Dec 13, 2025
The Agent Guardrails Shift From Chatbots to Autonomous Agents


Jackson Wells
Integrated Marketing
Jackson Wells
Integrated Marketing


Picture this: Your production agent accessed the wrong database overnight and combined customer data inappropriately. None of your content filters caught it. The problem wasn't what the agent said—it was what it did.
You're running guardrails designed for chatbots against systems that make autonomous decisions, access APIs, and interact with enterprise infrastructure. Content filters operate at output boundaries after actions are taken. Autonomous agents require proactive constraints embedded in decision-making processes.
According to NIST AI RMF, traditional safety mechanisms effective for conventional software are often insufficient for AI systems exhibiting autonomous behaviors. This article examines why chatbot-era guardrails fail for autonomous agents.

What Is the Agentic Shift in Enterprise AI?
The agentic shift represents the transition from chatbots that generate text responses to autonomous agents that make consequential decisions, execute actions, and interact directly with enterprise systems without predetermined execution paths.
The distinction between chatbots and autonomous agents isn't about sophistication: it's about control. When you deploy agents, the business implications extend far beyond improved chatbot responses. Your competitive differentiation depends on deploying autonomous systems that make consequential decisions faster than manual processes allow, while your risk profile escalates with every database query and API call agents execute without direct oversight.
According to Stanford research, in workflows, you control execution flow while the LLM provides generation. In agents, the LLM controls execution flow while you provide constraints and tools. Your agent selects tools, composes API calls, and executes database queries based on its reasoning process. Unlike chatbots, where output moderation can filter text before users see it, agent actions execute in the environment immediately. Output filtering cannot intercept actions already taken in databases, APIs, or external systems.
What Are the Key Differences Between Chatbots and Autonomous Agents?

Chatbots operate through workflows with predefined code paths where LLMs and tools are chained together with deterministic logic you control. Autonomous agents, by contrast, allow LLMs to dynamically direct their own processes and tool usage, maintaining control over decision-making themselves. This fundamental shift in control creates three critical architectural dimensions where agents diverge from chatbots:
Decision authority lives in the model. Your agents make runtime decisions about tool selection and reasoning paths without following predetermined sequences. When an agent decides to query CustomerDatabase rather than ProductCatalog, that choice happens during execution, not at design time.
Multi-step reasoning creates compounding risks. Agents use ReAct patterns: iterative cycles of thought generation, action selection, observation processing, and refinement across multiple turns until task completion. A single content filter evaluating each step independently misses progressive attacks that decompose malicious requests across interactions.
Tool access creates action surfaces beyond text. Your agents interact with databases, APIs, and enterprise systems. Content filtering operates at the wrong abstraction level; it monitors outputs when the safety challenge constrains actions.
Traditional guardrails designed to validate predetermined execution paths cannot constrain choices that emerge from agent reasoning. According to a vulnerability disclosure, researchers identified critical flaws where multi-step progressive prompting systematically bypassed existing guardrails.
Why Traditional AI Guardrails Fall Short for Agentic Systems
Your content filters catch 98% of toxic outputs in chatbot conversations. Deploy those same filters on autonomous agents, and critical safety failures slip through undetected. The MASTERKEY research achieved a 21.58% success rate against contemporary defense mechanisms, demonstrating that automated generation of jailbreaks operates at a faster cycle time than your manual red-teaming processes can identify and patch vulnerabilities.
The NIST Profile identifies risks unique to generative AI systems that your current guardrails fail to prevent: confabulation in multi-step reasoning chains, dangerous recommendations emerging from tool use, data privacy breaches when agents access or combine information sources, and information integrity failures in autonomous decision-making.
Your safety architecture must address these properties explicitly, not treat them as edge cases requiring occasional intervention.
How Do You Adapt Your Safety Strategy for Agentic Systems?
The architectural mismatch between chatbot-era guardrails and autonomous agents requires fundamental shifts in how you approach safety. Rather than reactive filtering after outputs are generated, your production systems need proactive behavioral constraints that operate at the decision layer itself.
Implement Proactive Behavioral Guardrails to Replace Reactive Filtering
How do you prevent database queries that expose customer data before they execute? By the time your filter sees a database query, the data has already been accessed, combined, and potentially exposed. This architectural timing problem explains why content filters designed for chatbots fail catastrophically for autonomous agents you deploy.
Behavioral guardrails solve this by operating proactively. NIST AI 600-1 defines them as mechanisms designed to guide behavior and prevent unsafe outputs before they occur.
Your production implementations require a multi-tier architecture: guardrails at model, governance, and execution layers operate simultaneously, shaping reasoning at the source rather than filtering outputs at boundaries. At the model layer, reinforcement learning reward models train on safety objectives.
At the governance layer, machine-readable compliance rules define boundaries. At the execution layer, real-time content safety filters combine with tool access mediation. No single layer provides complete protection; you architect assuming individual layers will fail or be circumvented.
Define Capability-Based Constraints to Control Agent Decisions
You've probably discovered this the hard way: database access controls fail the moment your agents begin making runtime decisions about which systems to query. NIST AI RMF guidance recommends capability-based constraints where you define explicit action spaces: specific tools agents can access, acceptable parameter ranges, and prohibited actions.
The OpenAI Preparedness Framework recommends increasing safeguards—such as limited action space, enhanced monitoring, human oversight, and infrastructure controls—as risk levels rise, though these requirements are described in principle rather than as fixed thresholds above Medium risk.
Your implementation relies on explicit allow-lists: specific tools the agent can access, acceptable parameter ranges, data sources it can query, and systems it can modify.
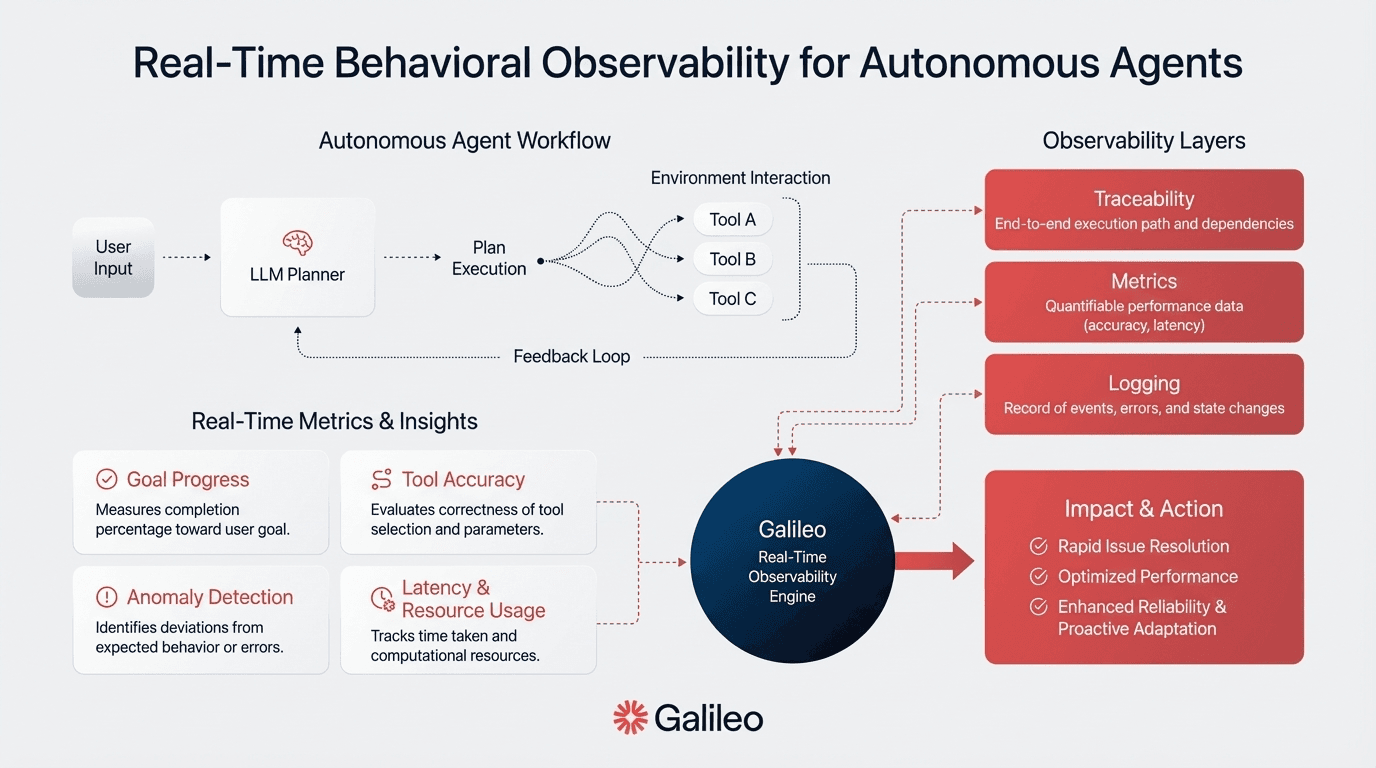
Deploy Real-Time Behavioral Observability Beyond Output Review
Quarterly security testing worked when threats evolved slowly. Automated attack generation changed the rules. Stanford's AutoRedTeamer research proves adversaries now iterate faster than your red teams can patch vulnerabilities, achieving 20% higher attack success rates with 46% cost reduction compared to manual approaches you're currently using.
You're staring at logs showing your agent accessed CustomerDatabase, ProductCatalog, and FinancialRecords in a single workflow. The logs tell you what happened, but you have no idea why the agent made those specific choices. Traditional logging captures actions but cannot reveal the reasoning chain that led to them.
Behavioral observability instruments your agent decision processes themselves, capturing tool selection rationale, reasoning traces, and state transitions. Comprehensive observability requires logging for decision capture, metrics for performance indicators, and tracing with spans for execution flow visualization. Platforms like Galileo's Insights Engine enable this through automated failure pattern detection across thousands of your agent workflows.
Integrate Continuous Adversarial Testing Into Your MLOps Pipelines
How do you test continuously without dedicating entire security teams to manual red teaming? Traditional security testing operates on quarterly cycles you maintain, while automated attack generation evolves continuously. The NIST guidelines provide a comprehensive taxonomy covering ML lifecycle stages, attacker goals, and attack categories.
Your production implementations combine automated and expert-led approaches. You use AI models to generate diverse adversarial examples alongside external expert teams. Hybrid approaches recognize that automated testing provides scale while expert evaluation identifies nuanced risks requiring domain knowledge that your automated systems lack.
Purpose-built evaluation platforms generate context-aware attack vectors that evolve with your agent capabilities, testing progressive jailbreaks at the speed of automated generation.
How Do You Scale Safe Autonomy Across the Enterprise?
Moving from pilot deployments to enterprise-wide agent systems requires frameworks that balance innovation with control. Your pilot agents succeed because you control everything: limited tool access, manual oversight, and a contained blast radius.
Implement Progressive Autonomy for Controlled Expansion
The AWS Security Matrix balances autonomy with control through staged deployment phases you can implement immediately. The core principle: your security controls should scale proportionally with agent autonomy.
The World Economic Forum governance framework operationalizes safety through five measurable deployment dimensions: agent role complexity and business impact, autonomy level from supervised to fully autonomous, authority scope defining decision boundaries, predictability of agent behaviors, and operational context and risk environment.
Your enterprise deployment strategies structure expansion across these dimensions with concrete graduation criteria: performance thresholds for accuracy provide quantitative gates, operational readiness assessments evaluate infrastructure capabilities, risk management validation ensures governance mechanisms function, and stakeholder approval gates require executive sign-off before autonomy expansion.
Design Engineering Patterns for Scalable and Adaptive Guardrails
Your guardrails work perfectly for Agent A processing customer inquiries, but fail completely for Agent B orchestrating supply chain decisions. Research on multi-layered guardrails applies the Swiss Cheese Model, recognizing that each guardrail layer has weaknesses, but multiple layers collectively provide comprehensive protection.
Your architecture implements guardrails across quality attributes, pipeline stages, and agent artifacts. Multiple mechanisms operate simultaneously: input filtering, output modification, adaptive fail-safes, real-time monitoring, and continuous validation. Architectural separation between planning and execution provides critical safety benefits. The planner decomposes goals into steps while the executor carries out actions and reports results.
This enables different resource controls, plan auditing before execution, and natural checkpoints for human intervention. The MI9 framework implements comprehensive runtime governance through agency-risk indexing, agent-semantic telemetry capture, continuous authorization monitoring, FSM-based conformance engines, goal-conditioned drift detection, and graduated containment strategies.
Align Governance With Emerging AI Regulations
When does your autonomous agent system require EU AI Act compliance? If your system manages critical infrastructure, makes employment decisions, or operates in law enforcement contexts, your compliance deadline is August 2, 2026, a date that's already 40% elapsed since the Act entered force.
According to the EU AI Act, high-risk systems are classified in Annex III, while their mandatory capabilities—such as continuous risk identification, data governance with bias detection, comprehensive technical documentation, transparency mechanisms, and human oversight—are set out in the main articles and annexes of the EU AI Act.
Penalties reach €35 million or 7% of your global annual turnover for high-risk system requirement violations. The NIST AI RMF provides a leading U.S. federal framework through four core functions: Govern establishes your organizational AI governance structures, Map identifies context and risks, Measure tracks metrics for trustworthiness, and Manage prioritizes risks and implements treatment strategies.
Build Actionable Metrics for VP-Level Safety Reporting
Executives don't care how many guardrail triggers fired last month. They want to know if the system is safe, compliant, and worth the investment. Reporting operational activity instead of business outcomes is why AI safety updates get deprioritized in board meetings.
Structure your reporting around three tiers that map to different decision-making levels.
Board-level metrics (monthly or quarterly):
Compliance Readiness Score (percentage alignment with EU AI Act and NIST AI RMF)
Mean Time to Incident Resolution (MTIR)
Safety Program Maturity Index
Risk-Adjusted Return on Safety Investment (RAROSI)
Executive operational metrics (weekly):
Agent Efficiency
Conversation Quality
Human Escalation Rate (HER)
Cost Per Guardrail Evaluation (CPGE)
Technical monitoring (real-time):
Action Advancement (how effectively each action progresses toward the goal)
Tool Selection Quality (whether agents chose the most appropriate tools)
Tool Error Rate (failures during tool or API execution)
Agent Flow (correctness and coherence of agentic trajectories)
User Intent Change (shifts in user goals during a session)
P50/P95/P99 Guardrail Latency
False Positive Rate (FPR) and False Negative Rate (FNR)
The goal is to translate technical telemetry into strategic insight. Board members need confidence that AI systems are controlled. Executives need visibility into operational health. Engineers need granular signals to debug and improve.
Why Chatbot-Era Guardrails Won't Protect Your Agents
Autonomous agents go beyond generating text. They make decisions, access systems, and execute actions. Content filters designed for chatbots operate too late to prevent harm. The shift to agentic AI demands proactive behavioral constraints, capability-based controls, and real-time observability embedded at the decision layer, not the output boundary.
Galileo is built for this shift. Agent Protect delivers real-time behavioral guardrails that operate before actions execute, not after outputs are generated. Here's more on how Galileo helps you with AI guardrails:
Automated quality guardrails in CI/CD: Galileo integrates directly into your development workflow, running comprehensive evaluations on every code change and blocking releases that fail quality thresholds
Multi-dimensional response evaluation: With Galileo's Luna-2 evaluation models, you can assess every output across dozens of quality dimensions—correctness, toxicity, bias, adherence—at 97% lower cost than traditional LLM-based evaluation approaches
Real-time runtime protection: Galileo's Agent Protect scans every prompt and response in production, blocking harmful outputs before they reach users while maintaining detailed compliance logs for audit requirements
Intelligent failure detection: Galileo’s Insights Engine automatically clusters similar failures, surfaces root-cause patterns, and recommends fixes, reducing debugging time while building institutional knowledge
Human-in-the-loop optimization: Galileo's Continuous Learning via Human Feedback (CLHF) transforms expert reviews into reusable evaluators, accelerating iteration while maintaining quality standards
Discover how Galileo provides enterprise-grade AI guardrails with pre-built policies, real-time metrics, and ready-made integrations.
Picture this: Your production agent accessed the wrong database overnight and combined customer data inappropriately. None of your content filters caught it. The problem wasn't what the agent said—it was what it did.
You're running guardrails designed for chatbots against systems that make autonomous decisions, access APIs, and interact with enterprise infrastructure. Content filters operate at output boundaries after actions are taken. Autonomous agents require proactive constraints embedded in decision-making processes.
According to NIST AI RMF, traditional safety mechanisms effective for conventional software are often insufficient for AI systems exhibiting autonomous behaviors. This article examines why chatbot-era guardrails fail for autonomous agents.

What Is the Agentic Shift in Enterprise AI?
The agentic shift represents the transition from chatbots that generate text responses to autonomous agents that make consequential decisions, execute actions, and interact directly with enterprise systems without predetermined execution paths.
The distinction between chatbots and autonomous agents isn't about sophistication: it's about control. When you deploy agents, the business implications extend far beyond improved chatbot responses. Your competitive differentiation depends on deploying autonomous systems that make consequential decisions faster than manual processes allow, while your risk profile escalates with every database query and API call agents execute without direct oversight.
According to Stanford research, in workflows, you control execution flow while the LLM provides generation. In agents, the LLM controls execution flow while you provide constraints and tools. Your agent selects tools, composes API calls, and executes database queries based on its reasoning process. Unlike chatbots, where output moderation can filter text before users see it, agent actions execute in the environment immediately. Output filtering cannot intercept actions already taken in databases, APIs, or external systems.
What Are the Key Differences Between Chatbots and Autonomous Agents?

Chatbots operate through workflows with predefined code paths where LLMs and tools are chained together with deterministic logic you control. Autonomous agents, by contrast, allow LLMs to dynamically direct their own processes and tool usage, maintaining control over decision-making themselves. This fundamental shift in control creates three critical architectural dimensions where agents diverge from chatbots:
Decision authority lives in the model. Your agents make runtime decisions about tool selection and reasoning paths without following predetermined sequences. When an agent decides to query CustomerDatabase rather than ProductCatalog, that choice happens during execution, not at design time.
Multi-step reasoning creates compounding risks. Agents use ReAct patterns: iterative cycles of thought generation, action selection, observation processing, and refinement across multiple turns until task completion. A single content filter evaluating each step independently misses progressive attacks that decompose malicious requests across interactions.
Tool access creates action surfaces beyond text. Your agents interact with databases, APIs, and enterprise systems. Content filtering operates at the wrong abstraction level; it monitors outputs when the safety challenge constrains actions.
Traditional guardrails designed to validate predetermined execution paths cannot constrain choices that emerge from agent reasoning. According to a vulnerability disclosure, researchers identified critical flaws where multi-step progressive prompting systematically bypassed existing guardrails.
Why Traditional AI Guardrails Fall Short for Agentic Systems
Your content filters catch 98% of toxic outputs in chatbot conversations. Deploy those same filters on autonomous agents, and critical safety failures slip through undetected. The MASTERKEY research achieved a 21.58% success rate against contemporary defense mechanisms, demonstrating that automated generation of jailbreaks operates at a faster cycle time than your manual red-teaming processes can identify and patch vulnerabilities.
The NIST Profile identifies risks unique to generative AI systems that your current guardrails fail to prevent: confabulation in multi-step reasoning chains, dangerous recommendations emerging from tool use, data privacy breaches when agents access or combine information sources, and information integrity failures in autonomous decision-making.
Your safety architecture must address these properties explicitly, not treat them as edge cases requiring occasional intervention.
How Do You Adapt Your Safety Strategy for Agentic Systems?
The architectural mismatch between chatbot-era guardrails and autonomous agents requires fundamental shifts in how you approach safety. Rather than reactive filtering after outputs are generated, your production systems need proactive behavioral constraints that operate at the decision layer itself.
Implement Proactive Behavioral Guardrails to Replace Reactive Filtering
How do you prevent database queries that expose customer data before they execute? By the time your filter sees a database query, the data has already been accessed, combined, and potentially exposed. This architectural timing problem explains why content filters designed for chatbots fail catastrophically for autonomous agents you deploy.
Behavioral guardrails solve this by operating proactively. NIST AI 600-1 defines them as mechanisms designed to guide behavior and prevent unsafe outputs before they occur.
Your production implementations require a multi-tier architecture: guardrails at model, governance, and execution layers operate simultaneously, shaping reasoning at the source rather than filtering outputs at boundaries. At the model layer, reinforcement learning reward models train on safety objectives.
At the governance layer, machine-readable compliance rules define boundaries. At the execution layer, real-time content safety filters combine with tool access mediation. No single layer provides complete protection; you architect assuming individual layers will fail or be circumvented.
Define Capability-Based Constraints to Control Agent Decisions
You've probably discovered this the hard way: database access controls fail the moment your agents begin making runtime decisions about which systems to query. NIST AI RMF guidance recommends capability-based constraints where you define explicit action spaces: specific tools agents can access, acceptable parameter ranges, and prohibited actions.
The OpenAI Preparedness Framework recommends increasing safeguards—such as limited action space, enhanced monitoring, human oversight, and infrastructure controls—as risk levels rise, though these requirements are described in principle rather than as fixed thresholds above Medium risk.
Your implementation relies on explicit allow-lists: specific tools the agent can access, acceptable parameter ranges, data sources it can query, and systems it can modify.
Deploy Real-Time Behavioral Observability Beyond Output Review
Quarterly security testing worked when threats evolved slowly. Automated attack generation changed the rules. Stanford's AutoRedTeamer research proves adversaries now iterate faster than your red teams can patch vulnerabilities, achieving 20% higher attack success rates with 46% cost reduction compared to manual approaches you're currently using.
You're staring at logs showing your agent accessed CustomerDatabase, ProductCatalog, and FinancialRecords in a single workflow. The logs tell you what happened, but you have no idea why the agent made those specific choices. Traditional logging captures actions but cannot reveal the reasoning chain that led to them.
Behavioral observability instruments your agent decision processes themselves, capturing tool selection rationale, reasoning traces, and state transitions. Comprehensive observability requires logging for decision capture, metrics for performance indicators, and tracing with spans for execution flow visualization. Platforms like Galileo's Insights Engine enable this through automated failure pattern detection across thousands of your agent workflows.
Integrate Continuous Adversarial Testing Into Your MLOps Pipelines
How do you test continuously without dedicating entire security teams to manual red teaming? Traditional security testing operates on quarterly cycles you maintain, while automated attack generation evolves continuously. The NIST guidelines provide a comprehensive taxonomy covering ML lifecycle stages, attacker goals, and attack categories.
Your production implementations combine automated and expert-led approaches. You use AI models to generate diverse adversarial examples alongside external expert teams. Hybrid approaches recognize that automated testing provides scale while expert evaluation identifies nuanced risks requiring domain knowledge that your automated systems lack.
Purpose-built evaluation platforms generate context-aware attack vectors that evolve with your agent capabilities, testing progressive jailbreaks at the speed of automated generation.
How Do You Scale Safe Autonomy Across the Enterprise?
Moving from pilot deployments to enterprise-wide agent systems requires frameworks that balance innovation with control. Your pilot agents succeed because you control everything: limited tool access, manual oversight, and a contained blast radius.
Implement Progressive Autonomy for Controlled Expansion
The AWS Security Matrix balances autonomy with control through staged deployment phases you can implement immediately. The core principle: your security controls should scale proportionally with agent autonomy.
The World Economic Forum governance framework operationalizes safety through five measurable deployment dimensions: agent role complexity and business impact, autonomy level from supervised to fully autonomous, authority scope defining decision boundaries, predictability of agent behaviors, and operational context and risk environment.
Your enterprise deployment strategies structure expansion across these dimensions with concrete graduation criteria: performance thresholds for accuracy provide quantitative gates, operational readiness assessments evaluate infrastructure capabilities, risk management validation ensures governance mechanisms function, and stakeholder approval gates require executive sign-off before autonomy expansion.
Design Engineering Patterns for Scalable and Adaptive Guardrails
Your guardrails work perfectly for Agent A processing customer inquiries, but fail completely for Agent B orchestrating supply chain decisions. Research on multi-layered guardrails applies the Swiss Cheese Model, recognizing that each guardrail layer has weaknesses, but multiple layers collectively provide comprehensive protection.
Your architecture implements guardrails across quality attributes, pipeline stages, and agent artifacts. Multiple mechanisms operate simultaneously: input filtering, output modification, adaptive fail-safes, real-time monitoring, and continuous validation. Architectural separation between planning and execution provides critical safety benefits. The planner decomposes goals into steps while the executor carries out actions and reports results.
This enables different resource controls, plan auditing before execution, and natural checkpoints for human intervention. The MI9 framework implements comprehensive runtime governance through agency-risk indexing, agent-semantic telemetry capture, continuous authorization monitoring, FSM-based conformance engines, goal-conditioned drift detection, and graduated containment strategies.
Align Governance With Emerging AI Regulations
When does your autonomous agent system require EU AI Act compliance? If your system manages critical infrastructure, makes employment decisions, or operates in law enforcement contexts, your compliance deadline is August 2, 2026, a date that's already 40% elapsed since the Act entered force.
According to the EU AI Act, high-risk systems are classified in Annex III, while their mandatory capabilities—such as continuous risk identification, data governance with bias detection, comprehensive technical documentation, transparency mechanisms, and human oversight—are set out in the main articles and annexes of the EU AI Act.
Penalties reach €35 million or 7% of your global annual turnover for high-risk system requirement violations. The NIST AI RMF provides a leading U.S. federal framework through four core functions: Govern establishes your organizational AI governance structures, Map identifies context and risks, Measure tracks metrics for trustworthiness, and Manage prioritizes risks and implements treatment strategies.
Build Actionable Metrics for VP-Level Safety Reporting
Executives don't care how many guardrail triggers fired last month. They want to know if the system is safe, compliant, and worth the investment. Reporting operational activity instead of business outcomes is why AI safety updates get deprioritized in board meetings.
Structure your reporting around three tiers that map to different decision-making levels.
Board-level metrics (monthly or quarterly):
Compliance Readiness Score (percentage alignment with EU AI Act and NIST AI RMF)
Mean Time to Incident Resolution (MTIR)
Safety Program Maturity Index
Risk-Adjusted Return on Safety Investment (RAROSI)
Executive operational metrics (weekly):
Agent Efficiency
Conversation Quality
Human Escalation Rate (HER)
Cost Per Guardrail Evaluation (CPGE)
Technical monitoring (real-time):
Action Advancement (how effectively each action progresses toward the goal)
Tool Selection Quality (whether agents chose the most appropriate tools)
Tool Error Rate (failures during tool or API execution)
Agent Flow (correctness and coherence of agentic trajectories)
User Intent Change (shifts in user goals during a session)
P50/P95/P99 Guardrail Latency
False Positive Rate (FPR) and False Negative Rate (FNR)
The goal is to translate technical telemetry into strategic insight. Board members need confidence that AI systems are controlled. Executives need visibility into operational health. Engineers need granular signals to debug and improve.
Why Chatbot-Era Guardrails Won't Protect Your Agents

Autonomous agents go beyond generating text. They make decisions, access systems, and execute actions. Content filters designed for chatbots operate too late to prevent harm. The shift to agentic AI demands proactive behavioral constraints, capability-based controls, and real-time observability embedded at the decision layer, not the output boundary.
Galileo is built for this shift. Agent Protect delivers real-time behavioral guardrails that operate before actions execute, not after outputs are generated. Here's more on how Galileo helps you with AI guardrails:
Automated quality guardrails in CI/CD: Galileo integrates directly into your development workflow, running comprehensive evaluations on every code change and blocking releases that fail quality thresholds
Multi-dimensional response evaluation: With Galileo's Luna-2 evaluation models, you can assess every output across dozens of quality dimensions—correctness, toxicity, bias, adherence—at 97% lower cost than traditional LLM-based evaluation approaches
Real-time runtime protection: Galileo's Agent Protect scans every prompt and response in production, blocking harmful outputs before they reach users while maintaining detailed compliance logs for audit requirements
Intelligent failure detection: Galileo’s Insights Engine automatically clusters similar failures, surfaces root-cause patterns, and recommends fixes, reducing debugging time while building institutional knowledge
Human-in-the-loop optimization: Galileo's Continuous Learning via Human Feedback (CLHF) transforms expert reviews into reusable evaluators, accelerating iteration while maintaining quality standards
Discover how Galileo provides enterprise-grade AI guardrails with pre-built policies, real-time metrics, and ready-made integrations.
Picture this: Your production agent accessed the wrong database overnight and combined customer data inappropriately. None of your content filters caught it. The problem wasn't what the agent said—it was what it did.
You're running guardrails designed for chatbots against systems that make autonomous decisions, access APIs, and interact with enterprise infrastructure. Content filters operate at output boundaries after actions are taken. Autonomous agents require proactive constraints embedded in decision-making processes.
According to NIST AI RMF, traditional safety mechanisms effective for conventional software are often insufficient for AI systems exhibiting autonomous behaviors. This article examines why chatbot-era guardrails fail for autonomous agents.

What Is the Agentic Shift in Enterprise AI?
The agentic shift represents the transition from chatbots that generate text responses to autonomous agents that make consequential decisions, execute actions, and interact directly with enterprise systems without predetermined execution paths.
The distinction between chatbots and autonomous agents isn't about sophistication: it's about control. When you deploy agents, the business implications extend far beyond improved chatbot responses. Your competitive differentiation depends on deploying autonomous systems that make consequential decisions faster than manual processes allow, while your risk profile escalates with every database query and API call agents execute without direct oversight.
According to Stanford research, in workflows, you control execution flow while the LLM provides generation. In agents, the LLM controls execution flow while you provide constraints and tools. Your agent selects tools, composes API calls, and executes database queries based on its reasoning process. Unlike chatbots, where output moderation can filter text before users see it, agent actions execute in the environment immediately. Output filtering cannot intercept actions already taken in databases, APIs, or external systems.
What Are the Key Differences Between Chatbots and Autonomous Agents?

Chatbots operate through workflows with predefined code paths where LLMs and tools are chained together with deterministic logic you control. Autonomous agents, by contrast, allow LLMs to dynamically direct their own processes and tool usage, maintaining control over decision-making themselves. This fundamental shift in control creates three critical architectural dimensions where agents diverge from chatbots:
Decision authority lives in the model. Your agents make runtime decisions about tool selection and reasoning paths without following predetermined sequences. When an agent decides to query CustomerDatabase rather than ProductCatalog, that choice happens during execution, not at design time.
Multi-step reasoning creates compounding risks. Agents use ReAct patterns: iterative cycles of thought generation, action selection, observation processing, and refinement across multiple turns until task completion. A single content filter evaluating each step independently misses progressive attacks that decompose malicious requests across interactions.
Tool access creates action surfaces beyond text. Your agents interact with databases, APIs, and enterprise systems. Content filtering operates at the wrong abstraction level; it monitors outputs when the safety challenge constrains actions.
Traditional guardrails designed to validate predetermined execution paths cannot constrain choices that emerge from agent reasoning. According to a vulnerability disclosure, researchers identified critical flaws where multi-step progressive prompting systematically bypassed existing guardrails.
Why Traditional AI Guardrails Fall Short for Agentic Systems
Your content filters catch 98% of toxic outputs in chatbot conversations. Deploy those same filters on autonomous agents, and critical safety failures slip through undetected. The MASTERKEY research achieved a 21.58% success rate against contemporary defense mechanisms, demonstrating that automated generation of jailbreaks operates at a faster cycle time than your manual red-teaming processes can identify and patch vulnerabilities.
The NIST Profile identifies risks unique to generative AI systems that your current guardrails fail to prevent: confabulation in multi-step reasoning chains, dangerous recommendations emerging from tool use, data privacy breaches when agents access or combine information sources, and information integrity failures in autonomous decision-making.
Your safety architecture must address these properties explicitly, not treat them as edge cases requiring occasional intervention.
How Do You Adapt Your Safety Strategy for Agentic Systems?
The architectural mismatch between chatbot-era guardrails and autonomous agents requires fundamental shifts in how you approach safety. Rather than reactive filtering after outputs are generated, your production systems need proactive behavioral constraints that operate at the decision layer itself.
Implement Proactive Behavioral Guardrails to Replace Reactive Filtering
How do you prevent database queries that expose customer data before they execute? By the time your filter sees a database query, the data has already been accessed, combined, and potentially exposed. This architectural timing problem explains why content filters designed for chatbots fail catastrophically for autonomous agents you deploy.
Behavioral guardrails solve this by operating proactively. NIST AI 600-1 defines them as mechanisms designed to guide behavior and prevent unsafe outputs before they occur.
Your production implementations require a multi-tier architecture: guardrails at model, governance, and execution layers operate simultaneously, shaping reasoning at the source rather than filtering outputs at boundaries. At the model layer, reinforcement learning reward models train on safety objectives.
At the governance layer, machine-readable compliance rules define boundaries. At the execution layer, real-time content safety filters combine with tool access mediation. No single layer provides complete protection; you architect assuming individual layers will fail or be circumvented.
Define Capability-Based Constraints to Control Agent Decisions
You've probably discovered this the hard way: database access controls fail the moment your agents begin making runtime decisions about which systems to query. NIST AI RMF guidance recommends capability-based constraints where you define explicit action spaces: specific tools agents can access, acceptable parameter ranges, and prohibited actions.
The OpenAI Preparedness Framework recommends increasing safeguards—such as limited action space, enhanced monitoring, human oversight, and infrastructure controls—as risk levels rise, though these requirements are described in principle rather than as fixed thresholds above Medium risk.
Your implementation relies on explicit allow-lists: specific tools the agent can access, acceptable parameter ranges, data sources it can query, and systems it can modify.
Deploy Real-Time Behavioral Observability Beyond Output Review
Quarterly security testing worked when threats evolved slowly. Automated attack generation changed the rules. Stanford's AutoRedTeamer research proves adversaries now iterate faster than your red teams can patch vulnerabilities, achieving 20% higher attack success rates with 46% cost reduction compared to manual approaches you're currently using.
You're staring at logs showing your agent accessed CustomerDatabase, ProductCatalog, and FinancialRecords in a single workflow. The logs tell you what happened, but you have no idea why the agent made those specific choices. Traditional logging captures actions but cannot reveal the reasoning chain that led to them.
Behavioral observability instruments your agent decision processes themselves, capturing tool selection rationale, reasoning traces, and state transitions. Comprehensive observability requires logging for decision capture, metrics for performance indicators, and tracing with spans for execution flow visualization. Platforms like Galileo's Insights Engine enable this through automated failure pattern detection across thousands of your agent workflows.
Integrate Continuous Adversarial Testing Into Your MLOps Pipelines
How do you test continuously without dedicating entire security teams to manual red teaming? Traditional security testing operates on quarterly cycles you maintain, while automated attack generation evolves continuously. The NIST guidelines provide a comprehensive taxonomy covering ML lifecycle stages, attacker goals, and attack categories.
Your production implementations combine automated and expert-led approaches. You use AI models to generate diverse adversarial examples alongside external expert teams. Hybrid approaches recognize that automated testing provides scale while expert evaluation identifies nuanced risks requiring domain knowledge that your automated systems lack.
Purpose-built evaluation platforms generate context-aware attack vectors that evolve with your agent capabilities, testing progressive jailbreaks at the speed of automated generation.
How Do You Scale Safe Autonomy Across the Enterprise?
Moving from pilot deployments to enterprise-wide agent systems requires frameworks that balance innovation with control. Your pilot agents succeed because you control everything: limited tool access, manual oversight, and a contained blast radius.
Implement Progressive Autonomy for Controlled Expansion
The AWS Security Matrix balances autonomy with control through staged deployment phases you can implement immediately. The core principle: your security controls should scale proportionally with agent autonomy.
The World Economic Forum governance framework operationalizes safety through five measurable deployment dimensions: agent role complexity and business impact, autonomy level from supervised to fully autonomous, authority scope defining decision boundaries, predictability of agent behaviors, and operational context and risk environment.
Your enterprise deployment strategies structure expansion across these dimensions with concrete graduation criteria: performance thresholds for accuracy provide quantitative gates, operational readiness assessments evaluate infrastructure capabilities, risk management validation ensures governance mechanisms function, and stakeholder approval gates require executive sign-off before autonomy expansion.
Design Engineering Patterns for Scalable and Adaptive Guardrails
Your guardrails work perfectly for Agent A processing customer inquiries, but fail completely for Agent B orchestrating supply chain decisions. Research on multi-layered guardrails applies the Swiss Cheese Model, recognizing that each guardrail layer has weaknesses, but multiple layers collectively provide comprehensive protection.
Your architecture implements guardrails across quality attributes, pipeline stages, and agent artifacts. Multiple mechanisms operate simultaneously: input filtering, output modification, adaptive fail-safes, real-time monitoring, and continuous validation. Architectural separation between planning and execution provides critical safety benefits. The planner decomposes goals into steps while the executor carries out actions and reports results.
This enables different resource controls, plan auditing before execution, and natural checkpoints for human intervention. The MI9 framework implements comprehensive runtime governance through agency-risk indexing, agent-semantic telemetry capture, continuous authorization monitoring, FSM-based conformance engines, goal-conditioned drift detection, and graduated containment strategies.
Align Governance With Emerging AI Regulations
When does your autonomous agent system require EU AI Act compliance? If your system manages critical infrastructure, makes employment decisions, or operates in law enforcement contexts, your compliance deadline is August 2, 2026, a date that's already 40% elapsed since the Act entered force.
According to the EU AI Act, high-risk systems are classified in Annex III, while their mandatory capabilities—such as continuous risk identification, data governance with bias detection, comprehensive technical documentation, transparency mechanisms, and human oversight—are set out in the main articles and annexes of the EU AI Act.
Penalties reach €35 million or 7% of your global annual turnover for high-risk system requirement violations. The NIST AI RMF provides a leading U.S. federal framework through four core functions: Govern establishes your organizational AI governance structures, Map identifies context and risks, Measure tracks metrics for trustworthiness, and Manage prioritizes risks and implements treatment strategies.
Build Actionable Metrics for VP-Level Safety Reporting
Executives don't care how many guardrail triggers fired last month. They want to know if the system is safe, compliant, and worth the investment. Reporting operational activity instead of business outcomes is why AI safety updates get deprioritized in board meetings.
Structure your reporting around three tiers that map to different decision-making levels.
Board-level metrics (monthly or quarterly):
Compliance Readiness Score (percentage alignment with EU AI Act and NIST AI RMF)
Mean Time to Incident Resolution (MTIR)
Safety Program Maturity Index
Risk-Adjusted Return on Safety Investment (RAROSI)
Executive operational metrics (weekly):
Agent Efficiency
Conversation Quality
Human Escalation Rate (HER)
Cost Per Guardrail Evaluation (CPGE)
Technical monitoring (real-time):
Action Advancement (how effectively each action progresses toward the goal)
Tool Selection Quality (whether agents chose the most appropriate tools)
Tool Error Rate (failures during tool or API execution)
Agent Flow (correctness and coherence of agentic trajectories)
User Intent Change (shifts in user goals during a session)
P50/P95/P99 Guardrail Latency
False Positive Rate (FPR) and False Negative Rate (FNR)
The goal is to translate technical telemetry into strategic insight. Board members need confidence that AI systems are controlled. Executives need visibility into operational health. Engineers need granular signals to debug and improve.
Why Chatbot-Era Guardrails Won't Protect Your Agents

Autonomous agents go beyond generating text. They make decisions, access systems, and execute actions. Content filters designed for chatbots operate too late to prevent harm. The shift to agentic AI demands proactive behavioral constraints, capability-based controls, and real-time observability embedded at the decision layer, not the output boundary.
Galileo is built for this shift. Agent Protect delivers real-time behavioral guardrails that operate before actions execute, not after outputs are generated. Here's more on how Galileo helps you with AI guardrails:
Automated quality guardrails in CI/CD: Galileo integrates directly into your development workflow, running comprehensive evaluations on every code change and blocking releases that fail quality thresholds
Multi-dimensional response evaluation: With Galileo's Luna-2 evaluation models, you can assess every output across dozens of quality dimensions—correctness, toxicity, bias, adherence—at 97% lower cost than traditional LLM-based evaluation approaches
Real-time runtime protection: Galileo's Agent Protect scans every prompt and response in production, blocking harmful outputs before they reach users while maintaining detailed compliance logs for audit requirements
Intelligent failure detection: Galileo’s Insights Engine automatically clusters similar failures, surfaces root-cause patterns, and recommends fixes, reducing debugging time while building institutional knowledge
Human-in-the-loop optimization: Galileo's Continuous Learning via Human Feedback (CLHF) transforms expert reviews into reusable evaluators, accelerating iteration while maintaining quality standards
Discover how Galileo provides enterprise-grade AI guardrails with pre-built policies, real-time metrics, and ready-made integrations.
Picture this: Your production agent accessed the wrong database overnight and combined customer data inappropriately. None of your content filters caught it. The problem wasn't what the agent said—it was what it did.
You're running guardrails designed for chatbots against systems that make autonomous decisions, access APIs, and interact with enterprise infrastructure. Content filters operate at output boundaries after actions are taken. Autonomous agents require proactive constraints embedded in decision-making processes.
According to NIST AI RMF, traditional safety mechanisms effective for conventional software are often insufficient for AI systems exhibiting autonomous behaviors. This article examines why chatbot-era guardrails fail for autonomous agents.

What Is the Agentic Shift in Enterprise AI?
The agentic shift represents the transition from chatbots that generate text responses to autonomous agents that make consequential decisions, execute actions, and interact directly with enterprise systems without predetermined execution paths.
The distinction between chatbots and autonomous agents isn't about sophistication: it's about control. When you deploy agents, the business implications extend far beyond improved chatbot responses. Your competitive differentiation depends on deploying autonomous systems that make consequential decisions faster than manual processes allow, while your risk profile escalates with every database query and API call agents execute without direct oversight.
According to Stanford research, in workflows, you control execution flow while the LLM provides generation. In agents, the LLM controls execution flow while you provide constraints and tools. Your agent selects tools, composes API calls, and executes database queries based on its reasoning process. Unlike chatbots, where output moderation can filter text before users see it, agent actions execute in the environment immediately. Output filtering cannot intercept actions already taken in databases, APIs, or external systems.
What Are the Key Differences Between Chatbots and Autonomous Agents?

Chatbots operate through workflows with predefined code paths where LLMs and tools are chained together with deterministic logic you control. Autonomous agents, by contrast, allow LLMs to dynamically direct their own processes and tool usage, maintaining control over decision-making themselves. This fundamental shift in control creates three critical architectural dimensions where agents diverge from chatbots:
Decision authority lives in the model. Your agents make runtime decisions about tool selection and reasoning paths without following predetermined sequences. When an agent decides to query CustomerDatabase rather than ProductCatalog, that choice happens during execution, not at design time.
Multi-step reasoning creates compounding risks. Agents use ReAct patterns: iterative cycles of thought generation, action selection, observation processing, and refinement across multiple turns until task completion. A single content filter evaluating each step independently misses progressive attacks that decompose malicious requests across interactions.
Tool access creates action surfaces beyond text. Your agents interact with databases, APIs, and enterprise systems. Content filtering operates at the wrong abstraction level; it monitors outputs when the safety challenge constrains actions.
Traditional guardrails designed to validate predetermined execution paths cannot constrain choices that emerge from agent reasoning. According to a vulnerability disclosure, researchers identified critical flaws where multi-step progressive prompting systematically bypassed existing guardrails.
Why Traditional AI Guardrails Fall Short for Agentic Systems
Your content filters catch 98% of toxic outputs in chatbot conversations. Deploy those same filters on autonomous agents, and critical safety failures slip through undetected. The MASTERKEY research achieved a 21.58% success rate against contemporary defense mechanisms, demonstrating that automated generation of jailbreaks operates at a faster cycle time than your manual red-teaming processes can identify and patch vulnerabilities.
The NIST Profile identifies risks unique to generative AI systems that your current guardrails fail to prevent: confabulation in multi-step reasoning chains, dangerous recommendations emerging from tool use, data privacy breaches when agents access or combine information sources, and information integrity failures in autonomous decision-making.
Your safety architecture must address these properties explicitly, not treat them as edge cases requiring occasional intervention.
How Do You Adapt Your Safety Strategy for Agentic Systems?
The architectural mismatch between chatbot-era guardrails and autonomous agents requires fundamental shifts in how you approach safety. Rather than reactive filtering after outputs are generated, your production systems need proactive behavioral constraints that operate at the decision layer itself.
Implement Proactive Behavioral Guardrails to Replace Reactive Filtering
How do you prevent database queries that expose customer data before they execute? By the time your filter sees a database query, the data has already been accessed, combined, and potentially exposed. This architectural timing problem explains why content filters designed for chatbots fail catastrophically for autonomous agents you deploy.
Behavioral guardrails solve this by operating proactively. NIST AI 600-1 defines them as mechanisms designed to guide behavior and prevent unsafe outputs before they occur.
Your production implementations require a multi-tier architecture: guardrails at model, governance, and execution layers operate simultaneously, shaping reasoning at the source rather than filtering outputs at boundaries. At the model layer, reinforcement learning reward models train on safety objectives.
At the governance layer, machine-readable compliance rules define boundaries. At the execution layer, real-time content safety filters combine with tool access mediation. No single layer provides complete protection; you architect assuming individual layers will fail or be circumvented.
Define Capability-Based Constraints to Control Agent Decisions
You've probably discovered this the hard way: database access controls fail the moment your agents begin making runtime decisions about which systems to query. NIST AI RMF guidance recommends capability-based constraints where you define explicit action spaces: specific tools agents can access, acceptable parameter ranges, and prohibited actions.
The OpenAI Preparedness Framework recommends increasing safeguards—such as limited action space, enhanced monitoring, human oversight, and infrastructure controls—as risk levels rise, though these requirements are described in principle rather than as fixed thresholds above Medium risk.
Your implementation relies on explicit allow-lists: specific tools the agent can access, acceptable parameter ranges, data sources it can query, and systems it can modify.
Deploy Real-Time Behavioral Observability Beyond Output Review
Quarterly security testing worked when threats evolved slowly. Automated attack generation changed the rules. Stanford's AutoRedTeamer research proves adversaries now iterate faster than your red teams can patch vulnerabilities, achieving 20% higher attack success rates with 46% cost reduction compared to manual approaches you're currently using.
You're staring at logs showing your agent accessed CustomerDatabase, ProductCatalog, and FinancialRecords in a single workflow. The logs tell you what happened, but you have no idea why the agent made those specific choices. Traditional logging captures actions but cannot reveal the reasoning chain that led to them.
Behavioral observability instruments your agent decision processes themselves, capturing tool selection rationale, reasoning traces, and state transitions. Comprehensive observability requires logging for decision capture, metrics for performance indicators, and tracing with spans for execution flow visualization. Platforms like Galileo's Insights Engine enable this through automated failure pattern detection across thousands of your agent workflows.
Integrate Continuous Adversarial Testing Into Your MLOps Pipelines
How do you test continuously without dedicating entire security teams to manual red teaming? Traditional security testing operates on quarterly cycles you maintain, while automated attack generation evolves continuously. The NIST guidelines provide a comprehensive taxonomy covering ML lifecycle stages, attacker goals, and attack categories.
Your production implementations combine automated and expert-led approaches. You use AI models to generate diverse adversarial examples alongside external expert teams. Hybrid approaches recognize that automated testing provides scale while expert evaluation identifies nuanced risks requiring domain knowledge that your automated systems lack.
Purpose-built evaluation platforms generate context-aware attack vectors that evolve with your agent capabilities, testing progressive jailbreaks at the speed of automated generation.
How Do You Scale Safe Autonomy Across the Enterprise?
Moving from pilot deployments to enterprise-wide agent systems requires frameworks that balance innovation with control. Your pilot agents succeed because you control everything: limited tool access, manual oversight, and a contained blast radius.
Implement Progressive Autonomy for Controlled Expansion
The AWS Security Matrix balances autonomy with control through staged deployment phases you can implement immediately. The core principle: your security controls should scale proportionally with agent autonomy.
The World Economic Forum governance framework operationalizes safety through five measurable deployment dimensions: agent role complexity and business impact, autonomy level from supervised to fully autonomous, authority scope defining decision boundaries, predictability of agent behaviors, and operational context and risk environment.
Your enterprise deployment strategies structure expansion across these dimensions with concrete graduation criteria: performance thresholds for accuracy provide quantitative gates, operational readiness assessments evaluate infrastructure capabilities, risk management validation ensures governance mechanisms function, and stakeholder approval gates require executive sign-off before autonomy expansion.
Design Engineering Patterns for Scalable and Adaptive Guardrails
Your guardrails work perfectly for Agent A processing customer inquiries, but fail completely for Agent B orchestrating supply chain decisions. Research on multi-layered guardrails applies the Swiss Cheese Model, recognizing that each guardrail layer has weaknesses, but multiple layers collectively provide comprehensive protection.
Your architecture implements guardrails across quality attributes, pipeline stages, and agent artifacts. Multiple mechanisms operate simultaneously: input filtering, output modification, adaptive fail-safes, real-time monitoring, and continuous validation. Architectural separation between planning and execution provides critical safety benefits. The planner decomposes goals into steps while the executor carries out actions and reports results.
This enables different resource controls, plan auditing before execution, and natural checkpoints for human intervention. The MI9 framework implements comprehensive runtime governance through agency-risk indexing, agent-semantic telemetry capture, continuous authorization monitoring, FSM-based conformance engines, goal-conditioned drift detection, and graduated containment strategies.
Align Governance With Emerging AI Regulations
When does your autonomous agent system require EU AI Act compliance? If your system manages critical infrastructure, makes employment decisions, or operates in law enforcement contexts, your compliance deadline is August 2, 2026, a date that's already 40% elapsed since the Act entered force.
According to the EU AI Act, high-risk systems are classified in Annex III, while their mandatory capabilities—such as continuous risk identification, data governance with bias detection, comprehensive technical documentation, transparency mechanisms, and human oversight—are set out in the main articles and annexes of the EU AI Act.
Penalties reach €35 million or 7% of your global annual turnover for high-risk system requirement violations. The NIST AI RMF provides a leading U.S. federal framework through four core functions: Govern establishes your organizational AI governance structures, Map identifies context and risks, Measure tracks metrics for trustworthiness, and Manage prioritizes risks and implements treatment strategies.
Build Actionable Metrics for VP-Level Safety Reporting
Executives don't care how many guardrail triggers fired last month. They want to know if the system is safe, compliant, and worth the investment. Reporting operational activity instead of business outcomes is why AI safety updates get deprioritized in board meetings.
Structure your reporting around three tiers that map to different decision-making levels.
Board-level metrics (monthly or quarterly):
Compliance Readiness Score (percentage alignment with EU AI Act and NIST AI RMF)
Mean Time to Incident Resolution (MTIR)
Safety Program Maturity Index
Risk-Adjusted Return on Safety Investment (RAROSI)
Executive operational metrics (weekly):
Agent Efficiency
Conversation Quality
Human Escalation Rate (HER)
Cost Per Guardrail Evaluation (CPGE)
Technical monitoring (real-time):
Action Advancement (how effectively each action progresses toward the goal)
Tool Selection Quality (whether agents chose the most appropriate tools)
Tool Error Rate (failures during tool or API execution)
Agent Flow (correctness and coherence of agentic trajectories)
User Intent Change (shifts in user goals during a session)
P50/P95/P99 Guardrail Latency
False Positive Rate (FPR) and False Negative Rate (FNR)
The goal is to translate technical telemetry into strategic insight. Board members need confidence that AI systems are controlled. Executives need visibility into operational health. Engineers need granular signals to debug and improve.
Why Chatbot-Era Guardrails Won't Protect Your Agents

Autonomous agents go beyond generating text. They make decisions, access systems, and execute actions. Content filters designed for chatbots operate too late to prevent harm. The shift to agentic AI demands proactive behavioral constraints, capability-based controls, and real-time observability embedded at the decision layer, not the output boundary.
Galileo is built for this shift. Agent Protect delivers real-time behavioral guardrails that operate before actions execute, not after outputs are generated. Here's more on how Galileo helps you with AI guardrails:
Automated quality guardrails in CI/CD: Galileo integrates directly into your development workflow, running comprehensive evaluations on every code change and blocking releases that fail quality thresholds
Multi-dimensional response evaluation: With Galileo's Luna-2 evaluation models, you can assess every output across dozens of quality dimensions—correctness, toxicity, bias, adherence—at 97% lower cost than traditional LLM-based evaluation approaches
Real-time runtime protection: Galileo's Agent Protect scans every prompt and response in production, blocking harmful outputs before they reach users while maintaining detailed compliance logs for audit requirements
Intelligent failure detection: Galileo’s Insights Engine automatically clusters similar failures, surfaces root-cause patterns, and recommends fixes, reducing debugging time while building institutional knowledge
Human-in-the-loop optimization: Galileo's Continuous Learning via Human Feedback (CLHF) transforms expert reviews into reusable evaluators, accelerating iteration while maintaining quality standards
Discover how Galileo provides enterprise-grade AI guardrails with pre-built policies, real-time metrics, and ready-made integrations.


Jackson Wells