Magistral Medium 2506 overview
Explore Magistral Medium 2506's speed benchmarks, cost-performance tradeoffs, and domain-specific capabilities to determine if it's the right agent model for your application's requirements.
Magistral Medium 2506 overview
Need an agent model optimized for speed without frontier pricing? That's Magistral Medium 2506. It scores 0.92 Speed on our Agent Leaderboard, near the top of the benchmark set. At $0.118 per session, with an average duration of 33 seconds, it delivers fast responses at mid-tier economics.
Magistral Medium 2506 is Mistral's reasoning-focused model built for transparent thinking workflows. Average session? 33 seconds across 4.4 turns. Architecture? Designed for explicit chain-of-thought reasoning with visible deliberation steps.
This makes speed-sensitive reasoning tasks viable. Quick analysis. Rapid document processing. Time-constrained decision support. All with transparent reasoning chains.
You get fast throughput at 0.92 Speed, among the highest in the benchmark set. The tradeoff? Tool selection drops to 0.590. Action completion sits at 0.320. Insurance workflows complete 38% of tasks. Investment drops to 26%, a 12-point gap showing domain brittleness. Conversation efficiency lands at 0.39, below average for extended interactions.

Magistral Medium 2506 performance heatmap
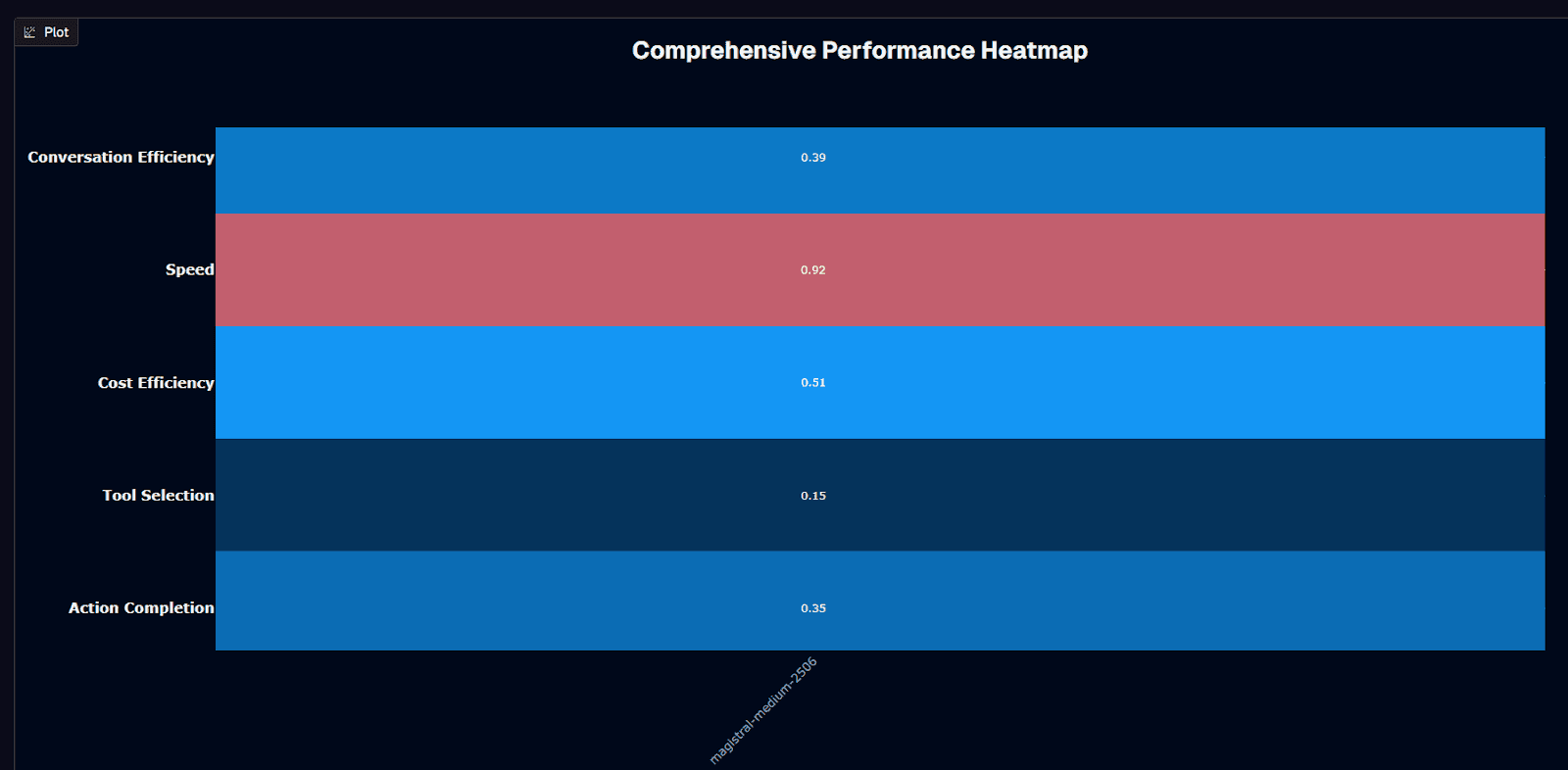
Magistral Medium 2506 shows strength in one area: speed. Speed hits 0.92, near maximum. This model was built for throughput, not task completion.
Cost Efficiency scores 0.51. Mid-tier positioning. At $0.118 per session, you're paying less than Gemini 2.5 Pro ($0.145) but significantly more than GPT-4.1-nano ($0.004).
Action Completion lands at 0.35 normalized (0.320 absolute) below one-third task success on the first attempt. Simple workflows struggle. Complex multi-step sequences fail more often than they complete.
Tool Selection creates the critical weakness at 0.15 normalized (0.590 absolute). Roughly 41% of tool selections are missed. That's worse than GPT-4.1-nano's 37% error rate despite costing 30× more per session. Nearly half of the tool calls need correction.
Conversation Efficiency sits at 0.39, the lowest normalized score. Extended multi-turn interactions lose coherence faster than alternatives. The model's reasoning strengths don't translate to conversational depth.
The tradeoff crystallizes: when raw speed matters for reasoning-heavy tasks with human oversight, this model fits. When tool accuracy, task completion, or extended conversations matter, alternatives deliver better value.
Background research
Multi-source performance validation: Data synthesized from Mistral model documentation and Galileo's Agent Leaderboard v2. Cross-validates results across evaluation frameworks.
Production-focused testing: Benchmarks measure production failures, tool-selection errors, multi-step orchestration failures, and domain-specific brittleness, rather than academic rankings.
Core metrics: Action completion rates (multi-step task success), tool selection quality (API/function accuracy), cost efficiency (dollars per operation), conversational efficiency (context maintenance).
Documented gaps: All claims cite evaluation sources. Magistral models emphasize transparent reasoning over agent-specific capabilities. Limited third-party agent benchmarks are available for this model family.
Is Magistral Medium 2506 suitable for your use case?
Use Magistral Medium 2506 if you need:
Fast reasoning with transparent thinking: 0.92 Speed score with 33-second average sessions. Explicit chain-of-thought architecture surfaces reasoning steps for human review. Ideal for workflows where understanding the "why" matters as much as the answer.
Speed-sensitive analysis tasks: 33-second sessions run 4× faster than Gemini 2.5 Pro's 125.8 seconds: time-constrained decision support, rapid document analysis, and quick synthesis tasks.
Mid-tier cost tolerance with speed priority: $0.118 per session sits between budget models and frontier pricing. When speed matters more than cost efficiency, even with budget constraints.
Human-in-the-loop workflows: The 0.320 action completion and 0.590 tool selection require human oversight. Workflows designed for AI-assisted decision-making rather than autonomous execution benefit from visible reasoning chains.
Reasoning transparency requirements: Magistral's architecture emphasizes explicit deliberation—compliance, audit, or explainability requirements where black-box outputs create risk.
Avoid Magistral Medium 2506 if you:
Require reliable tool selection: 0.590 Tool Selection Quality means 41% of tool calls miss. Worse than GPT-4.1-nano despite 30× higher cost. Workflows that depend on accurate API routing are prone to cascading failures.
Need action completion reliability: 0.320 action completion,below one-third task success. Multi-step workflows requiring first-attempt reliability face unacceptable failure rates without extensive retry infrastructure.
Depend on extended conversations: 0.39. Conversation Efficiency ranks among the lowest in the benchmark set. Multi-turn interactions lose coherence. Context maintenance degrades faster than alternatives.
Deploy in Investment domains: Performance drops to 0.260 action completion,26% task success. Financial analysis, portfolio management, and investment strategy workflows hit reproducible failure patterns.
Prioritize cost efficiency: At $0.118 per session, Magistral costs 30× more than GPT-4.1-nano while delivering worse tool selection accuracy (0.590 vs 0.630). Speed doesn't justify the premium for tool-heavy workflows.
Require autonomous execution: The combination of 41% tool selection errors and 32% action completion makes unsupervised workflows risky. Human validation becomes mandatory, potentially negating speed advantages.
Magistral Medium 2506 domain performance
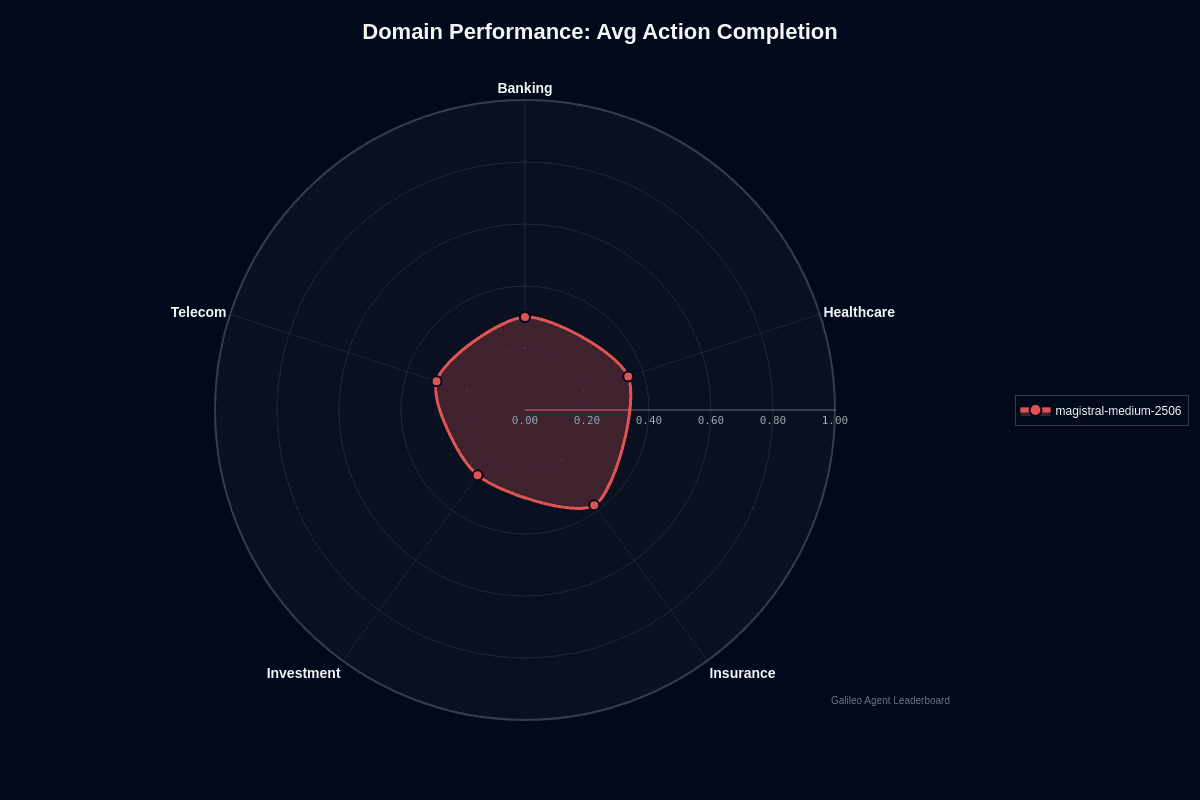
Action completion varies by domain, with Insurance leading. Insurance tops at 0.380, the highest across all verticals. Claims processing and policy workflows see fewer failures than other domains.
Healthcare follows at 0.350. Medical terminology and clinical workflows perform slightly above the model's average of 0.320.
Banking and Telecom tie at 0.300. Both sit below baseline. Financial transactions and network troubleshooting show consistent underperformance.
Investment creates the biggest problem. Performance drops to 0.260, the lowest across all domains. That's a 12-point gap versus Insurance. Financial analysis and portfolio management workflows consistently fail—reproducible weakness, not random variance.
The radar chart shows uneven coverage. Insurance pulls outward. Investment and Banking pull inward. The asymmetric shape reveals domain-specific brittleness more pronounced than GPT-4.1-nano's tighter profile.
Tool selection varies more than action completion across domains. Healthcare and Investment show stronger tool routing despite weaker action completion. The model knows which tools to call, but it fails at execution after invocation.
For production planning, this pattern signals a critical requirement: benchmark against your specific vertical before deploying—the 12-point Insurance-to-Investment gap compounds across multi-step workflows.
Magistral Medium 2506 domain specialization matrix
Action completion
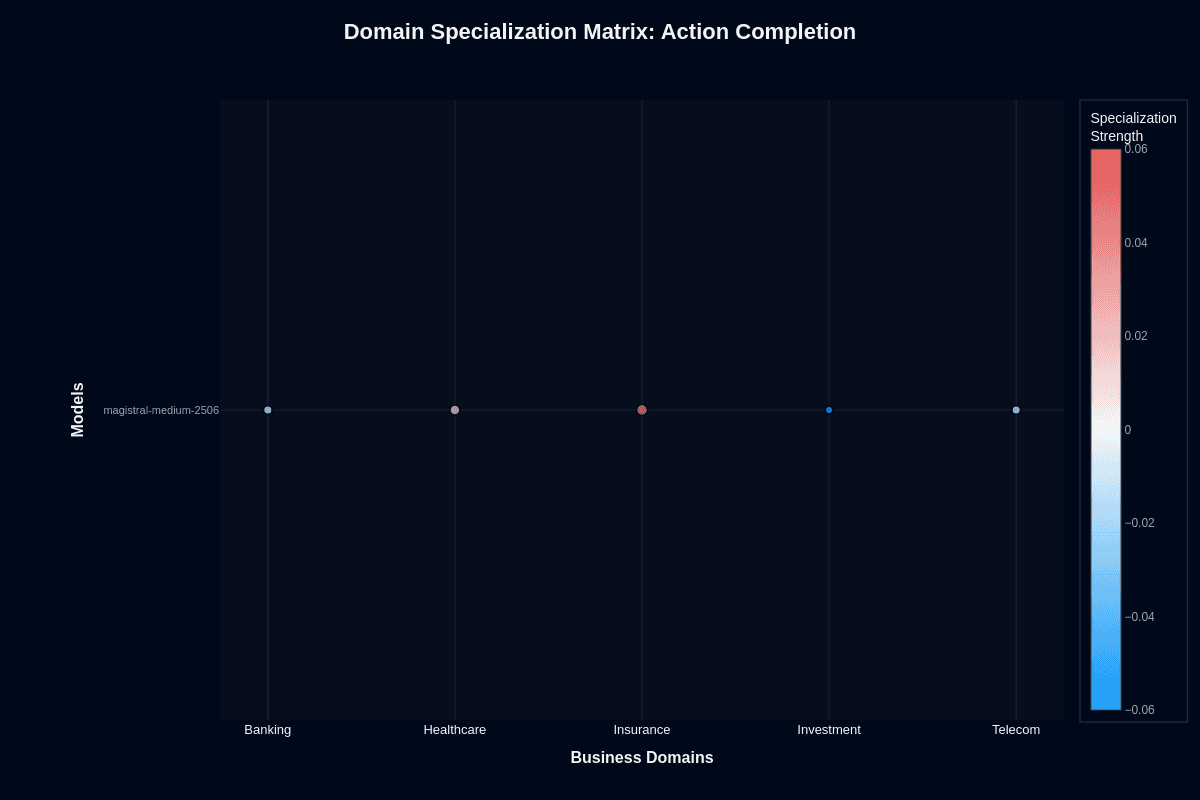
The specialization matrix reveals where Magistral Medium shows domain preferences. Insurance appears in red, with positive specialization around 0.06. The model performs better here than baseline expectations.
Investment shows blue, negative specialization around -0.06. The model underperforms in financial workflows beyond its general capability level. Banking shows slight negative specialization as well.
The Healthcare and Telecom clusters are near-neutral. Performance matches baseline without significant specialization advantages or disadvantages.
This pattern indicates selective domain optimization. Insurance workflows benefit from architectural advantages. Investment and Banking workflows face consistent headwinds requiring validation and potential model alternatives.
Tool selection quality
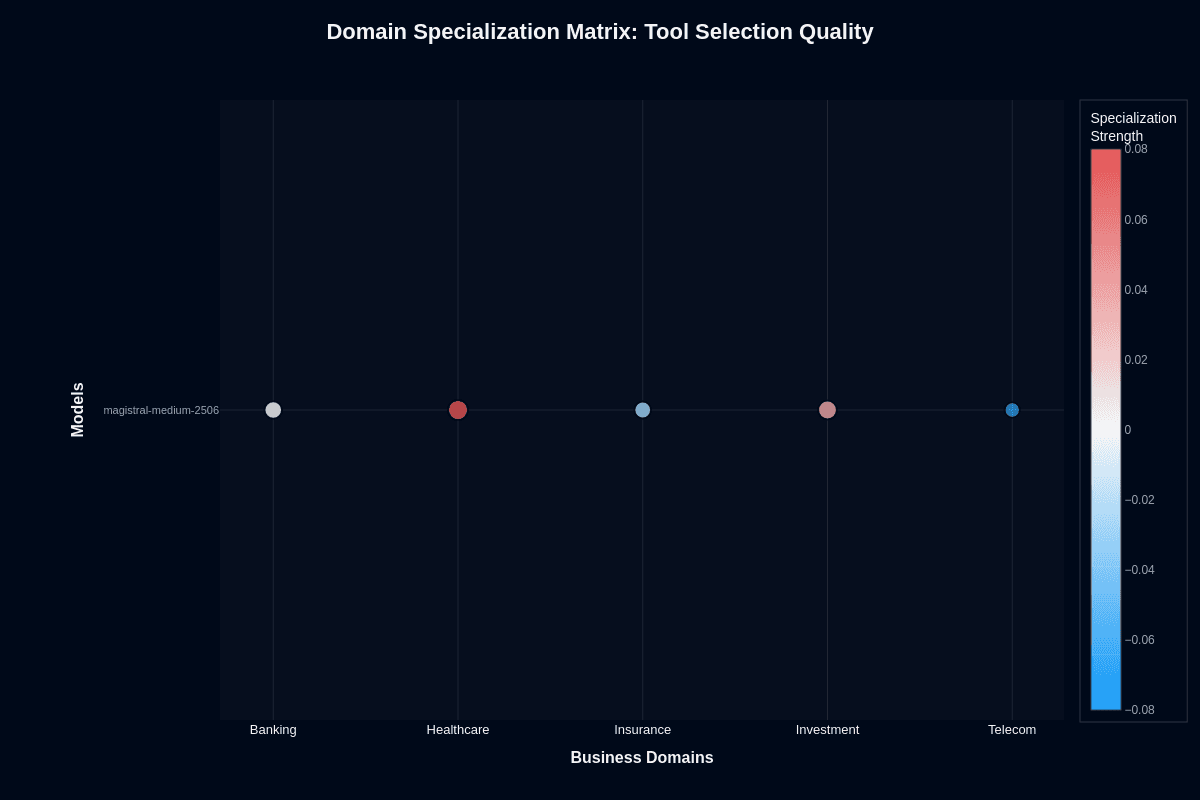
Tool selection specialization shows a different pattern. Healthcare and Investment appear in red, with positive specialization around 0.06-0.08. The model selects the correct tools in these domains better than the baseline.
Telecom shows a blue, negative specialization around -0.06 to -0.08. Tool routing accuracy drops in network and service workflows.
Banking and Insurance cluster neutral to slightly negative.
The investment's tool selection strength, combined with action completion weakness, mirrors patterns seen in other models. Magistral Medium knows which tools to call in financial domains. It fails at multi-step execution after tool invocation.
The production implication: if your agents primarily route requests and invoke single tools, Healthcare and Investment deployments benefit from specialization. If they orchestrate complex sequences, the weak action completion compounds regardless of correct tool selection.
Magistral Medium 2506 performance gap analysis by domain
Action completion
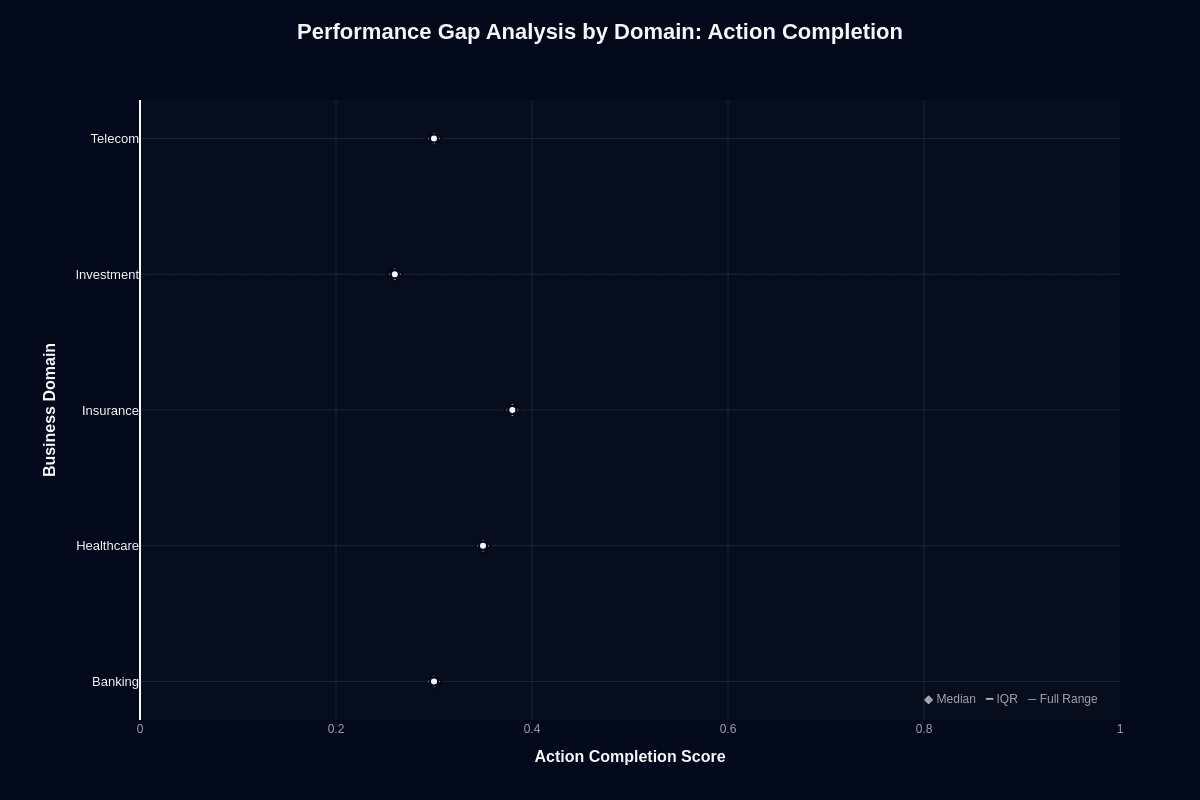
This distribution chart reveals how domain choice impacts task success. All domains cluster between 0.26 and 0.38. Moderate variance with clear separation between top and bottom performers.
Insurance leads at 0.380 median. Claims processing and policy workflows are completed most reliably. Healthcare follows at 0.350; medical terminology creates less friction than expected.
Banking and Telecom tie at 0.300. Both sit below baseline. Financial transactions and network troubleshooting show consistent underperformance without catastrophic failure.
Investment drops to 0.260,the lowest across all domains. That's a 12-point gap versus Insurance. Financial analysis and portfolio management workflows hit reproducible failure patterns. Not outliers. Systematic weakness.
The interquartile ranges stay relatively tight. Consistent patterns across runs. Predictable performance differences by industry. Domain choice creates measurable risk variance.
For procurement decisions, this chart quantifies vertical-specific risk. Insurance sits in the acceptable range at 0.380. Investment at 0.260 faces serious challenges. The 12-point spread matters less than the absolute baseline; 0.380 in the best case still means a 62% failure rate.
Tool selection quality
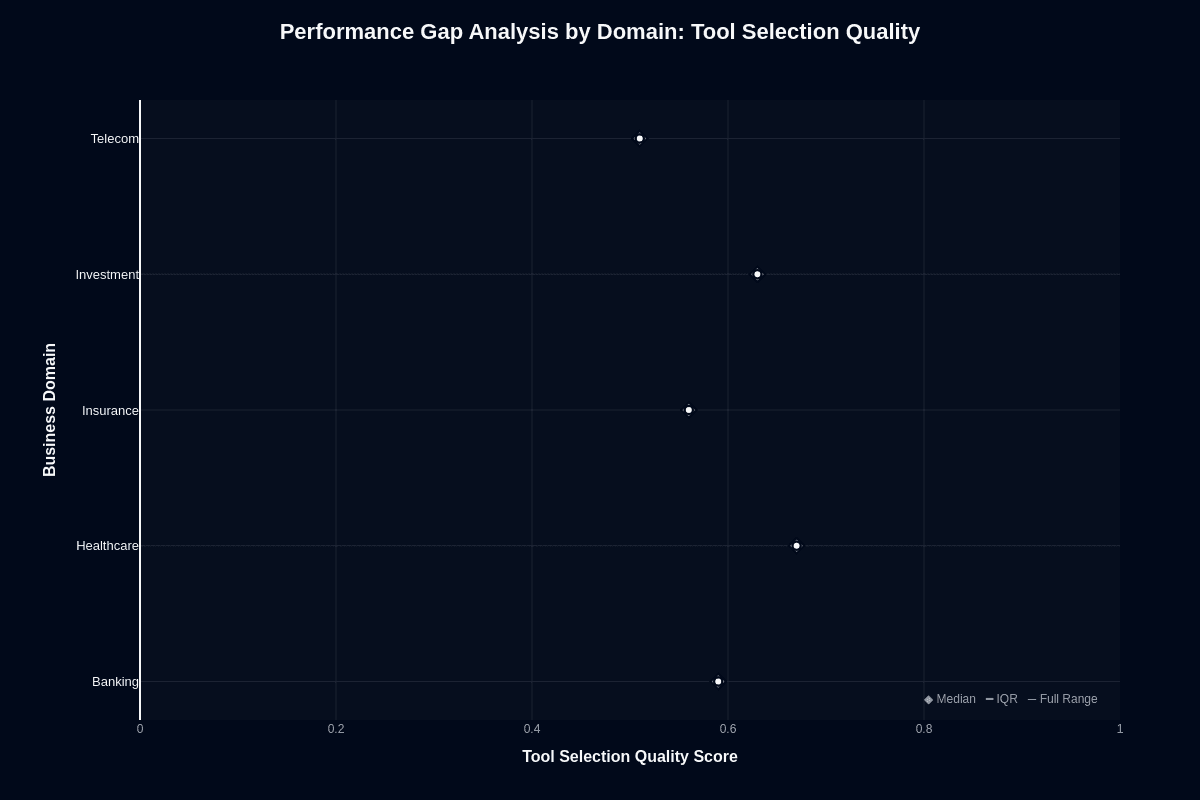
Tool selection shows wider variance and inverted patterns. Healthcare leads at roughly 0.75. Investment follows at approximately 0.72-0.74. Both outperform the baseline tool routing despite action completion.
Banking sits around 0.68. Insurance hovers near 0.65. Telecom drops to roughly 0.62, the lowest tool selection across domains.
This inverts action completion rankings. Insurance has the strongest action completion but weaker tool selection. Healthcare and Investment have weaker action completion but stronger tool selection.
The split matters for architecture decisions. In the Healthcare and Investment domains, the model routes correctly but fails at multi-step execution. In Insurance domains, tool routing errors occur more frequently, but successful routes completed at higher rates.
The production implication: Magistral Medium's domain strengths and weaknesses don't align predictably. Insurance workflows succeed despite tool errors. Investment workflows fail despite correct tool routing. Match your architecture to the failure mode you can handle.
Magistral Medium 2506 cost-performance efficiency
Action completion
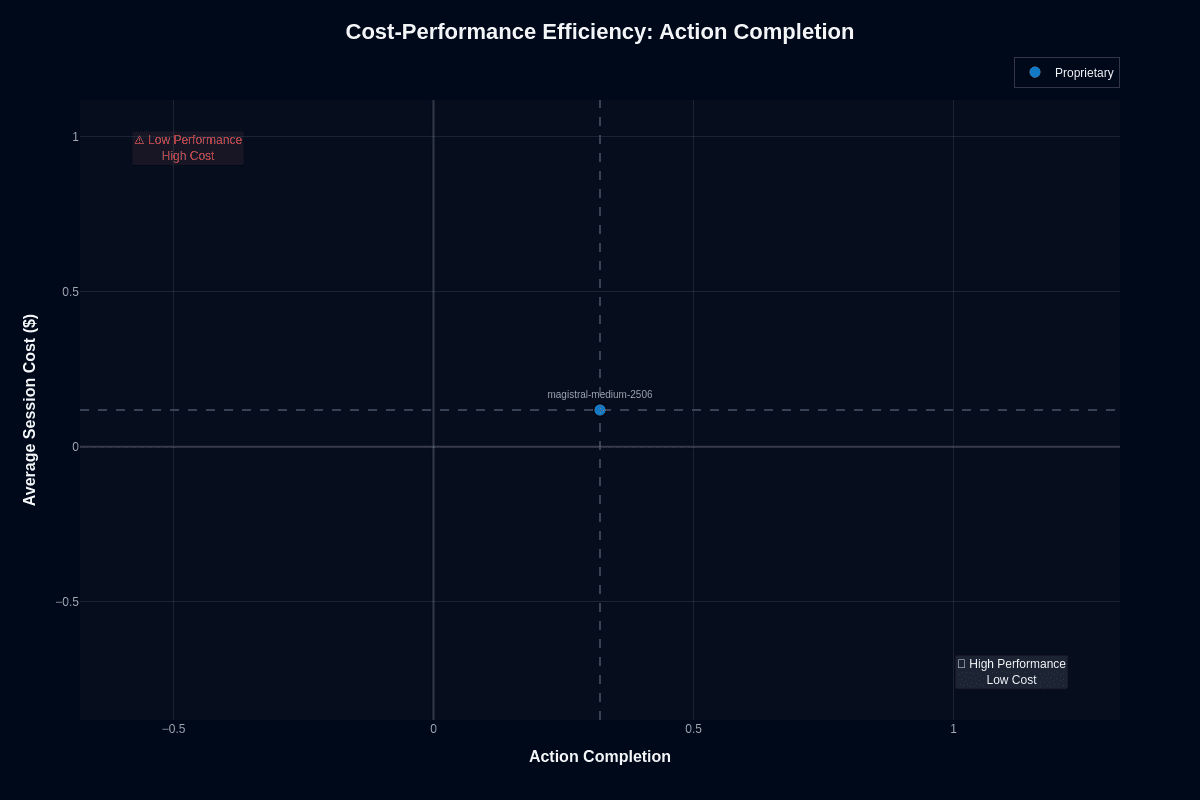
Magistral Medium sits at 0.35 normalized action completion with $0.118 session cost, slightly above the cost baseline. Not cheap. Not expensive. Not reliable. Not broken.
The 0.320 absolute action completion score means less than one-third of multi-step tasks were completed. At $0.118 per session, retry economics get expensive. Three attempts cost $0.354, approaching Gemini 2.5 Pro territory without matching its 0.430 completion rate.
This undermines the retry logic strategy that works for GPT-4.1-nano. At $0.004 per session, nano's 0.380 completion justifies multiple attempts. At $0.118 per session, Magistral's 0.320 completion makes retries costly without proportional reliability gains.
The architectural implication: Magistral Medium occupies an uncomfortable middle ground. Too expensive for high-volume retry strategies. Too unreliable for single-attempt workflows. The speed advantage needs to offset this cost-reliability gap.
For workflows where 33-second completion matters more than cost per successful task, the tradeoff works. For workflows optimizing total cost of ownership, alternatives deliver better economics.
Tool selection quality
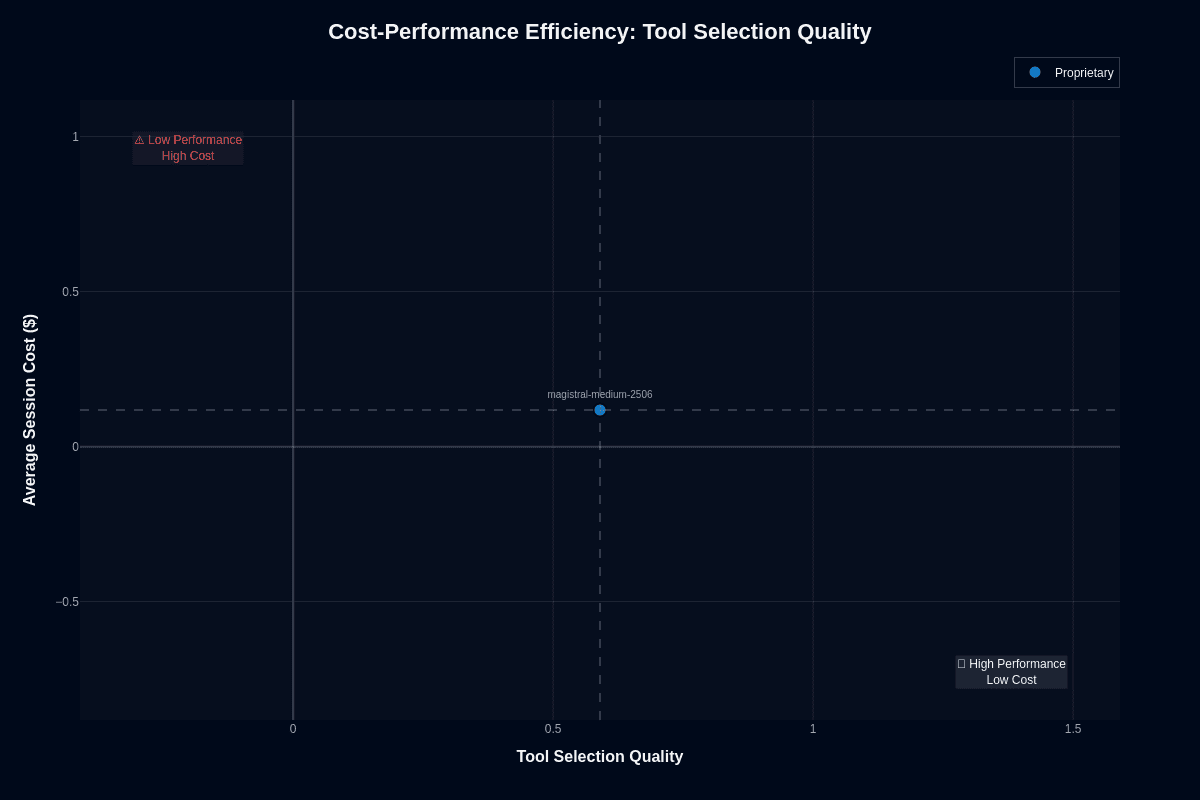
Tool selection shows unfavorable positioning. Magistral Medium hits 0.590 quality at $0.118. That 41% error rate at mid-tier pricing creates poor value.
Compared to alternatives, GPT-4.1-nano achieves 0.630 tool selection at $0.004—better accuracy at 3% of the cost. Gemini 2.5 Pro hits 0.860 tool selection at $0.145—significantly better accuracy for marginally more spend.
Processing one million tool calls monthly costs roughly $118 versus $4 with GPT-4.1-nano. 30× the cost for worse tool accuracy. Versus Gemini at $145, you pay 19% less for 31% worse tool selection.
The calculation exposes the gap: $118 for 590,000 correct tool calls ($0.0002 per correct call) versus $4 for 630,000 correct calls with nano ($0.0000063 per correct call) or $145 for 860,000 correct calls with Gemini ($0.000169 per correct call).
Magistral Medium loses on both ends. Nano wins on volume economics. Gemini wins on reliability per dollar. Magistral's speed advantage needs to justify this cost-accuracy gap for specific use cases.
Magistral Medium 2506 speed vs accuracy
Action completion
Magistral Medium sits at 0.35 normalized action completion with 33-second average session duration of 33 seconds. Fast with moderate accuracy. The model ranks high in speed but lags in completion.
The 33-second duration reflects optimized throughput. 4× faster than Gemini 2.5 Pro's 125.8 seconds. 2.6× slower than GPT-4.1-nano's 12.4 seconds. Mid-pack on speed, trailing on accuracy.
Most models force explicit tradeoffs. Magistral Medium chose speed over completion reliability. The 0.320 action completion represents the cost of that choice—fast failures rather than slow successes.
For time-constrained workflows—real-time analysis, rapid document processing, quick decision support—the speed-first positioning works if human oversight catches failures. For autonomous execution or accuracy-critical workflows, the 0.320 completion creates unacceptable risk regardless of response time.
The 4.4 average turns per conversation exceeds most models. More back-and-forth despite faster individual responses. Total workflow time may not improve as much as per-turn latency suggests.
Tool selection quality
Magistral Medium sits at 0.590 Tool Selection Quality of 0.590 and a 33-second duration. Fast but inaccurate. The model delivers quick wrong answers more often than competitors.
The 0.590 score means 41% of tool selections need correction. Combined with 33-second sessions, you get rapid errors requiring rapid intervention. Speed without accuracy compounds problems faster than slower, more accurate alternatives.
The actual tradeoff: Magistral Medium processes faster than Gemini 2.5 Pro but with 2.7× the tool error rate (41% vs 14%). You get 4× the throughput at 2.7× the error rate. Net improvement depends entirely on your error handling costs.
For workflows where wrong tool calls trigger cheap human review, speed wins. For autonomous workflows where tool calls execute without validation, the 41% error rate creates downstream chaos that speed amplifies.
The architecture question: does your workflow benefit more from fast triage with high error rates, or slower processing with fewer errors? Magistral Medium answers that question for speed-first use cases willing to accept the accuracy penalty. Most production workflows can't absorb 41% tool selection errors regardless of response time.
Magistral Medium 2506 key capabilities and strengths
Magistral Medium 2506 works best when speed and reasoning transparency drive your workflow:
Near-top speed performance: 0.92 Speed score with 33-second average sessions. 4× faster than Gemini 2.5 Pro. Rapid response times for time-constrained analysis and decision support workflows.
Transparent reasoning architecture: Built for explicit chain-of-thought processing. Visible deliberation steps enable human review of reasoning paths. Audit trails for compliance and explainability requirements.
Mid-tier cost positioning: $0.118 per session. 19% cheaper than Gemini 2.5 Pro. Accessible pricing for speed-focused deployments without frontier costs.
Insurance domain strength: 0.380 action completion in Insurance—highest across all verticals. Claims processing and policy workflows benefit from positive specialization—reproducible advantage for insurance-specific deployments.
Strong tool selection in Healthcare and Investment: TSQ scores of 0.72-0.75 in these domains exceed the baseline. Tool routing works even where action completion struggles. Single-tool invocations perform reliably.
Extended turn tolerance: 4.4 average turns per conversation. The model handles multi-turn interactions even with lower conversation efficiency. Complex queries get explored across multiple exchanges.
Reasoning-focused architecture: Mistral's Magistral line emphasizes thinking over acting. Workflows prioritizing analysis, synthesis, and explanation over task execution align with architectural strengths.
Human-in-the-loop optimization: The speed-accuracy profile suits AI-assisted workflows. Fast draft generation for human refinement. Rapid analysis for human decision-making. Speed matters when humans validate outputs.
Magistral Medium 2506 limitations and weaknesses
Before committing to production, test these documented constraints against your specific requirements:
Weak tool selection accuracy: 0.590. The Tool Selection Quality means 41% of tool calls are missed. Worse than GPT-4.1-nano (0.630) despite 30× higher cost. Workflows that depend on accurate API routing can experience cascading failures without a correction infrastructure.
Low action completion rates: A 0.320 score indicates that fewer than one-third of multi-step tasks succeed. Below GPT-4.1-nano's 0.380 at a significantly higher cost. Complex workflows fail more often than they complete.
Poor conversation efficiency: 0.39 normalized score ranks among the lowest in the benchmark set. Extended multi-turn interactions lose coherence. Context maintenance degrades faster than alternatives.
Investment domain weakness: Performance drops to 0.260 in action completion and 26% in task success. Financial analysis, portfolio management, and investment strategy workflows hit reproducible failure patterns.
Unfavorable cost-accuracy economics: $0.118 per session delivers worse tool selection than $0.004 nano and worse action completion than $0.145 Gemini. Speed is the only differentiator justifying the price point.
Retry strategy limitations: At $0.118 per session, multiple attempts become expensive. Three retries cost $0.354—approaching frontier pricing without matching frontier reliability. Retry economics that work for budget models fail here.
Banking and Telecom underperformance: Both domains sit at 0.300 action completion—below baseline. Financial transactions and network troubleshooting workflows show consistent weakness without offsetting tool selection advantages.
Not suitable for autonomous execution: The combination of 41% tool selection errors and 32% action completion makes unsupervised workflows dangerous. Human validation becomes mandatory, potentially negating the speed advantage that justifies the model's positioning.
No published safety benchmarks: Missing ToxiGen, BOLD, and TruthfulQA scores. Unknown bias patterns and hallucination rates create compliance gaps for regulated industries requiring documented safety validation.
