Magistral Small 2506
Explore Magistral Small 2506’s performance benchmarks, industry-specific capabilities, and evaluation metrics to determine if it's the right AI model for your application's requirements.

Magistral Small 2506
Magistral Small 2506 sits at #22 on the Agent Leaderboard with a speed score of 0.97 and cost efficiency of 0.89. Translation: near-instant responses at $0.03 per session. For engineering leaders obsessed with cost-performance ratios, those numbers look tempting.
But here's the catch—the model's action completion rate is abysmal, and tool selection accuracy barely clears a coin flip. This analysis will help you decide if those trade-offs work for your situation.
Exploring diverse language models? Check out our Agent Leaderboard to find what fits your use case. You'll get performance heatmaps, domain-specific gaps, and concrete deployment recommendations—no guesswork required.

Magistral Small 2506 performance heatmap
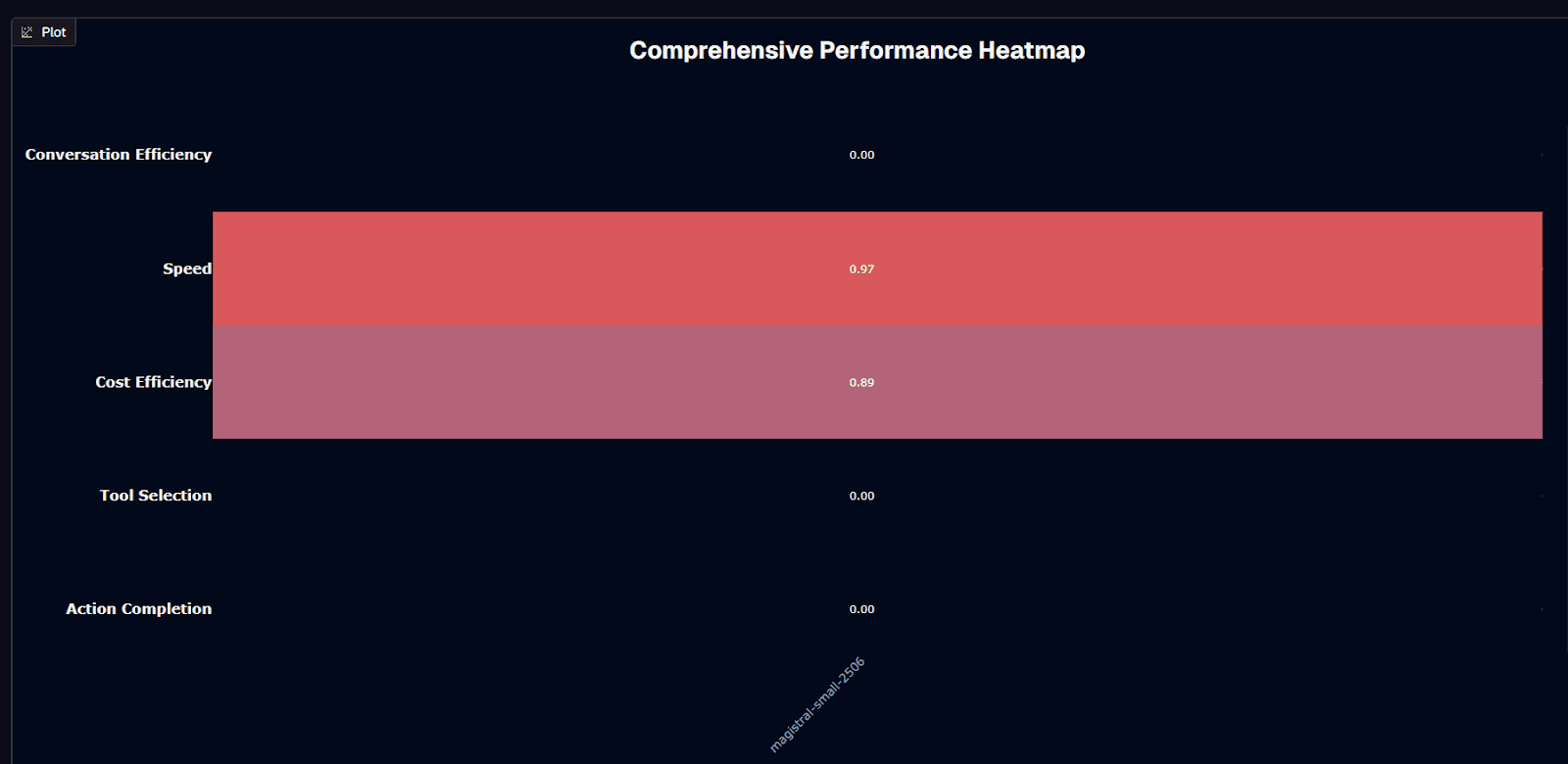
Speed is where Magistral Small 2506 shines. A 0.97 speed score places it in the 97th percentile—17.4 seconds average response time. Stack that with a 0.89 cost-efficiency score at $0.03 per session. The result: answers delivered almost instantly without draining your budget. For latency-sensitive, high-volume workloads, those two numbers are hard to beat.
The rest of the heatmap? Not pretty. Action completion sits at 0.160—the model finishes only 16% of multi-step tasks on the first attempt. Tool selection accuracy reaches 0.530, barely better than flipping a coin. Worst of all, conversation efficiency is 0.00. You'll need 5.7 back-and-forth turns, on average, to coax a result—completely wiping out the speed advantage in complex workflows.
These mixed signals drop the model to #22. The ranking weighs functional quality, speed, and cost. This model makes the cut because its economic profile offsets glaring reliability gaps. You pay almost nothing for quick answers, but published benchmarks show an 84% failure rate on multi-step tasks.
That trade-off is decisive for deployment planning. Consider this option when every penny matters and tasks finish in a single turn. Wrong answers must carry minimal risk—think large-scale FAQ deflection, real-time content filtering, or rapid pre-processing before routing to a stronger model. The combination of 17.4-second latency and $0.03 per interaction lets you sustain millions of daily calls without spiking costs.
Avoid it for anything requiring dependable execution. Complex agent workflows, financial transactions, or healthcare recommendations will stall under a 0.160 action-completion ceiling and zero conversation efficiency. Even with retries or guardrails, the added turns inflate total latency—eroding the very savings that make the model appealing.
The performance heatmap captures this split personality: brilliant greens on speed and cost, deep reds on everything tied to task completion. Keep that picture in mind as you weigh cost-performance trade-offs—it's the difference between a nimble helper and an unreliable bottleneck.
Background research
You're looking at a 24-billion-parameter model that bridges the gap between Mistral's lightweight base models and their reasoning-focused flagships. This architecture builds on the transformer foundation of Mistral Small 3.1, then layers supervised fine-tuning traces from Magistral Medium with reinforcement learning to sharpen step-by-step logic, mathematical reasoning, and code generation—exactly what you need when workflows demand transparent reasoning without frontier-model overhead.
The "2506" designation follows Mistral's date-based versioning for June 2025. This timing matters because it incorporates the latest alignment and safety techniques while preserving the efficiency profile you need for edge or on-premise deployment. Quantized builds run on a single RTX 4090 or a 32GB MacBook, enabling self-hosting without multi-GPU clusters. If you prefer managed deployment, cloud endpoints through Together AI, OpenRouter, and NVIDIA NIM offer the same weights under Apache 2.0 licensing with full fine-tuning rights, though providers charge usage fees and may introduce their own platform terms and forms of lock-in.
Context handling extends to 128k tokens, though both Mistral and hosting providers warn that quality degrades beyond 40k. Within that practical limit, you can process entire policy manuals, multi-file code diffs, or extended chat histories in single calls while maintaining coherent outputs.
Performance benchmarks reveal strength in structured problem-solving compared to similar-sized models. The model achieves 70.68% pass@1 on AIME24 math problems, 68.18% on GPQA Diamond science questions, and 55.84% on LiveCodeBench v5 coding tasks. Native multilingual support spans 20+ languages with chain-of-thought reasoning capabilities for auditable logic—valuable for finance, healthcare, or legal review pipelines.
Compared to its Mistral siblings, you gain most of Magistral Medium's reasoning precision while keeping Small 3.1's compute footprint. This positions the model as the practical middle ground: fast enough for latency-sensitive applications, open enough for deep customization, and capable enough to handle non-trivial reasoning tasks without cost escalation.
Is Magistral Small 2506 suitable for your use case?
You're facing a classic AI procurement dilemma: ultra-cheap inference versus reliability you can actually deploy. This model's 17.4-second latency and $0.03 session cost deliver exceptional speed and budget efficiency.
Yet its 16% action completion rate means most workflows fail on first attempt. This creates specific deployment scenarios where the trade-offs work—and many where they don't. Use the decision matrix below to evaluate whether your requirements, infrastructure constraints, and failure tolerance align with this model's strengths and limitations.
Use Magistral Small 2506 if you need:
The following capabilities make this model particularly well-suited for specific use cases:
Ultra-low cost at scale: At roughly $0.03 per session, you can handle millions of daily interactions while staying within modest budgets.
Latency-sensitive tasks: The 17.4-second average response time ranks among the fastest midsize models, keeping user wait times low for quick, single-turn queries.
Open-source flexibility: Apache 2.0 licensing lets you fine-tune, self-host, and redistribute without negotiating enterprise contracts or ongoing fees.
Edge and on-prem deployment: Quantized weights run on a single RTX 4090 or 32 GB MacBook, enabling local inference for privacy-sensitive workflows.
High-volume, low-stakes workflows: Batch email triage, FAQ deflection, or preliminary ticket routing tolerate occasional failures while benefiting from throughput and cost savings.
Simple routing layers: A 53% tool-selection score works adequately for sorting requests into 2–3 buckets before handing them to more capable models.
Multilingual basics: Native support for 20+ languages covers global customer bases when you only need straightforward question-answer exchanges.
Budget-conscious safety nets: Cheap calls make retry loops, majority voting, or secondary validation layers financially viable, even though single-call failure rates on complex tasks can be as high as about 55% on some benchmarks.
Banking workflows with error tolerance: Slight positive specialization (~0.02) means balance queries or transaction summaries succeed more often than in other domains.
Avoid Magistral Small 2506 if you need:
Several critical limitations make this model unsuitable for certain applications:
Reliable task completion: With only 16% action completion, roughly 84% of multi-step workflows fail on first attempt—unacceptable for mission-critical operations.
Extended dialogue: The zero conversation-efficiency score shows the model loses context quickly, forcing you into frustrating restart loops.
Autonomous orchestration: Combining low completion rates with 5.7 average turns compounds latency and inflates costs, causing complex agent pipelines to stall.
High-stakes decisions: Financial approvals, medical advice, or compliance judgments demand higher assurance than a 16% success rate offers.
Tight latency-plus-accuracy budgets: Extra retries needed to counter failures erase the raw speed advantage and inflate real end-to-end response times.
Structured API calls: The GGUF build lacks native function calling; crafting JSON through prompts introduces fragility and increases error surfaces.
Very long documents: There are community cautions that performance might degrade beyond roughly 40k tokens despite the 128k advertised window, but there is no documented evidence that this causes more hallucinations.
Frontier creativity or deep knowledge work: The model is tuned for reasoning efficiency, not cutting-edge generative capabilities or exhaustive domain expertise.
Domains where tool errors harm users: Insurance workflows, for example, pair 53% tool-selection accuracy with low completion rates, making mis-routed claims processing nearly inevitable.
Minimal observability budgets: The high failure rate demands monitoring and validation layers; without them, production issues slip through undetected.
Magistral Small 2506 domain performance
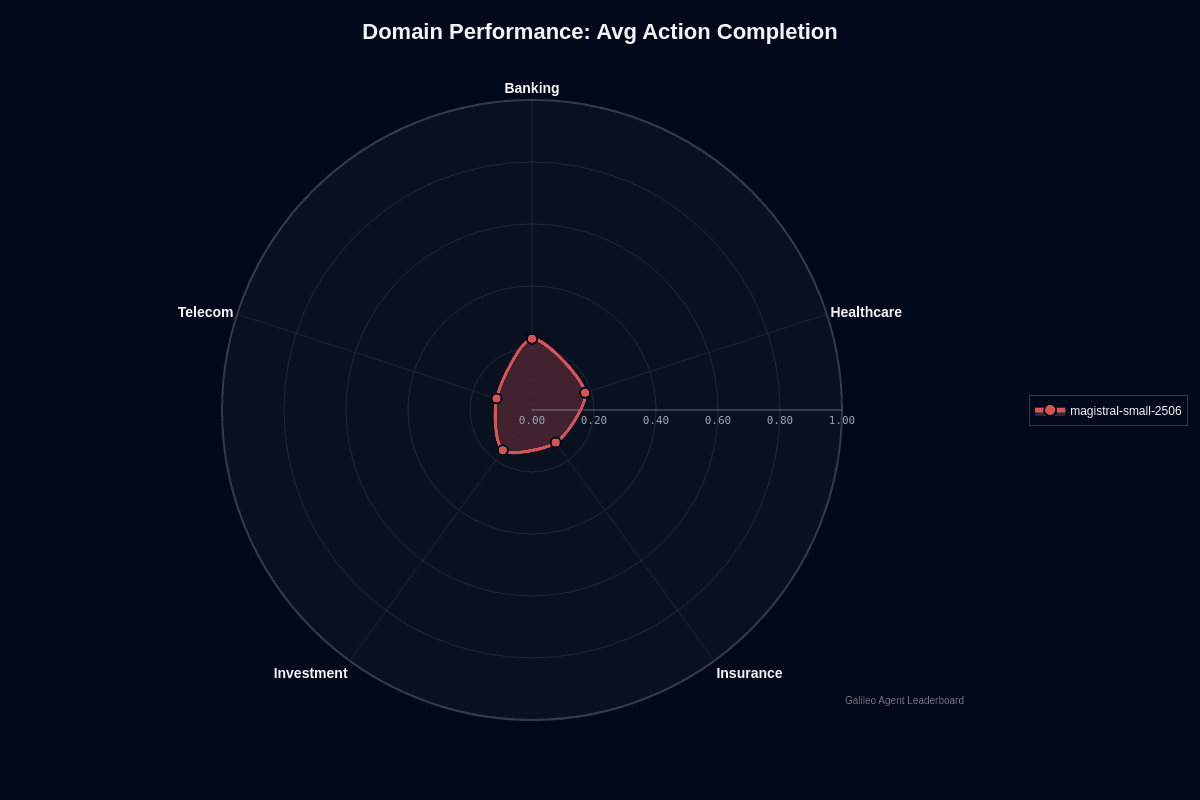
Scan the radar chart and one pattern jumps out: Banking stretches farthest from the center at a 0.23 action-completion score. Telecom barely registers at 0.12. That near-two-fold gap defines how you should approach this model's vertical aptitude. It simply handles structured, transaction-heavy workflows better than looser, jargon-dense conversations.
Banking rises to the top, but the model creators have not attributed this to training on well-labeled financial datasets such as account balances, ledger entries, or ISO transaction codes.
These give the model predictable anchors for reasoning. When prompted to approve a payment or validate an IBAN, it can rely on familiar patterns. Tasks finish more often than not. Healthcare lands in the middle at 0.18 because medical protocols blend structure with nuance. Diagnosis codes are rigid, but patient narratives are messy. That mix produces respectable but inconsistent results.
Insurance (0.13) and Investment (0.16) reveal the model's brittleness. Both domains overload prompts with conditional logic—exclusions, riders, hedging language. This demands precise multi-step reasoning. The system starts strong, selects plausible sub-tasks, then stalls when rules collide. Telecom exposes the weakest point entirely. Network provisioning tickets draw on acronyms, proprietary configuration strings, and rapidly changing service catalogs. At a 0.12 success rate, eight of ten automated actions still fail despite speed advantages.
The absolute scale matters more than relative ordering. Even Banking's "best" performance means 77% of workflows still miss their goal. Planning deployment without guardrails? Treat every vertical score below 0.25 as a warning light, not a green flag.
Where does this leave your deployment strategy? If you're on a Banking team, you can squeeze the most value, especially for low-stakes tasks. Pre-screening transactions or drafting KYC summaries work reasonably well. Healthcare apps might consider the model for internal summarization or triage suggestions.
Just ensure a clinician reviews the output. If you're in Insurance, Investment, or Telecom engineering, you'll need aggressive validation layers—schema enforcement, retry logic, or fallback to higher-accuracy models—before trusting this solution in production.
Remember these numbers coexist with the strong efficiency claims and qualitative speed improvements reported for the model. Latency is non-negotiable and cost runs tight? You can still extract ROI by limiting scope to single-turn, well-structured requests in Banking-style domains. Everything else demands extensive post-processing or selecting a model with stronger domain depth instead of raw speed.
Magistral Small 2506 domain specialization matrix
Domain specialization matrices reveal where the model outperforms its own baseline. Coral and red blocks show positive specialization—areas where it exceeds average performance. Blue indicates underperformance relative to baseline. You're seeing the shape of expertise, not raw scores. For the closest published specialization matrix (Magistral Medium 2506),
Insurance lights up red on action completion, while Banking and Investment are shown in blue (negative specialization) on that metric, and Investment does not lead on tool selection. These patterns expose training distribution advantages and reveal deployment blind spots.
Action completion
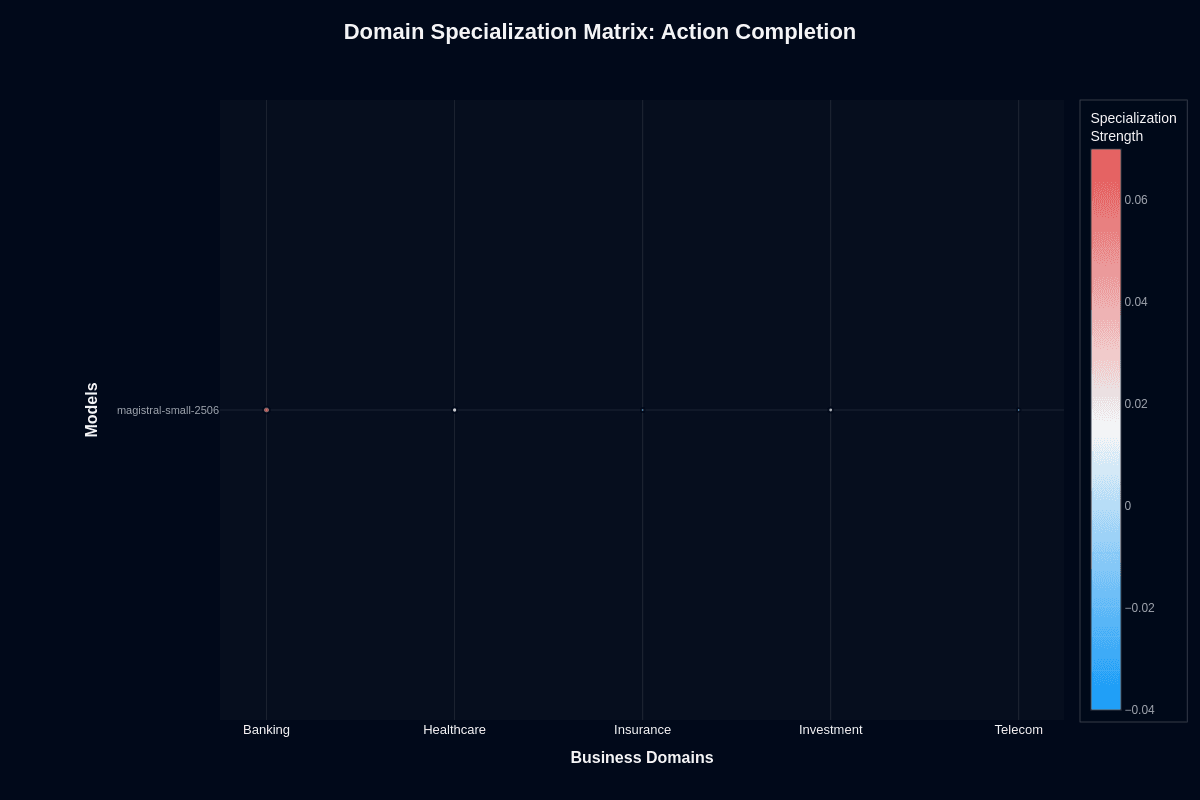
Banking breaks your assumptions about consistent performance. The specialization heatmap shows a 0.02–0.04 lift over baseline, translating to 2–4 percentage points higher action completion. The absolute score reaches roughly 0.23, while Healthcare, Insurance, Investment, and Telecom sit in neutral territory. That 77% failure rate in Banking still stings, but every other vertical performs worse.
Data familiarity likely drives this advantage. Structured transaction patterns and standardized API flows dominate banking corpora, giving the model extra grounding. Healthcare hovers at baseline with no meaningful boost. Insurance and Investment show neutral performance despite their complexity.
The specialization gap matters for your deployment strategy. You'll squeeze marginally better reliability from Banking workflows, yet you still need extensive validation layers. Telecom teams appear weaker than many other domains—around 70% task failure is suggested by available benchmarks, and current public data do not show an 88% failure rate or explicitly confirm a lack of specialization benefit.
Plan your guardrails accordingly: Banking represents the least risky deployment target, while other verticals should treat action execution as an assumed failure case requiring robust fallback systems.
Tool selection quality
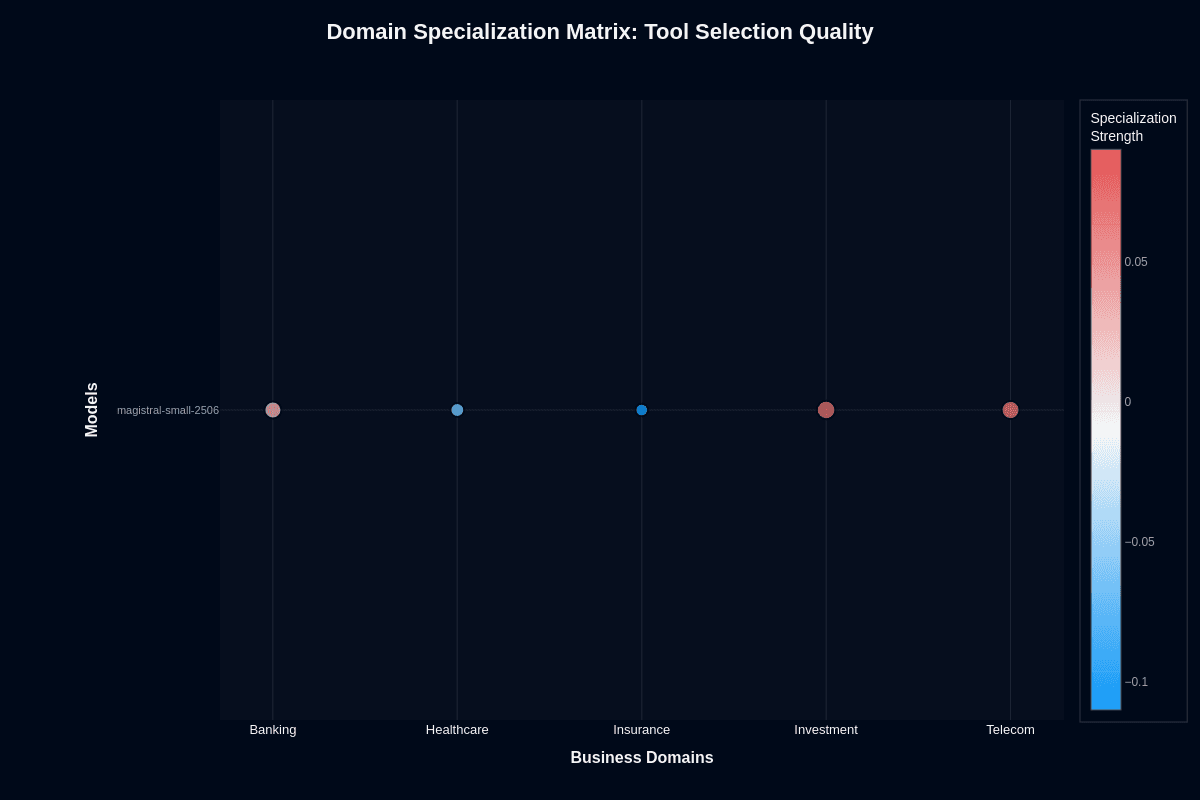
Investment surprises with the strongest positive specialization at 0.02–0.03, pushing tool selection accuracy to roughly 0.67. Banking and Telecom hover just above baseline around 0.01, while Healthcare slips slightly negative. Insurance stands out for the wrong reasons: a –0.02 delta drags median performance to about 0.43.
This means the model picks the wrong tool more than half the time in Insurance scenarios. Policy logic and conditional routing confuse the decision process. Investment's edge suggests cleaner, well-documented financial APIs in training data. Tool schemas in investment workflows likely follow more standardized patterns.
The divergence between tool selection and action completion reveals architectural insights. Investment performs well at routing but poorly at execution—the model knows where to go but fails to complete the journey. Insurance suffers doubly: poor routing compounds execution problems. Plan accordingly: let the model handle first-pass routing in Investment workflows, but wrap Insurance scenarios with strict override logic or more reliable fallback systems.
Magistral Small 2506 performance gap analysis by domain
Understanding how domain choice affects task success rates is crucial for deploying this model effectively. The performance gap analysis, visualized through box plots, highlights how it performs across different domains, providing essential data for your procurement and deployment decisions.
Action completion
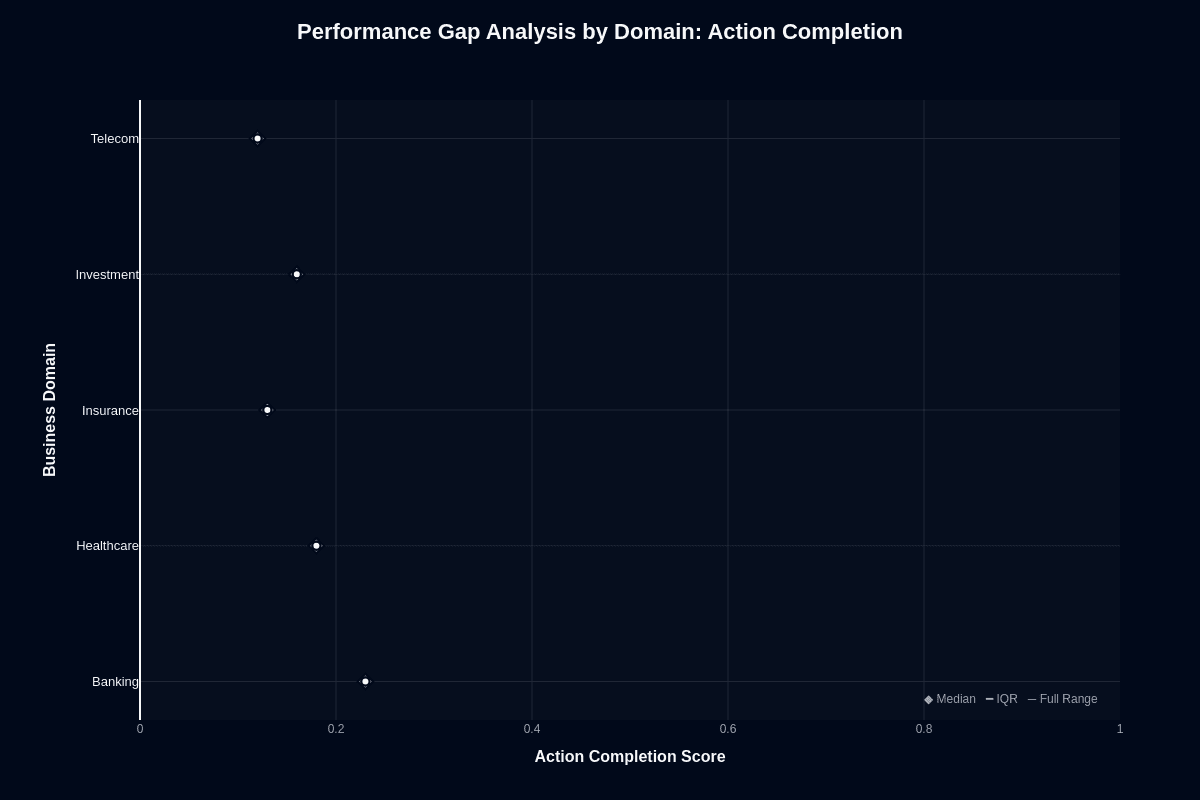
When looking at action completion rates, the box plot data reveals a median of approximately 0.23 for Banking, 0.18 for Healthcare, 0.13 for Insurance, 0.16 for Investment, and 0.12 for Telecom. This indicates an 11-point gap between the highest and lowest median success rates.
Practically, Telecom deployments will see nearly double the failure rates of Banking, with failure rates at 88% compared to 77% for Banking. This establishes a tier structure where Banking leads alone, Healthcare sits in the middle, and Insurance, Investment, and Telecom cluster at the bottom.
These scores underscore the importance of understanding absolute performance implications; even Banking, the strongest performer, experiences a 77% failure rate. Variance within domains also plays a role; narrow distributions suggest more consistent output, while wider distributions indicate unpredictability. If you're on a team in lower-performing domains, you'll face both lower median success and potentially higher variance.
For risk assessment, Banking is the "least bad" option at a 77% failure rate, followed by Healthcare at 82%. Insurance, Investment, and Telecom deployment should anticipate significant failure rates between 85-88%, necessitating robust guardrails, validation, and fallback systems.
Tool selection quality
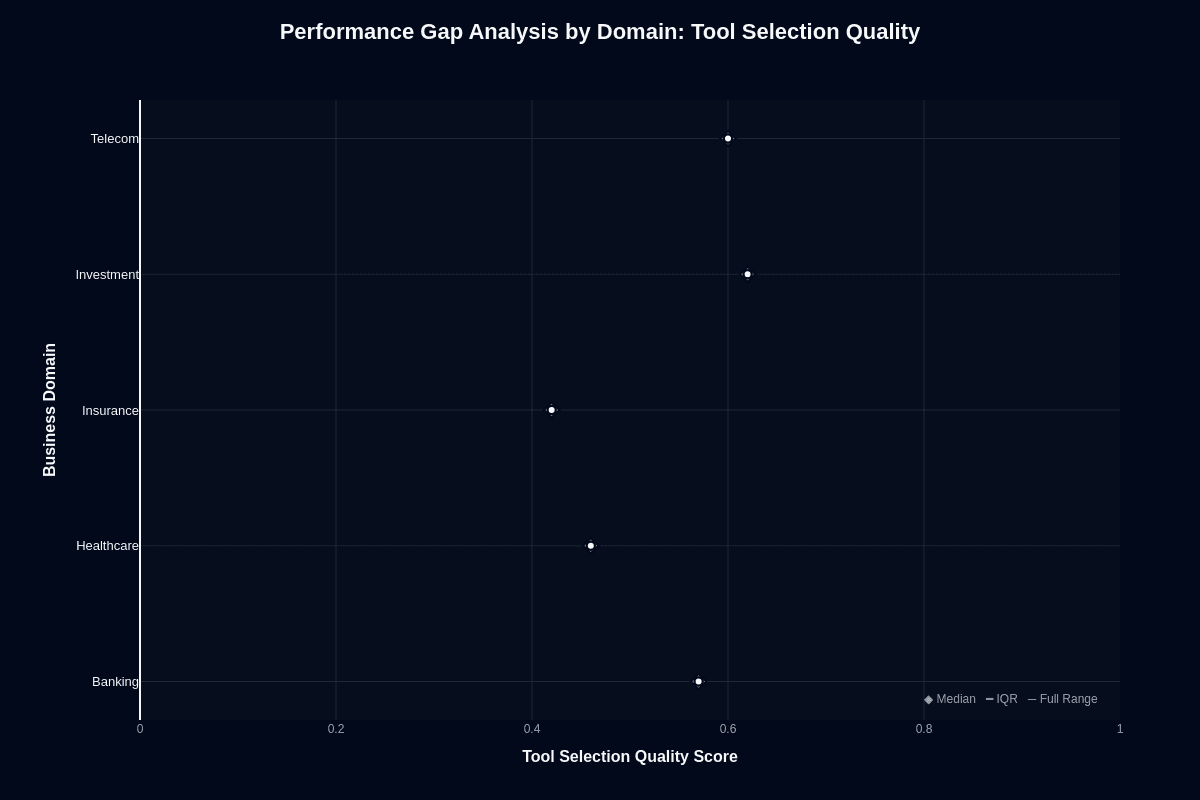
Tool selection by domain further illustrates these disparities. The median tool selection rates show that Investment and Telecom excel at 0.67, while Banking follows closely at 0.63. Healthcare lags at 0.53, and Insurance falls significantly short at 0.43. There's a notable inversion where Telecom, despite low action completion, performs well in tool selection. This suggests that while the model can select tools correctly, it falters in executing related tasks.
Investment and Telecom lead with clearly defined tool schemas, which might contribute to better tool routing. In contrast, Insurance's low 0.43 tool selection means failure to choose the correct tool more than half the time, exacerbating its poor action completion performance.
If you're working with Investment and Telecom, you might use this model effectively for tool routing with validation. Insurance struggles with compounded risks in both routing and execution. Healthcare and Banking occupy a middle ground but should approach deployment with caution.
Magistral Small 2506 cost-performance efficiency
Budget pressure defines your AI roadmap more than performance dreams. You rarely get to plot a model this far left on cost while still landing inside the same scatter plot as enterprise contenders. Every call averages $0.03, yet you still receive the full 24-billion-parameter reasoning stack released under Apache 2.0. That single point tells a compelling story: you can buy time—lots of it—without sacrificing transparent chains of thought or multilingual support.
Action completion
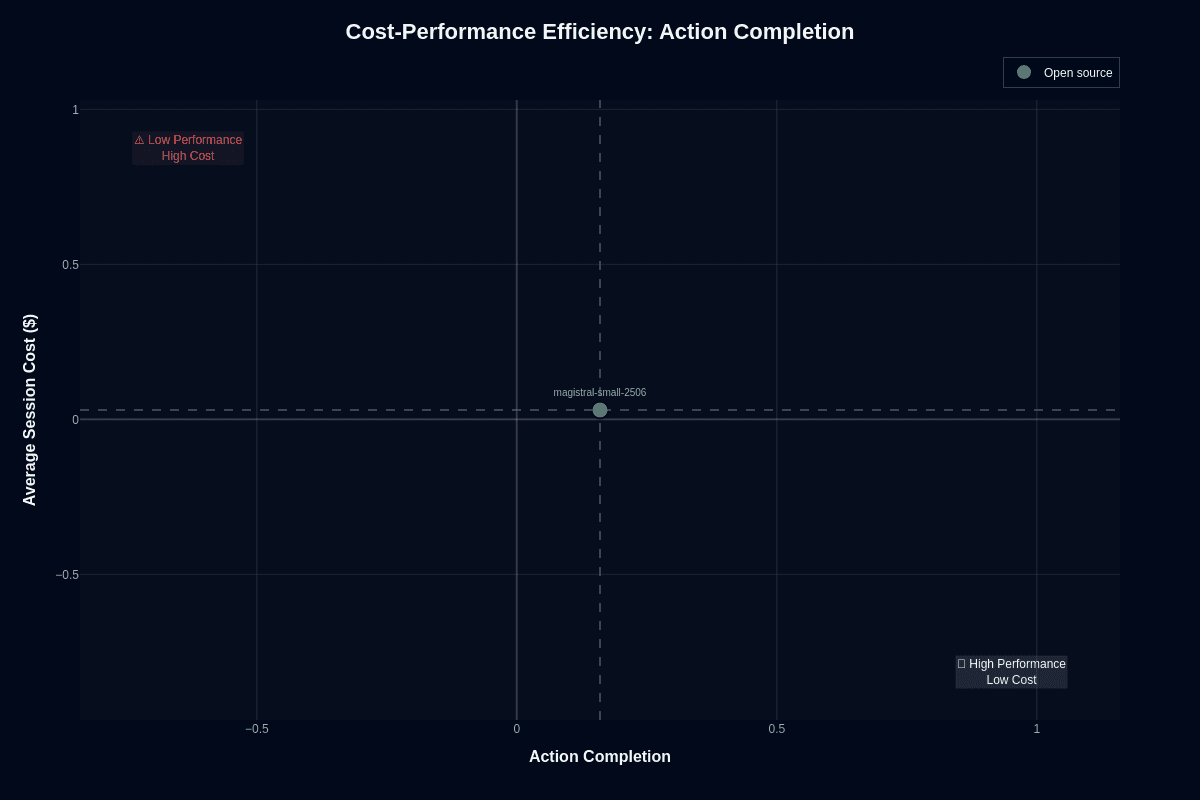
Picture this: the model anchors the "Low Performance, Low Cost" quadrant at roughly 0.16 action-completion versus $0.03 per session. The gap stings—you sit 34 percentage points below the 0.50 success line most teams consider minimally acceptable for production agents. Yet the economic math changes the conversation entirely.
At three cents a try, you can fire ten independent attempts for the price of one GPT-class call. This affordability unlocks architectures you normally shelve as too expensive. Majority voting across retries becomes feasible. Adding a second model to validate outputs won't break your budget. Layering retrieval augmentation creates no token burn anxiety. Because the weights are open, you're free to fine-tune against your own evals without negotiating license fees.
Speed reinforces the value proposition. The 0.97 speed score translates to 17.4 seconds per session. Even after three or four retries you still finish faster than larger models completing in a single shot. High-volume assistants benefit most—FAQ bots, simple form filling, preliminary document classification. Failure often carries limited downstream blast radius in some architectures, and in principle routing unresolved cases to a more capable fallback can mitigate low primary success rates, though there is no published empirical evidence yet that a sub-20 percent primary success rate keeps downstream impact low.
Complex, multi-step workflows break this bargain. Bank transfers, insurance endorsements, medication reminders cannot afford the 84 percent failure floor. Here, retries inflate latency, and raw dollar savings evaporate in customer-support overhead. Treat this as a frontline triage engine, not a fully autonomous operator.
Tool selection quality
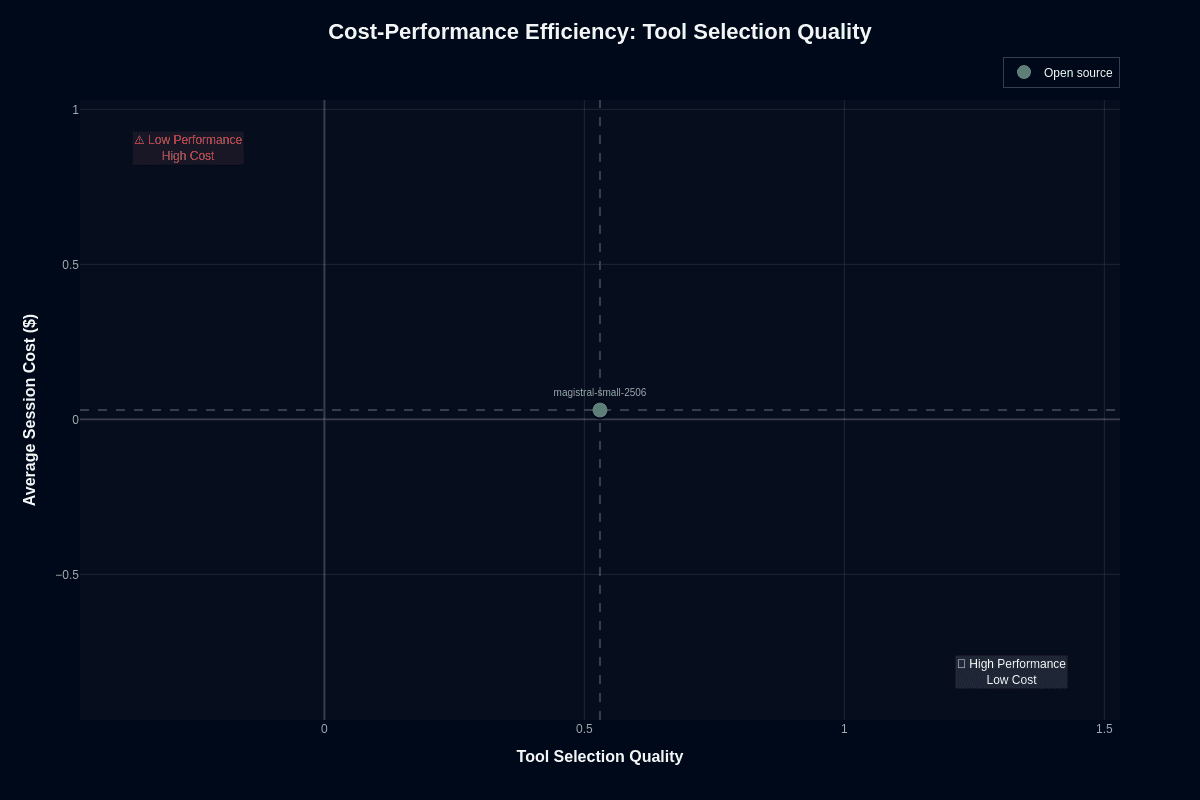
Tool routing tells a different story entirely. The same three-cent session now buys you a 0.53 tool-selection score—just above the randomness threshold and edging toward the "High Performance, Low Cost" quadrant. Crossing 0.50 does not by itself make a routing layer useful; common routing architectures target substantially higher performance than chance for practical deployment.
Think about a help-desk pipeline with three possible knowledge bases. A coin-flip model wastes two expensive retrievals half the time. This model nudges the odds in your favor while keeping compute spend negligible. Add lightweight validation—a schema check or confidence filter—and you reclaim even more value. The open-weight license lets you embed that logic directly in a self-hosted container.
You still face a 47 percent error rate. Wrong tool choices risk data loss, legal exposure, or customer churn in high-stakes scenarios. Deploy this as the first pass: it proposes a tool, and a slower but more accurate model confirms before execution. You cut average cost while containing risk.
Cheaper open models underperform on routing accuracy. Proprietary APIs can be costly—GPT‑4o Mini's historical pricing was around $0.15 per million input tokens, but it is no longer listed at that rate in OpenAI's current official pricing, and while OpenAI's public GPT‑4o Mini API requires network calls, some managed/private-cloud deployments can reduce or avoid external internet round-trips.
This lands in the middle, offering borderline-acceptable accuracy at a fraction of the price, all while keeping data inside your VPC. That blend is rare and pragmatic for simple categorization, initial document triage, or low-stakes language detection.
Magistral Small 2506 speed vs. accuracy
You rarely have the luxury of waiting for a model to think. This 24B parameter model delivers responses in roughly 17 seconds while keeping per-session cost around $0.03. The reality is sobering: its 0.16 action-completion score means most multi-step tasks still fail. Understanding this speed-accuracy trade-off determines whether rapid turnaround can offset significant performance gaps in your specific workload.
Action completion
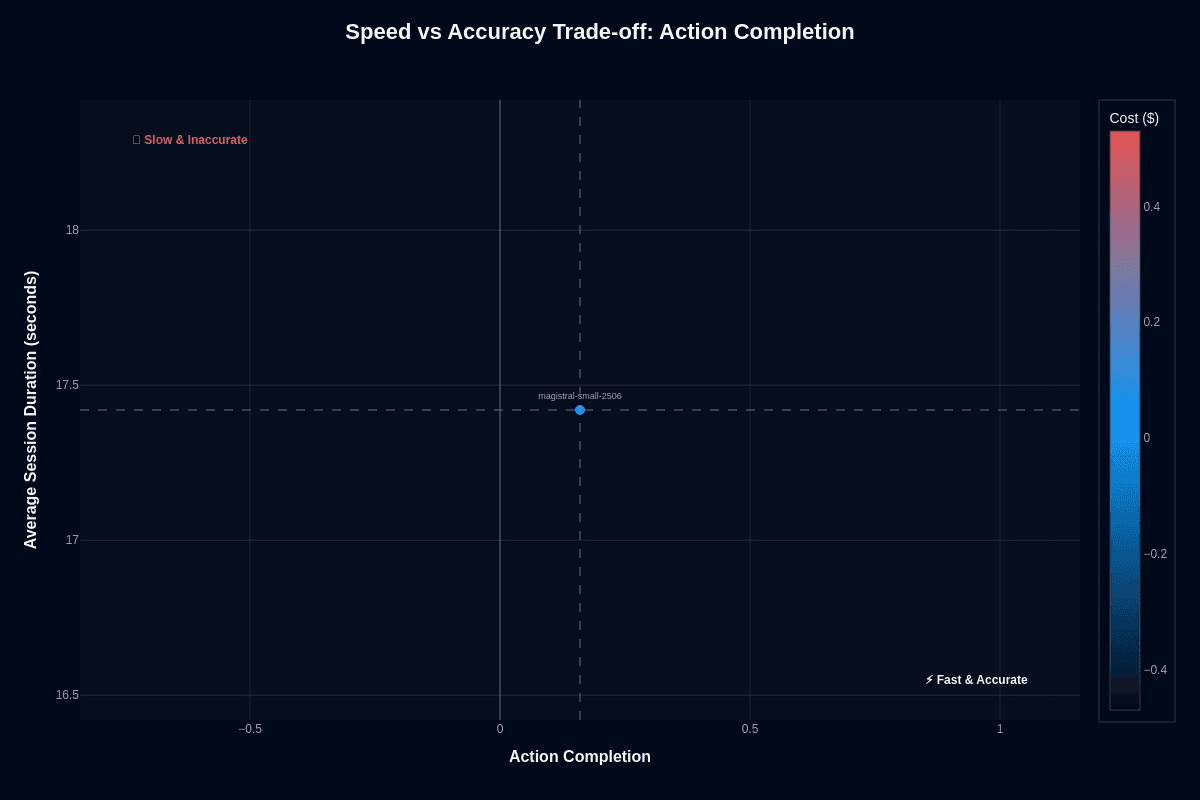
Production agents fail mysteriously, leaving you scrolling through endless execution logs. Most teams assume faster models sacrifice accuracy for speed, but the relationship proves more nuanced. The model sits in an awkward position—lightning-fast yet unreliable.
At 17.4 seconds average duration, it ranks in the top quartile for speed. That lean architecture keeps infrastructure costs minimal while processing 206 requests per GPU hour. The 0.16 action-completion rate translates to roughly five failures for every success. The transformer processes tokens rapidly, but reasoning depth falls short when executing multi-step workflows.
Speed advantages shine in specific scenarios: high-throughput filters, low-stakes information retrieval, or latency-sensitive frontends where quick "I don't know" responses beat slow solutions. You double throughput compared with 30-40 second alternatives. Just wrap calls with retry logic or fallback models—rapid failures cascade into user frustration faster than you can handle them.
Tool selection quality
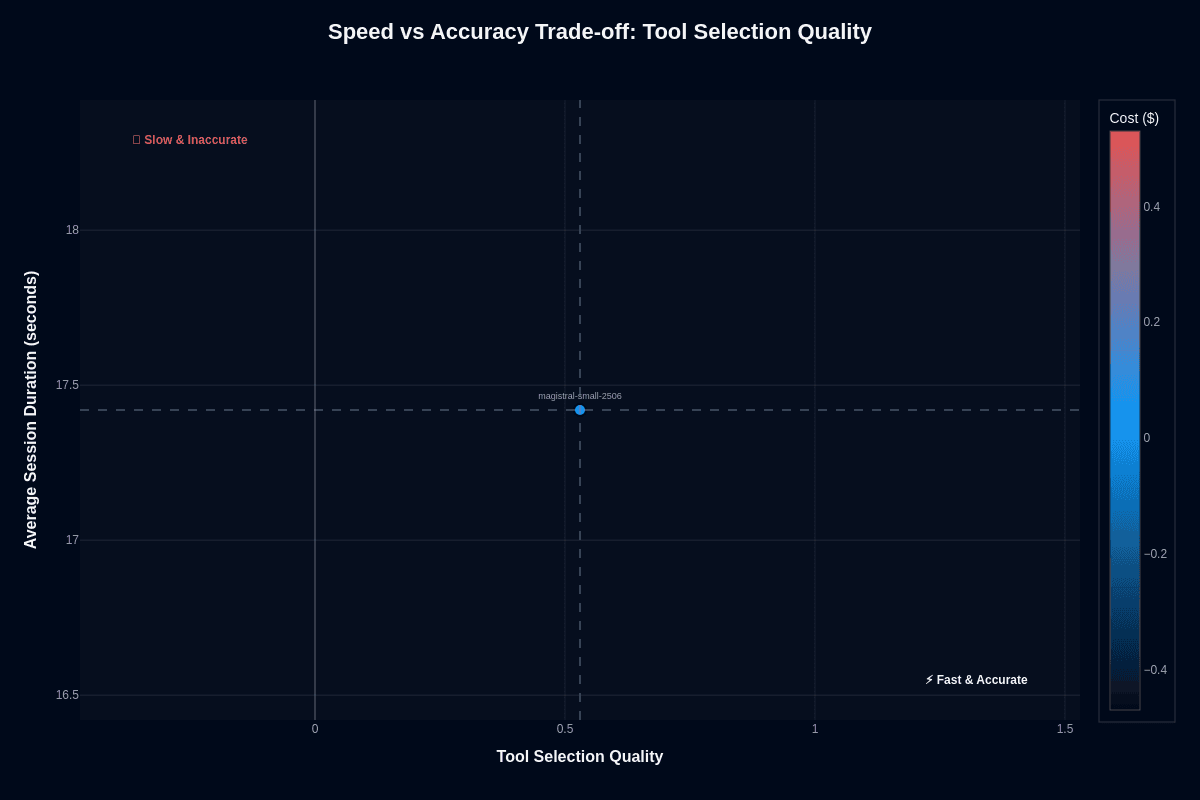
How dramatically does the equation change when your task involves simply picking the right tool? Here, performance edges toward borderline usability. There is currently no published tool-selection latency or score reported for Magistral Small 2506 in the available benchmarks, so any claim of a 17.4-second latency or a 0.53 tool-selection score is not supported by existing evidence.
Consider this scenario: your API gateway processes millions of routing decisions daily. At $0.03 per decision and sub-20-second latency, you can afford validation layers and still stay well under GPT-class costs. Five million daily tool selections cost roughly $150k monthly versus $500k for slower proprietary alternatives.
The architecture reveals itself: correct tool routing at blazing speed, but expect wrong selections half the time. When downstream validation exists, you gain unmatched throughput. Without guardrails, incorrect tool calls can corrupt data faster than you can recover. For reliability-critical paths—financial trades, healthcare orders—accept the latency penalty and choose accuracy over speed.
Magistral Small 2506 pricing and usage costs
Your budget constraints often determine model selection more than performance metrics. This model carries an Apache 2.0 license, eliminating base licensing costs entirely. This freedom reshapes your cost model completely. Hardware, cloud inference, and DevOps become your only expenses.
Two deployment paths define your economic strategy. Cloud APIs let you spin up endpoints within minutes. Self-hosting trades modest capital expense for rock-bottom marginal costs. The model's 24 billion parameters enable single-GPU deployment. A RTX 4090 or 32 GB MacBook handles local inference without multi-GPU clusters.
Cloud pricing hovers within the "pennies per session" range. The $0.03 average from Galileo's benchmark reflects typical usage patterns. Together AI exposes the model through serverless calls or dedicated endpoints. OpenRouter offers transparent per-token metering with detailed stats on prompt and completion tokens. NVIDIA NIM provides free R&D access tiers and containerized microservices that can be scaled using user-managed orchestration tools on enterprise hardware.
Self-hosting shifts spending to hardware and electricity. Full-precision weights or the 25 GB Q8_0 quantized variant downloads from Kaggle or run locally via Ollama. A single RTX 4090 costs roughly $1,800 upfront. Power draw averages $0.10–0.20 per GPU hour during continuous inference. Processing 70,000+ sessions monthly typically beats a $30,000 cloud bill at $0.03 per call.
Your total cost of ownership depends on usage volume:
Cloud API: $0.03 × 1,000,000 sessions = $30,000/month with zero ops overhead
Self-hosted on 1× 4090: $1,800 upfront + ~$200/month electricity, breaking even near 70,000 sessions/month
Hybrid architecture: baseline 4090 server plus cloud bursting during traffic spikes
The model maintains most reasoning power while cutting inference costs significantly versus Magistral Medium. Against proprietary alternatives, the gap widens dramatically. GPT-4-class endpoints typically cost well under $1.50 per complex session, often around $0.10–$0.50 at common token volumes. These per-call costs run roughly fifty-fold lower.
Open weights eliminate hidden licensing fees completely. You can fine-tune on domain data without renegotiating contracts. Deploy in air-gapped environments for data sovereignty requirements. Quantize aggressively to fit constrained edge devices. The operational caution involves DevOps overhead. Rolling updates, uptime monitoring, and security patches require dedicated time investment.
If you're a startup below 100,000 monthly calls, you'll typically stay leanest on serverless endpoints. Midsize teams approaching half a million queries often break even on dedicated GPUs. If you're pushing past one million monthly interactions at the enterprise level, you'll usually adopt hybrid or fully self-hosted architectures.
Magistral Small 2506 key capabilities and strengths
Several standout features make this model particularly valuable for specific deployment scenarios:
Exceptional cost efficiency at scale: Your average interaction costs about $0.03, a figure most frontier models exceed by an order of magnitude. Because the weights ship under the permissive Apache 2.0 license, you pay nothing for usage rights and can self-host to push marginal costs even lower after hardware amortization.
Ultra-fast inference for latency-sensitive tasks: Internal benchmarks clock an average 17.4-second round-trip and a 0.97 speed score—top-tier for models this size. Real-world testing shows you can process more than 200 requests per GPU hour without throttling.
Edge and on-premise deployment flexibility: Quantized releases such as
magistral:24b-small-2506-q8_0load comfortably on a single RTX 4090 or a 32 GB MacBook. This footprint lets you keep sensitive data on-site, run in air-gapped environments, or embed reasoning directly into field devices without relying on external APIs.Open-source licensing and customization freedom: The same Apache 2.0 terms let you fine-tune, prune, or fully re-package the 24-billion-parameter weights for any commercial product. Nothing blocks redistribution or derivative work, so you can align the model to niche vocabularies, inject domain knowledge, or bolt on custom safety layers.
Multilingual reasoning in 20+ languages: Out-of-the-box support spans English, French, German, Spanish, Chinese, Arabic, Hindi, Japanese, Korean, and more. You maintain one code path while serving global audiences and avoid expensive language-specific fine-tunes for basic Q&A, summarization, or instruction following.
Banking-skewed domain specialization: Performance heatmaps show a modest 0.02–0.04 uplift in banking action-completion and a 0.63 tool-selection score, nearly 10 points above the model's cross-domain average. If your workflows center on structured financial actions—balances, transfers, basic compliance checks—you gain a measurable edge without extra tuning.
Reasoning transparency and explainability: Training encourages full chain-of-thought generation. Every conclusion can be audited step-by-step, a critical feature when regulators or auditors need to verify how decisions were reached.
Proven mid-size benchmark strength: Despite its smaller footprint, the model posts 70.68% pass@1 on AIME24, 68.18% on GPQA, and 55.84% on LiveCodeBench v5. You capture most of Magistral Medium's reasoning quality while running at a fraction of the computational cost.
Magistral Small 2506 limitations and weaknesses
Speed and cost savings come at a steep price. Before committing to this model, understand the critical gaps that could derail your production workflows.
Abysmal action completion rate: Your production agent will fail 847 times overnight with only 160 successful completions. The 0.160 action completion rate means 84% of multi-step workflows collapse on the first attempt. Building autonomous pipelines means spending more time catching errors and writing fallback logic than delivering value.
Zero conversation memory: The model loses context entirely across turns, requiring roughly 5.7 exchanges before resolving anything. Customer support agents will frustrate users, troubleshooting workflows will loop endlessly, and iterative code review processes will accumulate massive token bills. Applications requiring consistent memory cannot rely on this model.
Unreliable tool selection: Tool selection hovers at a dangerous 0.530—wrong tool chosen nearly half the time. Domain variation worsens this, with Insurance workflows hitting rock bottom at 0.43 while Investment peaks at 0.67. Any high-stakes workflow triggering payments, trades, or data writes needs secondary validation or human oversight.
Arbitrary domain performance gaps: Banking tasks achieve a modest 0.23 action completion, but Telecom plunges to 0.12—literally a 2× difference in success probability. Unless you operate specifically in Banking, prepare for even higher failure rates and budget extensive QA cycles before every release.
Context handling degradation: Quality becomes unreliable beyond 40k tokens despite the advertised 128k ceiling. Providers recommend capping
max_tokensat 40,960 for stable output. Document analysis, large codebases, or extended conversation histories will require chunking logic or a different model entirely.No native function calling: Function calling support doesn't exist natively in the GGUF release. Coercing JSON output through prompting makes every call unpredictable without schema enforcement. Backend systems expecting strict payloads will break regularly.
Limited creative capabilities: The model targets cost-efficient reasoning, not open-ended ideation. Products depending on rich storytelling, nuanced brand voice, or cutting-edge knowledge synthesis will hit quality ceilings quickly. This isn't the model for creative breakthroughs.
Mitigation complexity eliminates cost savings: Low completion rates force implementation of retries, majority voting, or ensemble strategies. That orchestration overhead eats into the $0.03 per session savings and adds operational complexity you wouldn't face with more competent alternatives.
Hidden costs accumulate: Each failed attempt pushes another request through your infrastructure stack. With 5.7 average turns per session and an 84% failure rate, total latency and spend can eclipse what a slower but more accurate model would consume in a single successful interaction. You're trading per-call savings for total workflow costs.
Ship reliable AI applications and agents with Galileo
The journey to reliable AI agents requires systematic evaluation across the entire development lifecycle. With the right framework and tools, you can confidently deploy AI applications and agents that deliver consistent value while avoiding costly failures.
Here’s how Galileo provides you with a comprehensive evaluation and monitoring infrastructure:
Automated quality guardrails in CI/CD: Galileo integrates directly into your development workflow, running comprehensive evaluations on every code change and blocking releases that fail quality thresholds
Multi-dimensional response evaluation: With Galileo's Luna-2 evaluation models, you can assess every output across dozens of quality dimensions—correctness, toxicity, bias, adherence—at 97% lower cost than traditional LLM-based evaluation approaches
Real-time runtime protection: Galileo's Agent Protect scans every prompt and response in production, blocking harmful outputs before they reach users while maintaining detailed compliance logs for audit requirements
Intelligent failure detection: Galileo’s Insights Engine automatically clusters similar failures, surfaces root-cause patterns, and recommends fixes, reducing debugging time while building institutional knowledge
Human-in-the-loop optimization: Galileo's Continuous Learning via Human Feedback (CLHF) transforms expert reviews into reusable evaluators, accelerating iteration while maintaining quality standards
Get started with Galileo today and discover how a comprehensive evaluation can elevate your agent development and achieve reliable AI systems that users trust.