid deployment without setup friction
Bridges evaluation and production operations effectively
Apache 2.0 licensing with commercial support available
Component-level assessment enables targeted debugging
Weaknesses
Smaller community compared to more established alternatives
Documentation depth varies across features
Teams may need to invest more time in initial configuration
Use Cases
Component-level assessment separates retrieval from generation quality, enabling targeted debugging when metrics indicate issues. UpTrain is ideal for teams needing rapid deployment without extensive configuration and those requiring both development evaluation and continuous production monitoring. Organizations with domain-specific requirements benefit from custom metrics capabilities.
LangFuse
Data sovereignty requirements create a dilemma for regulated industries. Commercial evaluation platforms force data into external systems, while internal tools lack production-grade capabilities. LangFuse's MIT-licensed, self-hosting architecture solves this—on-premises or private cloud deployment with complete data control.
Key Features
MIT-licensed, self-hosting architecture for on-premises or private cloud deployment
LLM-as-a-judge for automated evaluation
Human annotation workflows for manual assessment
Integration with Ragas providing comprehensive RAG metrics
Context Precision, Context Recall, and Context Relevancy for retrieval quality
Faithfulness, Answer Relevancy, and Aspect Critique for generation quality
Trace-level evaluation linking quality metrics directly to execution traces
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
Complete data control through self-hosting architecture
Hybrid evaluation approaches combining automated and human-in-the-loop assessment
MIT license provides deployment flexibility
Ragas integration offers comprehensive RAG metrics
Weaknesses
Self-hosting introduces operational overhead for infrastructure management
Integration ecosystems smaller than those of commercial platforms backed by larger engineering teams
Use Cases
Data governance requirements driving on-premises deployment align with LangFuse's self-hosting architecture. Hybrid evaluation approaches combining automated and human-in-the-loop assessment provide flexibility for quality assurance workflows. LangFuse is ideal for regulated industries with strict data sovereignty requirements and organizations preferring complete infrastructure control over managed services.
7. Ragas
Debugging RAG quality issues wastes days when you can't isolate the root cause. Is retrieval surfacing irrelevant documents? Or is generation ignoring good context?
Ragas provides six component-specific metrics that separate retrieval quality (Context Precision, Recall, Relevancy) from generation quality (Faithfulness, Answer Relevancy, Aspect Critique). This component-level debugging enables teams to diagnose whether quality issues stem from retrieval failures or generation problems.
Key Features
Six component-specific metrics separating retrieval and generation quality
Context Precision, Recall, and Relevancy for retrieval assessment
Faithfulness, Answer Relevancy, and Aspect Critique for generation assessment
Hybrid evaluation combining LLMs with deterministic algorithms like string similarity, BLEU, and ROUGE
Reference-free evaluation for most metrics eliminating ground truth requirements
Extensive integration ecosystem including LangChain, LlamaIndex, Haystack, Griptape, Amazon Bedrock, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Gen AI, Meta's LlamaStack, R2R, Swarm, and Langfuse
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
Component-level metrics enable precise root cause diagnosis
Hybrid evaluation approach enables large-scale assessment without prohibitive costs
Apache 2.0 license with extensive integration ecosystem
Reference-free evaluation eliminates need for ground truth datasets
Weaknesses
Evaluation quality depends on LLM judge accuracy
No standardization across different judge models
Potential consistency challenges when comparing results across implementations
Use Cases
Evaluation approaches balance nuance and efficiency, making Ragas ideal for teams needing large-scale assessment without prohibitive costs. The extensive integration ecosystem enables adoption across diverse technology stacks. Ragas suits teams requiring component-level debugging to isolate retrieval versus generation issues and organizations working across multiple frameworks who need a consistent evaluation methodology.
Ensuring Scalable and Efficient RAG Systems
Without real-time monitoring, retrieval accuracy can degrade, leading to irrelevant or incomplete AI responses.
Here’s how Galileo ensures system reliability:
Monitor query effectiveness and response alignment with Galileo RAG & Agent Analytics.
Set automated alerts for retrieval failures and latency spikes using Galileo Guardrail Metrics.
Continuously refine chunking, ranking, and indexing based on real-time insights from Galileo Evaluate.
Get started with Galileo and maintain peak retrieval performance with real-time analytics.
FAQs
How is RAG evaluation different from general LLM evaluation?
RAG evaluation requires bi-phasic assessment measuring both retrieval quality (whether relevant documents are surfaced) and generation faithfulness (whether responses stay grounded in retrieved context). General LLM evaluation only assesses generation quality without considering retrieval dynamics. This enables faster debugging by isolating whether quality issues stem from retrieval failures or generation problems.
How do teams evaluate RAG systems without ground truth reference answers?
Reference-free evaluation uses Context Adherence measuring whether generated text aligns with retrieved context, Context Relevance assessing retrieval quality through semantic similarity, and Hallucination Detection identifying unsupported claims without reference answers. LLM-as-judge approaches analyze queries, retrieved documents, and generated responses, with ensemble methods achieving greater than 85% correlation with human assessments.
When should we implement RAG evaluation—during development or in production?
Both. Offline evaluation during development enables systematic testing before deployment and regression detection catching quality degradation. Online evaluation in production provides continuous quality monitoring and real-time alerting when metrics degrade. Infrastructure requirements differ—development prioritizes evaluation thoroughness while production requires low-latency assessment (typically under 200ms) to avoid degrading system performance.
What metrics matter most for preventing hallucinations in RAG systems?
Faithfulness and Context Adherence represent the most direct hallucination detection metrics, measuring whether generated content is supported by retrieved context. Stanford research shows hallucination rates range from 17-33% across leading RAG-based legal research tools. Complementary metrics include Groundedness and Citation Precision verifying source attribution accuracy.
How does Galileo's Luna-2 compare to using GPT-4 for RAG evaluation?
Luna-2's 3B-8B parameter models deliver evaluation at $0.02 per 1M tokens with ~152ms latency. Luna-2 is specifically fine-tuned for evaluation workloads, providing token-level probabilities for granular quality assessment. Luna-2's cost-performance profile makes systematic evaluation economically feasible at scale.


Pratik Bhavsar