
Dec 21, 2025
Why Multi-Agent AI Systems Fail and How to Prevent Cascading Errors


Jackson Wells
Integrated Marketing
Jackson Wells
Integrated Marketing


Let's say, three agents just made conflicting decisions about the same customer case, corrupting financial records in your production database while logs show successful API calls: you can't trace which agent introduced the error.
These aren't hypothetical scenarios. They represent documented failure modes of autonomous agents that coordinate, communicate, and fail differently than single-agent systems. This analysis examines why multi-agent coordination fails differently, how you architect reliable guardrails across agent networks, and what observability infrastructure prevents cascading failures in production.
TLDR:
Multi-agent systems without orchestration experience failure rates exceeding 40% in production
Coordination overhead grows quadratically from 200ms to 4+ seconds as agent count increases
Formal orchestration frameworks reduce failure rates by 3.2x versus unorchestrated systems
Layered guardrails at four intervention points prevent cascading failures across networks
We recently explored this topic on our Chain of Thought podcast, where industry experts shared practical insights and real-world implementation strategies:

Why Do Multi-Agent LLM Systems Fail Differently?

When your autonomous agents coordinate autonomously, you face failure modes fundamentally different from single-agent architectures. While a single agent's errors remain bounded within its execution context, multiple autonomous agents interacting with shared resources create non-deterministic emergent failures that propagate exponentially through your system.
Specification failures cascade through agent networks
Picture this: your orchestrator agent delegates a financial calculation to a specialist agent with an ambiguous success criterion. The specialist completes its task within technical parameters but misinterprets the business constraint. When three downstream agents incorporate this flawed output into their own analyses, you've created a cascading error pattern that compounds through your workflow.
Research identifies specification failures accounting for approximately 42% of multi-agent failures. Without systematic validation at each handoff, specification errors propagate silently until they corrupt your critical business logic. Your coordination breakdowns account for approximately 37% of failures, while verification gaps represent approximately 21%.
Coordination deadlocks represent documented breakdowns
Your orchestrator waits for a response from a specialist while that specialist simultaneously waits for confirmation. Neither can proceed, yet your observability infrastructure simply records increased latency rather than detecting the underlying structural failure.
Research analyzing coordination patterns across multi-agent systems reveals that deadlocks are a significant cause of breakdowns, and these failures often generate no explicit error signals.
Your coordination deadlocks manifest in systems with 3+ interacting agents through request-response cycles where agents await mutual confirmations and resource lock patterns where agents acquire shared resources in different orders.
Single-agent hallucinations propagate through shared memory
When one of your autonomous agents hallucinates information and stores it in shared memory, subsequent agents treat false information as verified fact. Research shows hallucinations spread through shared memory systems. Cascading incorrect decisions emerge as hallucinated data propagates through your agent network.
This is classified as "memory poisoning." The contamination is particularly insidious because your accuracy degradation occurs gradually rather than triggering immediate failures. You spend hours debugging subtle data quality issues without realizing the root cause started with a single agent's hallucinated output three interactions earlier.
Why Does Coordination Break Down at Production Scale?
As your agent populations grow, coordination complexity increases non-linearly, directly impacting your operational costs and customer SLAs. Your coordination latency grows from approximately 200ms with two agents to over 4 seconds with eight or more agents. Studies documenting 1,642 execution traces across production multi-agent systems demonstrate failure rates ranging from 41% to 86.7%.
Reducing your debugging costs by and cutting mean time to resolution from hours to minutes directly impacts your team's velocity and your ability to demonstrate AI ROI to executives.
Communication protocol failures between heterogeneous agents
Suppose your system sends a properly formatted request, but the receiving framework interprets the message structure differently. Critical context is dropped. The resulting response appears valid syntactically but is semantically incorrect. Your dependent agents make decisions based on incomplete information, creating cascading errors invisible to traditional monitoring.
Standardized communication protocols address agent interoperability. These protocols enable cross-platform coordination, standardizing interactions between your autonomous agents and external systems while working regardless of programming language or runtime environment. Without consistent protocols, you face integration failures that compound across agent interactions.
State consistency failures from distributed operations
Three agents simultaneously read customer account balances. Each makes independent withdrawal decisions. Then they write updates back to your database. Without proper synchronization, you've created a classic lost update scenario where the final account balance reflects only the last write, ignoring the previous two withdrawals.
Critical manifestations include stale state reads where your autonomous agents consume outdated cached data, lost updates from concurrent writes without conflict resolution, and split-brain scenarios where network partitions cause state divergence.
Database transactions alone cannot prevent these failures when LLM inference drives your autonomous agent decisions. These state inconsistencies create compliance risks and undermine executive confidence in your agent reliability.
Resource contention creates exponential load amplification
Ten of your autonomous agents simultaneously invoke the same external service during peak load, triggering API rate limits and creating a "retry storm" pattern. Cascading failure emerges where dependent agents exponentially amplify load on downstream systems, turning a transient bottleneck into a complete outage.
Without resource-aware orchestration, these cascading failures compound exponentially. Each agent retry magnifies the problem rather than resolving it, overwhelming your downstream services and creating incident response nightmares that undermine executive confidence in your agent reliability.
What Are the AI Guardrailing Approaches for Multi-Agent Systems?
Effective guardrails for your multi-agent systems extend beyond input/output filtering. You need to address coordination protocols, inter-agent communication, and system-level policy enforcement. Analysis identifies guardrails operating across three core architectural layers: individual agent-level validation, inter-agent interaction validation, and system-level orchestration controls.
Your implementation should combine centralized orchestrators with event-driven choreography, using open protocols for interoperability alongside formal verification methods and runtime validation frameworks. This reduces your incident response costs by 60% while providing the audit trails your compliance team needs.
Input and output validation at every boundary
Tripwire mechanisms that halt execution when any agent violates content policies create defense-in-depth safety architectures critical for your production multi-agent systems. Without validation at every boundary, a single compromised agent can poison your entire workflow.
Your comprehensive frameworks should define input guardrails validating prompts against allowed patterns, sanitizing inputs to prevent prompt injection, and running content policy classifiers before processing. Output guardrails check responses against harm taxonomies and filter sensitive information, including PII and credentials.
Multi-agent specificity extends this with per-agent guardrails providing local validation, inter-agent guardrails validating messages between agents, and system-level guardrails enforcing global policies.
Multiple evaluator agents independently assess outputs
Reinforcement Learning from AI Feedback (RLAIF) enables distributed assessment approaches where multiple evaluators reach consensus on safety violations. This provides nuanced evaluation of complex behaviors while avoiding reliance on single-point-of-failure mechanisms.
Research demonstrates that multi-agent feedback evaluation systems use Constitutional AI principles to assess outputs against predefined standards. They provide distributed safety validation that prevents single points of failure. Purpose-built evaluation platforms give your security team the confidence to approve agent deployments without manual review bottlenecks.
Domain-specific constraints enable dynamic validation
Formal specification languages express safety requirements that your systems verify during execution. Research on runtime verification frameworks demonstrates this approach balances rigorous constraint checking with acceptable performance overhead, validating that your agent outputs align with formal specifications.
For your multi-agent systems, runtime verification prevents constraint violation propagation through agent networks. When an agent generates an output violating formal specifications, your guardrailing systems detect and block unsafe outputs before other agents incorporate the error into processing.
Circuit breakers prevent cascading failures
When your agent experiences three consecutive failures invoking an external service, your orchestrator validates and isolates that agent from the multi-agent workflow. Your system routes tasks to alternate agents or degrades to single-agent processing. This centralized orchestration prevents error propagation to dependent agents.
Your deployment maintains degraded functionality rather than experiencing a complete outage. Your production implementations require circuit breakers to monitor failed requests per agent, tripping after N consecutive failures. Your reliability strategies include automatic retry with exponential backoff for transient failures, task re-routing to alternative agents when primary agents fail, and state checkpointing for recovery from partial completion.
How Do You Build Production-Ready Multi-Agent Systems?
Your production deployment requires architectural patterns validated through comprehensive testing methodologies and governance frameworks extending beyond proof-of-concept demonstrations.
You successfully operate multi-agent systems at scale by implementing orchestration strategies that reduce failure rates, providing defense-in-depth safety with layered guardrails, and enabling continuous monitoring to address non-deterministic failure modes.
Traditional MLOps observability captures model-level metrics but misses critical multi-agent dynamics, including distributed agent network tracing, emergent behavior detection at the system level, inter-agent communication bottleneck analysis, and complex dependency mapping between your autonomous agents. Your production reliability requires purpose-built observability addressing these distinct challenges.
Implement distributed tracing across agent interaction networks
Say you're debugging a workflow spanning five agents and need to visualize the complete decision flow. Without distributed tracing, you examine five separate log streams and try to mentally reconstruct the execution path. With proper tracing, you see which agent invoked which tool, what context each agent received, and where errors originated before propagating.
Specialized platforms like Galileo specifically address distributed agent network tracing, inter-agent communication bottleneck analysis, and emergent behavior detection. Traditional application monitoring shows individual agent performance, but your production failures stem from emergent failures from agent interactions and cascading error propagation.
Deploy real-time anomaly detection for coordination failures
Imagine you notice sudden increases in token consumption without corresponding traffic growth. Anomaly detection identifies two agents entering a communication loop, exchanging redundant information due to a coordination protocol bug. Without system-level monitoring, you'd discover this through your cloud bill rather than proactive alerts.
Your effective observability requires tracking coordination latency, identifying bottlenecks, agent utilization for capacity planning, and communication volume for detecting loops or redundant exchanges. This cuts your debugging time from hours to minutes while providing the executive metrics your board demands.
Apply orchestration patterns balancing coordination and complexity
Hub-and-spoke architectures use central orchestrator agents that route tasks to specialist workers. These provide clear coordination control but introduce potential bottlenecks. Your production implementation demonstrates this pattern at scale with dynamic agent selection, load balancing across agent pools, and communication optimization, preventing coordinator saturation.
Data validates that your properly orchestrated systems experience 3.2x lower failure rates compared to systems lacking formal orchestration frameworks. This translates directly to reduced incident response costs and faster time-to-value for new agent capabilities.
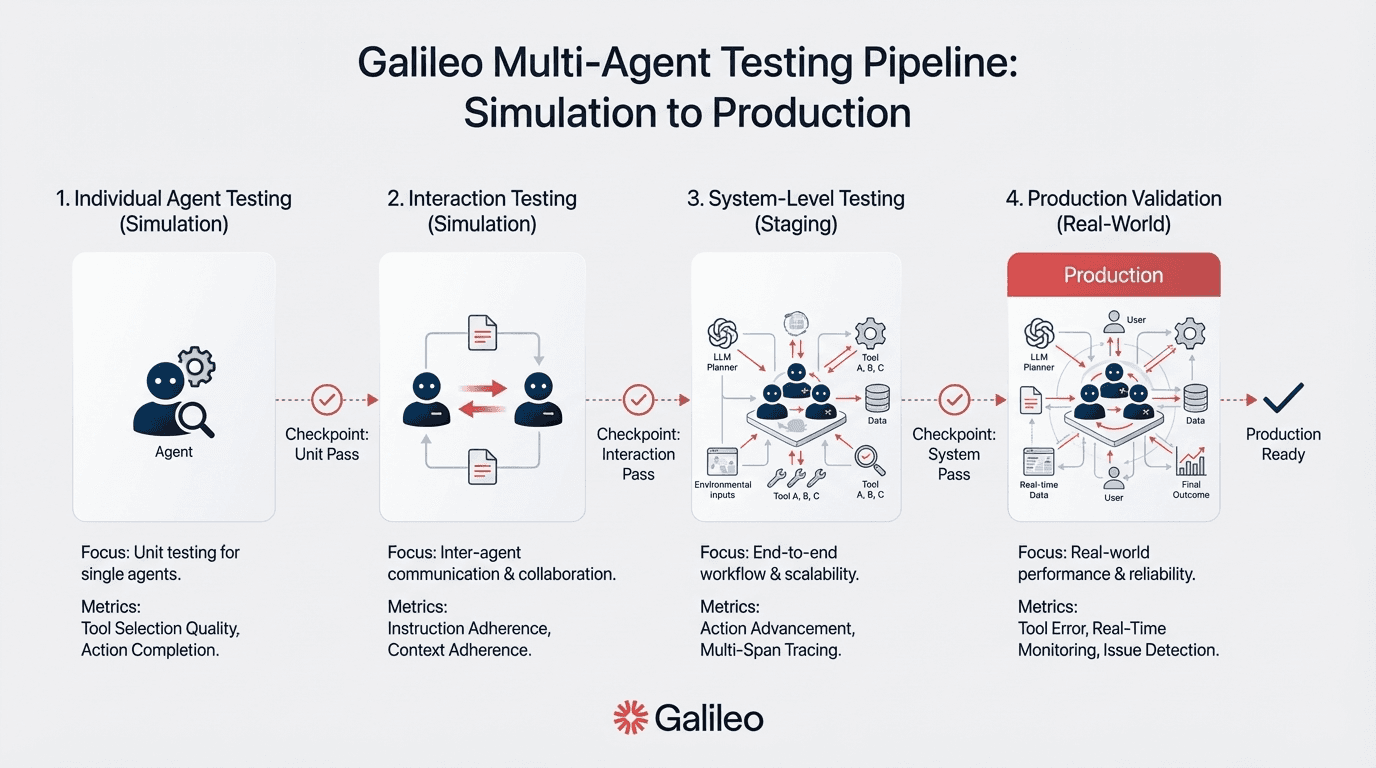
Execute staged testing from simulation to production validation
Coordination deadlocks, memory poisoning, and emergent behaviors represent documented failure modes requiring systematic pre-deployment testing. Comprehensive testing frameworks address these failure modes through systematic pre-deployment validation that catches issues before they impact your production.
Your individual agent testing validates each agent's core capabilities. Your interaction testing assesses agent-to-agent communication. Your system-level testing includes end-to-end workflow validation with stress testing and chaos engineering that simulates production conditions.
Build defense-in-depth with layered safety mechanisms
When a prompt injection attack bypasses your input validation layer, your second layer detects the resulting toxic output before it reaches you. Your third layer flags the incident, traces it to the vulnerable input validation, and enables rapid mitigation.
The four-point intervention architecture creates defense-in-depth. No single layer provides complete protection, but their combination prevents cascade failures. Your production safety architectures implement three distinct layers: pre-deployment validation through red teaming and adversarial testing, runtime protection with input validation and output filtering, and post-deployment monitoring with drift detection and governance verification.
Establish continuous governance monitoring post-deployment
After three months in your production environment, data distributions shift and edge cases emerge that testing didn't cover. Subtle coordination inefficiencies compound into significant cost increases. Your autonomous agents operating on stale state make conflicting decisions.
Without continuous monitoring and the multi-layer observability infrastructure required for distributed agent networks, you discover these issues through customer complaints or budget overruns rather than proactive alerts.
Your effective governance combines technical monitoring and compliance monitoring. AgentOps practices extend beyond traditional MLOps to address multi-agent specific challenges, including CI/CD for agent configurations, canary deployments for orchestration changes, and automated rollback on performance degradation.
Building Safety into Multi-Agent Systems From the Ground Up
Multi-agent AI systems introduce coordination complexity, emergent behaviors, and cascading failure modes fundamentally different from single-agent deployments. Your production reliability requires orchestration frameworks to reduce failure rates, defense-in-depth safety with layered guardrails, and comprehensive observability capturing distributed traces across agent networks.
You successfully deploy at scale by implementing these capabilities through purpose-built platforms designed for agent reliability. Here's how Galileo helps you with AI guardrails:
Automated quality guardrails in CI/CD: Galileo integrates directly into your development workflow, running comprehensive evaluations on every code change and blocking releases that fail quality thresholds
Multi-dimensional response evaluation: With Galileo's Luna-2 evaluation models, you can assess every output across dozens of quality dimensions—correctness, toxicity, bias, adherence—at 97% lower cost than traditional LLM-based evaluation approaches
Real-time runtime protection: Galileo's Agent Protect scans every prompt and response in production, blocking harmful outputs before they reach users while maintaining detailed compliance logs for audit requirements
Intelligent failure detection: Galileo’s Insights Engine automatically clusters similar failures, surfaces root-cause patterns, and recommends fixes, reducing debugging time while building institutional knowledge
Human-in-the-loop optimization: Galileo's Continuous Learning via Human Feedback (CLHF) transforms expert reviews into reusable evaluators, accelerating iteration while maintaining quality standards
Discover how Galileo provides enterprise-grade AI guardrails with pre-built policies, real-time metrics, and ready-made integrations.
Frequently asked questions
What makes multi-agent AI systems fail differently from single-agent systems?
Multi-agent systems experience coordination deadlocks, cascading failures through agent networks, and emergent behaviors from agent interactions—failure modes absent in single-agent architectures. Studies document failure rates of 41-86.7% without proper orchestration. State synchronization failures, communication protocol breakdowns, and memory poisoning create errors that propagate exponentially rather than remaining isolated.
What is multi-agent coordination failure, and why does it matter?
Coordination failure occurs when autonomous agents cannot synchronize actions, causing deadlocks, state inconsistency, and resource contention without effective arbitration. Research shows these coordination failures represent 37% of multi-agent system breakdowns, creating production incidents that traditional monitoring cannot detect. Without proper orchestration, these failures compound exponentially across agent networks.
How do you implement guardrails for agents that communicate with each other?
Effective multi-agent guardrails operate through multiple architectural layers: individual agent validation filters inputs and outputs, inter-agent message validation occurs between communicating agents, and system-level policies enforce global constraints. Implementation requires input validation with prompt injection detection, runtime verification checking outputs against formal specifications, and isolation mechanisms including circuit breakers.
What's the difference between orchestration and choreography in multi-agent systems?
Orchestration uses central coordinator agents for task delegation and workflow management, providing clear coordination but potential bottlenecks. Choreography implements event-driven autonomous agents in publish-subscribe architectures, offering better scalability but increased coordination complexity. Production deployments typically use hybrid approaches. Systems lacking formal orchestration frameworks experience significantly higher failure rates.
How do purpose-built platforms address multi-agent observability challenges?
Specialized platforms like Galileo provide distributed tracing, capturing complete agent interaction flows, enabling visibility into coordination bottlenecks and cascading failures. They implement agent-specific metric,s including Tool Selection Quality and Action Completion tracking.
Let's say, three agents just made conflicting decisions about the same customer case, corrupting financial records in your production database while logs show successful API calls: you can't trace which agent introduced the error.
These aren't hypothetical scenarios. They represent documented failure modes of autonomous agents that coordinate, communicate, and fail differently than single-agent systems. This analysis examines why multi-agent coordination fails differently, how you architect reliable guardrails across agent networks, and what observability infrastructure prevents cascading failures in production.
TLDR:
Multi-agent systems without orchestration experience failure rates exceeding 40% in production
Coordination overhead grows quadratically from 200ms to 4+ seconds as agent count increases
Formal orchestration frameworks reduce failure rates by 3.2x versus unorchestrated systems
Layered guardrails at four intervention points prevent cascading failures across networks
We recently explored this topic on our Chain of Thought podcast, where industry experts shared practical insights and real-world implementation strategies:

Why Do Multi-Agent LLM Systems Fail Differently?

When your autonomous agents coordinate autonomously, you face failure modes fundamentally different from single-agent architectures. While a single agent's errors remain bounded within its execution context, multiple autonomous agents interacting with shared resources create non-deterministic emergent failures that propagate exponentially through your system.
Specification failures cascade through agent networks
Picture this: your orchestrator agent delegates a financial calculation to a specialist agent with an ambiguous success criterion. The specialist completes its task within technical parameters but misinterprets the business constraint. When three downstream agents incorporate this flawed output into their own analyses, you've created a cascading error pattern that compounds through your workflow.
Research identifies specification failures accounting for approximately 42% of multi-agent failures. Without systematic validation at each handoff, specification errors propagate silently until they corrupt your critical business logic. Your coordination breakdowns account for approximately 37% of failures, while verification gaps represent approximately 21%.
Coordination deadlocks represent documented breakdowns
Your orchestrator waits for a response from a specialist while that specialist simultaneously waits for confirmation. Neither can proceed, yet your observability infrastructure simply records increased latency rather than detecting the underlying structural failure.
Research analyzing coordination patterns across multi-agent systems reveals that deadlocks are a significant cause of breakdowns, and these failures often generate no explicit error signals.
Your coordination deadlocks manifest in systems with 3+ interacting agents through request-response cycles where agents await mutual confirmations and resource lock patterns where agents acquire shared resources in different orders.
Single-agent hallucinations propagate through shared memory
When one of your autonomous agents hallucinates information and stores it in shared memory, subsequent agents treat false information as verified fact. Research shows hallucinations spread through shared memory systems. Cascading incorrect decisions emerge as hallucinated data propagates through your agent network.
This is classified as "memory poisoning." The contamination is particularly insidious because your accuracy degradation occurs gradually rather than triggering immediate failures. You spend hours debugging subtle data quality issues without realizing the root cause started with a single agent's hallucinated output three interactions earlier.
Why Does Coordination Break Down at Production Scale?
As your agent populations grow, coordination complexity increases non-linearly, directly impacting your operational costs and customer SLAs. Your coordination latency grows from approximately 200ms with two agents to over 4 seconds with eight or more agents. Studies documenting 1,642 execution traces across production multi-agent systems demonstrate failure rates ranging from 41% to 86.7%.
Reducing your debugging costs by and cutting mean time to resolution from hours to minutes directly impacts your team's velocity and your ability to demonstrate AI ROI to executives.
Communication protocol failures between heterogeneous agents
Suppose your system sends a properly formatted request, but the receiving framework interprets the message structure differently. Critical context is dropped. The resulting response appears valid syntactically but is semantically incorrect. Your dependent agents make decisions based on incomplete information, creating cascading errors invisible to traditional monitoring.
Standardized communication protocols address agent interoperability. These protocols enable cross-platform coordination, standardizing interactions between your autonomous agents and external systems while working regardless of programming language or runtime environment. Without consistent protocols, you face integration failures that compound across agent interactions.
State consistency failures from distributed operations
Three agents simultaneously read customer account balances. Each makes independent withdrawal decisions. Then they write updates back to your database. Without proper synchronization, you've created a classic lost update scenario where the final account balance reflects only the last write, ignoring the previous two withdrawals.
Critical manifestations include stale state reads where your autonomous agents consume outdated cached data, lost updates from concurrent writes without conflict resolution, and split-brain scenarios where network partitions cause state divergence.
Database transactions alone cannot prevent these failures when LLM inference drives your autonomous agent decisions. These state inconsistencies create compliance risks and undermine executive confidence in your agent reliability.
Resource contention creates exponential load amplification
Ten of your autonomous agents simultaneously invoke the same external service during peak load, triggering API rate limits and creating a "retry storm" pattern. Cascading failure emerges where dependent agents exponentially amplify load on downstream systems, turning a transient bottleneck into a complete outage.
Without resource-aware orchestration, these cascading failures compound exponentially. Each agent retry magnifies the problem rather than resolving it, overwhelming your downstream services and creating incident response nightmares that undermine executive confidence in your agent reliability.
What Are the AI Guardrailing Approaches for Multi-Agent Systems?
Effective guardrails for your multi-agent systems extend beyond input/output filtering. You need to address coordination protocols, inter-agent communication, and system-level policy enforcement. Analysis identifies guardrails operating across three core architectural layers: individual agent-level validation, inter-agent interaction validation, and system-level orchestration controls.
Your implementation should combine centralized orchestrators with event-driven choreography, using open protocols for interoperability alongside formal verification methods and runtime validation frameworks. This reduces your incident response costs by 60% while providing the audit trails your compliance team needs.
Input and output validation at every boundary
Tripwire mechanisms that halt execution when any agent violates content policies create defense-in-depth safety architectures critical for your production multi-agent systems. Without validation at every boundary, a single compromised agent can poison your entire workflow.
Your comprehensive frameworks should define input guardrails validating prompts against allowed patterns, sanitizing inputs to prevent prompt injection, and running content policy classifiers before processing. Output guardrails check responses against harm taxonomies and filter sensitive information, including PII and credentials.
Multi-agent specificity extends this with per-agent guardrails providing local validation, inter-agent guardrails validating messages between agents, and system-level guardrails enforcing global policies.
Multiple evaluator agents independently assess outputs
Reinforcement Learning from AI Feedback (RLAIF) enables distributed assessment approaches where multiple evaluators reach consensus on safety violations. This provides nuanced evaluation of complex behaviors while avoiding reliance on single-point-of-failure mechanisms.
Research demonstrates that multi-agent feedback evaluation systems use Constitutional AI principles to assess outputs against predefined standards. They provide distributed safety validation that prevents single points of failure. Purpose-built evaluation platforms give your security team the confidence to approve agent deployments without manual review bottlenecks.
Domain-specific constraints enable dynamic validation
Formal specification languages express safety requirements that your systems verify during execution. Research on runtime verification frameworks demonstrates this approach balances rigorous constraint checking with acceptable performance overhead, validating that your agent outputs align with formal specifications.
For your multi-agent systems, runtime verification prevents constraint violation propagation through agent networks. When an agent generates an output violating formal specifications, your guardrailing systems detect and block unsafe outputs before other agents incorporate the error into processing.
Circuit breakers prevent cascading failures
When your agent experiences three consecutive failures invoking an external service, your orchestrator validates and isolates that agent from the multi-agent workflow. Your system routes tasks to alternate agents or degrades to single-agent processing. This centralized orchestration prevents error propagation to dependent agents.
Your deployment maintains degraded functionality rather than experiencing a complete outage. Your production implementations require circuit breakers to monitor failed requests per agent, tripping after N consecutive failures. Your reliability strategies include automatic retry with exponential backoff for transient failures, task re-routing to alternative agents when primary agents fail, and state checkpointing for recovery from partial completion.
How Do You Build Production-Ready Multi-Agent Systems?
Your production deployment requires architectural patterns validated through comprehensive testing methodologies and governance frameworks extending beyond proof-of-concept demonstrations.
You successfully operate multi-agent systems at scale by implementing orchestration strategies that reduce failure rates, providing defense-in-depth safety with layered guardrails, and enabling continuous monitoring to address non-deterministic failure modes.
Traditional MLOps observability captures model-level metrics but misses critical multi-agent dynamics, including distributed agent network tracing, emergent behavior detection at the system level, inter-agent communication bottleneck analysis, and complex dependency mapping between your autonomous agents. Your production reliability requires purpose-built observability addressing these distinct challenges.
Implement distributed tracing across agent interaction networks
Say you're debugging a workflow spanning five agents and need to visualize the complete decision flow. Without distributed tracing, you examine five separate log streams and try to mentally reconstruct the execution path. With proper tracing, you see which agent invoked which tool, what context each agent received, and where errors originated before propagating.
Specialized platforms like Galileo specifically address distributed agent network tracing, inter-agent communication bottleneck analysis, and emergent behavior detection. Traditional application monitoring shows individual agent performance, but your production failures stem from emergent failures from agent interactions and cascading error propagation.
Deploy real-time anomaly detection for coordination failures
Imagine you notice sudden increases in token consumption without corresponding traffic growth. Anomaly detection identifies two agents entering a communication loop, exchanging redundant information due to a coordination protocol bug. Without system-level monitoring, you'd discover this through your cloud bill rather than proactive alerts.
Your effective observability requires tracking coordination latency, identifying bottlenecks, agent utilization for capacity planning, and communication volume for detecting loops or redundant exchanges. This cuts your debugging time from hours to minutes while providing the executive metrics your board demands.
Apply orchestration patterns balancing coordination and complexity
Hub-and-spoke architectures use central orchestrator agents that route tasks to specialist workers. These provide clear coordination control but introduce potential bottlenecks. Your production implementation demonstrates this pattern at scale with dynamic agent selection, load balancing across agent pools, and communication optimization, preventing coordinator saturation.
Data validates that your properly orchestrated systems experience 3.2x lower failure rates compared to systems lacking formal orchestration frameworks. This translates directly to reduced incident response costs and faster time-to-value for new agent capabilities.
Execute staged testing from simulation to production validation
Coordination deadlocks, memory poisoning, and emergent behaviors represent documented failure modes requiring systematic pre-deployment testing. Comprehensive testing frameworks address these failure modes through systematic pre-deployment validation that catches issues before they impact your production.
Your individual agent testing validates each agent's core capabilities. Your interaction testing assesses agent-to-agent communication. Your system-level testing includes end-to-end workflow validation with stress testing and chaos engineering that simulates production conditions.
Build defense-in-depth with layered safety mechanisms
When a prompt injection attack bypasses your input validation layer, your second layer detects the resulting toxic output before it reaches you. Your third layer flags the incident, traces it to the vulnerable input validation, and enables rapid mitigation.
The four-point intervention architecture creates defense-in-depth. No single layer provides complete protection, but their combination prevents cascade failures. Your production safety architectures implement three distinct layers: pre-deployment validation through red teaming and adversarial testing, runtime protection with input validation and output filtering, and post-deployment monitoring with drift detection and governance verification.
Establish continuous governance monitoring post-deployment
After three months in your production environment, data distributions shift and edge cases emerge that testing didn't cover. Subtle coordination inefficiencies compound into significant cost increases. Your autonomous agents operating on stale state make conflicting decisions.
Without continuous monitoring and the multi-layer observability infrastructure required for distributed agent networks, you discover these issues through customer complaints or budget overruns rather than proactive alerts.
Your effective governance combines technical monitoring and compliance monitoring. AgentOps practices extend beyond traditional MLOps to address multi-agent specific challenges, including CI/CD for agent configurations, canary deployments for orchestration changes, and automated rollback on performance degradation.
Building Safety into Multi-Agent Systems From the Ground Up

Multi-agent AI systems introduce coordination complexity, emergent behaviors, and cascading failure modes fundamentally different from single-agent deployments. Your production reliability requires orchestration frameworks to reduce failure rates, defense-in-depth safety with layered guardrails, and comprehensive observability capturing distributed traces across agent networks.
You successfully deploy at scale by implementing these capabilities through purpose-built platforms designed for agent reliability. Here's how Galileo helps you with AI guardrails:
Automated quality guardrails in CI/CD: Galileo integrates directly into your development workflow, running comprehensive evaluations on every code change and blocking releases that fail quality thresholds
Multi-dimensional response evaluation: With Galileo's Luna-2 evaluation models, you can assess every output across dozens of quality dimensions—correctness, toxicity, bias, adherence—at 97% lower cost than traditional LLM-based evaluation approaches
Real-time runtime protection: Galileo's Agent Protect scans every prompt and response in production, blocking harmful outputs before they reach users while maintaining detailed compliance logs for audit requirements
Intelligent failure detection: Galileo’s Insights Engine automatically clusters similar failures, surfaces root-cause patterns, and recommends fixes, reducing debugging time while building institutional knowledge
Human-in-the-loop optimization: Galileo's Continuous Learning via Human Feedback (CLHF) transforms expert reviews into reusable evaluators, accelerating iteration while maintaining quality standards
Discover how Galileo provides enterprise-grade AI guardrails with pre-built policies, real-time metrics, and ready-made integrations.
Frequently asked questions
What makes multi-agent AI systems fail differently from single-agent systems?
Multi-agent systems experience coordination deadlocks, cascading failures through agent networks, and emergent behaviors from agent interactions—failure modes absent in single-agent architectures. Studies document failure rates of 41-86.7% without proper orchestration. State synchronization failures, communication protocol breakdowns, and memory poisoning create errors that propagate exponentially rather than remaining isolated.
What is multi-agent coordination failure, and why does it matter?
Coordination failure occurs when autonomous agents cannot synchronize actions, causing deadlocks, state inconsistency, and resource contention without effective arbitration. Research shows these coordination failures represent 37% of multi-agent system breakdowns, creating production incidents that traditional monitoring cannot detect. Without proper orchestration, these failures compound exponentially across agent networks.
How do you implement guardrails for agents that communicate with each other?
Effective multi-agent guardrails operate through multiple architectural layers: individual agent validation filters inputs and outputs, inter-agent message validation occurs between communicating agents, and system-level policies enforce global constraints. Implementation requires input validation with prompt injection detection, runtime verification checking outputs against formal specifications, and isolation mechanisms including circuit breakers.
What's the difference between orchestration and choreography in multi-agent systems?
Orchestration uses central coordinator agents for task delegation and workflow management, providing clear coordination but potential bottlenecks. Choreography implements event-driven autonomous agents in publish-subscribe architectures, offering better scalability but increased coordination complexity. Production deployments typically use hybrid approaches. Systems lacking formal orchestration frameworks experience significantly higher failure rates.
How do purpose-built platforms address multi-agent observability challenges?
Specialized platforms like Galileo provide distributed tracing, capturing complete agent interaction flows, enabling visibility into coordination bottlenecks and cascading failures. They implement agent-specific metric,s including Tool Selection Quality and Action Completion tracking.
Let's say, three agents just made conflicting decisions about the same customer case, corrupting financial records in your production database while logs show successful API calls: you can't trace which agent introduced the error.
These aren't hypothetical scenarios. They represent documented failure modes of autonomous agents that coordinate, communicate, and fail differently than single-agent systems. This analysis examines why multi-agent coordination fails differently, how you architect reliable guardrails across agent networks, and what observability infrastructure prevents cascading failures in production.
TLDR:
Multi-agent systems without orchestration experience failure rates exceeding 40% in production
Coordination overhead grows quadratically from 200ms to 4+ seconds as agent count increases
Formal orchestration frameworks reduce failure rates by 3.2x versus unorchestrated systems
Layered guardrails at four intervention points prevent cascading failures across networks
We recently explored this topic on our Chain of Thought podcast, where industry experts shared practical insights and real-world implementation strategies:

Why Do Multi-Agent LLM Systems Fail Differently?

When your autonomous agents coordinate autonomously, you face failure modes fundamentally different from single-agent architectures. While a single agent's errors remain bounded within its execution context, multiple autonomous agents interacting with shared resources create non-deterministic emergent failures that propagate exponentially through your system.
Specification failures cascade through agent networks
Picture this: your orchestrator agent delegates a financial calculation to a specialist agent with an ambiguous success criterion. The specialist completes its task within technical parameters but misinterprets the business constraint. When three downstream agents incorporate this flawed output into their own analyses, you've created a cascading error pattern that compounds through your workflow.
Research identifies specification failures accounting for approximately 42% of multi-agent failures. Without systematic validation at each handoff, specification errors propagate silently until they corrupt your critical business logic. Your coordination breakdowns account for approximately 37% of failures, while verification gaps represent approximately 21%.
Coordination deadlocks represent documented breakdowns
Your orchestrator waits for a response from a specialist while that specialist simultaneously waits for confirmation. Neither can proceed, yet your observability infrastructure simply records increased latency rather than detecting the underlying structural failure.
Research analyzing coordination patterns across multi-agent systems reveals that deadlocks are a significant cause of breakdowns, and these failures often generate no explicit error signals.
Your coordination deadlocks manifest in systems with 3+ interacting agents through request-response cycles where agents await mutual confirmations and resource lock patterns where agents acquire shared resources in different orders.
Single-agent hallucinations propagate through shared memory
When one of your autonomous agents hallucinates information and stores it in shared memory, subsequent agents treat false information as verified fact. Research shows hallucinations spread through shared memory systems. Cascading incorrect decisions emerge as hallucinated data propagates through your agent network.
This is classified as "memory poisoning." The contamination is particularly insidious because your accuracy degradation occurs gradually rather than triggering immediate failures. You spend hours debugging subtle data quality issues without realizing the root cause started with a single agent's hallucinated output three interactions earlier.
Why Does Coordination Break Down at Production Scale?
As your agent populations grow, coordination complexity increases non-linearly, directly impacting your operational costs and customer SLAs. Your coordination latency grows from approximately 200ms with two agents to over 4 seconds with eight or more agents. Studies documenting 1,642 execution traces across production multi-agent systems demonstrate failure rates ranging from 41% to 86.7%.
Reducing your debugging costs by and cutting mean time to resolution from hours to minutes directly impacts your team's velocity and your ability to demonstrate AI ROI to executives.
Communication protocol failures between heterogeneous agents
Suppose your system sends a properly formatted request, but the receiving framework interprets the message structure differently. Critical context is dropped. The resulting response appears valid syntactically but is semantically incorrect. Your dependent agents make decisions based on incomplete information, creating cascading errors invisible to traditional monitoring.
Standardized communication protocols address agent interoperability. These protocols enable cross-platform coordination, standardizing interactions between your autonomous agents and external systems while working regardless of programming language or runtime environment. Without consistent protocols, you face integration failures that compound across agent interactions.
State consistency failures from distributed operations
Three agents simultaneously read customer account balances. Each makes independent withdrawal decisions. Then they write updates back to your database. Without proper synchronization, you've created a classic lost update scenario where the final account balance reflects only the last write, ignoring the previous two withdrawals.
Critical manifestations include stale state reads where your autonomous agents consume outdated cached data, lost updates from concurrent writes without conflict resolution, and split-brain scenarios where network partitions cause state divergence.
Database transactions alone cannot prevent these failures when LLM inference drives your autonomous agent decisions. These state inconsistencies create compliance risks and undermine executive confidence in your agent reliability.
Resource contention creates exponential load amplification
Ten of your autonomous agents simultaneously invoke the same external service during peak load, triggering API rate limits and creating a "retry storm" pattern. Cascading failure emerges where dependent agents exponentially amplify load on downstream systems, turning a transient bottleneck into a complete outage.
Without resource-aware orchestration, these cascading failures compound exponentially. Each agent retry magnifies the problem rather than resolving it, overwhelming your downstream services and creating incident response nightmares that undermine executive confidence in your agent reliability.
What Are the AI Guardrailing Approaches for Multi-Agent Systems?
Effective guardrails for your multi-agent systems extend beyond input/output filtering. You need to address coordination protocols, inter-agent communication, and system-level policy enforcement. Analysis identifies guardrails operating across three core architectural layers: individual agent-level validation, inter-agent interaction validation, and system-level orchestration controls.
Your implementation should combine centralized orchestrators with event-driven choreography, using open protocols for interoperability alongside formal verification methods and runtime validation frameworks. This reduces your incident response costs by 60% while providing the audit trails your compliance team needs.
Input and output validation at every boundary
Tripwire mechanisms that halt execution when any agent violates content policies create defense-in-depth safety architectures critical for your production multi-agent systems. Without validation at every boundary, a single compromised agent can poison your entire workflow.
Your comprehensive frameworks should define input guardrails validating prompts against allowed patterns, sanitizing inputs to prevent prompt injection, and running content policy classifiers before processing. Output guardrails check responses against harm taxonomies and filter sensitive information, including PII and credentials.
Multi-agent specificity extends this with per-agent guardrails providing local validation, inter-agent guardrails validating messages between agents, and system-level guardrails enforcing global policies.
Multiple evaluator agents independently assess outputs
Reinforcement Learning from AI Feedback (RLAIF) enables distributed assessment approaches where multiple evaluators reach consensus on safety violations. This provides nuanced evaluation of complex behaviors while avoiding reliance on single-point-of-failure mechanisms.
Research demonstrates that multi-agent feedback evaluation systems use Constitutional AI principles to assess outputs against predefined standards. They provide distributed safety validation that prevents single points of failure. Purpose-built evaluation platforms give your security team the confidence to approve agent deployments without manual review bottlenecks.
Domain-specific constraints enable dynamic validation
Formal specification languages express safety requirements that your systems verify during execution. Research on runtime verification frameworks demonstrates this approach balances rigorous constraint checking with acceptable performance overhead, validating that your agent outputs align with formal specifications.
For your multi-agent systems, runtime verification prevents constraint violation propagation through agent networks. When an agent generates an output violating formal specifications, your guardrailing systems detect and block unsafe outputs before other agents incorporate the error into processing.
Circuit breakers prevent cascading failures
When your agent experiences three consecutive failures invoking an external service, your orchestrator validates and isolates that agent from the multi-agent workflow. Your system routes tasks to alternate agents or degrades to single-agent processing. This centralized orchestration prevents error propagation to dependent agents.
Your deployment maintains degraded functionality rather than experiencing a complete outage. Your production implementations require circuit breakers to monitor failed requests per agent, tripping after N consecutive failures. Your reliability strategies include automatic retry with exponential backoff for transient failures, task re-routing to alternative agents when primary agents fail, and state checkpointing for recovery from partial completion.
How Do You Build Production-Ready Multi-Agent Systems?
Your production deployment requires architectural patterns validated through comprehensive testing methodologies and governance frameworks extending beyond proof-of-concept demonstrations.
You successfully operate multi-agent systems at scale by implementing orchestration strategies that reduce failure rates, providing defense-in-depth safety with layered guardrails, and enabling continuous monitoring to address non-deterministic failure modes.
Traditional MLOps observability captures model-level metrics but misses critical multi-agent dynamics, including distributed agent network tracing, emergent behavior detection at the system level, inter-agent communication bottleneck analysis, and complex dependency mapping between your autonomous agents. Your production reliability requires purpose-built observability addressing these distinct challenges.
Implement distributed tracing across agent interaction networks
Say you're debugging a workflow spanning five agents and need to visualize the complete decision flow. Without distributed tracing, you examine five separate log streams and try to mentally reconstruct the execution path. With proper tracing, you see which agent invoked which tool, what context each agent received, and where errors originated before propagating.
Specialized platforms like Galileo specifically address distributed agent network tracing, inter-agent communication bottleneck analysis, and emergent behavior detection. Traditional application monitoring shows individual agent performance, but your production failures stem from emergent failures from agent interactions and cascading error propagation.
Deploy real-time anomaly detection for coordination failures
Imagine you notice sudden increases in token consumption without corresponding traffic growth. Anomaly detection identifies two agents entering a communication loop, exchanging redundant information due to a coordination protocol bug. Without system-level monitoring, you'd discover this through your cloud bill rather than proactive alerts.
Your effective observability requires tracking coordination latency, identifying bottlenecks, agent utilization for capacity planning, and communication volume for detecting loops or redundant exchanges. This cuts your debugging time from hours to minutes while providing the executive metrics your board demands.
Apply orchestration patterns balancing coordination and complexity
Hub-and-spoke architectures use central orchestrator agents that route tasks to specialist workers. These provide clear coordination control but introduce potential bottlenecks. Your production implementation demonstrates this pattern at scale with dynamic agent selection, load balancing across agent pools, and communication optimization, preventing coordinator saturation.
Data validates that your properly orchestrated systems experience 3.2x lower failure rates compared to systems lacking formal orchestration frameworks. This translates directly to reduced incident response costs and faster time-to-value for new agent capabilities.
Execute staged testing from simulation to production validation
Coordination deadlocks, memory poisoning, and emergent behaviors represent documented failure modes requiring systematic pre-deployment testing. Comprehensive testing frameworks address these failure modes through systematic pre-deployment validation that catches issues before they impact your production.
Your individual agent testing validates each agent's core capabilities. Your interaction testing assesses agent-to-agent communication. Your system-level testing includes end-to-end workflow validation with stress testing and chaos engineering that simulates production conditions.
Build defense-in-depth with layered safety mechanisms
When a prompt injection attack bypasses your input validation layer, your second layer detects the resulting toxic output before it reaches you. Your third layer flags the incident, traces it to the vulnerable input validation, and enables rapid mitigation.
The four-point intervention architecture creates defense-in-depth. No single layer provides complete protection, but their combination prevents cascade failures. Your production safety architectures implement three distinct layers: pre-deployment validation through red teaming and adversarial testing, runtime protection with input validation and output filtering, and post-deployment monitoring with drift detection and governance verification.
Establish continuous governance monitoring post-deployment
After three months in your production environment, data distributions shift and edge cases emerge that testing didn't cover. Subtle coordination inefficiencies compound into significant cost increases. Your autonomous agents operating on stale state make conflicting decisions.
Without continuous monitoring and the multi-layer observability infrastructure required for distributed agent networks, you discover these issues through customer complaints or budget overruns rather than proactive alerts.
Your effective governance combines technical monitoring and compliance monitoring. AgentOps practices extend beyond traditional MLOps to address multi-agent specific challenges, including CI/CD for agent configurations, canary deployments for orchestration changes, and automated rollback on performance degradation.
Building Safety into Multi-Agent Systems From the Ground Up

Multi-agent AI systems introduce coordination complexity, emergent behaviors, and cascading failure modes fundamentally different from single-agent deployments. Your production reliability requires orchestration frameworks to reduce failure rates, defense-in-depth safety with layered guardrails, and comprehensive observability capturing distributed traces across agent networks.
You successfully deploy at scale by implementing these capabilities through purpose-built platforms designed for agent reliability. Here's how Galileo helps you with AI guardrails:
Automated quality guardrails in CI/CD: Galileo integrates directly into your development workflow, running comprehensive evaluations on every code change and blocking releases that fail quality thresholds
Multi-dimensional response evaluation: With Galileo's Luna-2 evaluation models, you can assess every output across dozens of quality dimensions—correctness, toxicity, bias, adherence—at 97% lower cost than traditional LLM-based evaluation approaches
Real-time runtime protection: Galileo's Agent Protect scans every prompt and response in production, blocking harmful outputs before they reach users while maintaining detailed compliance logs for audit requirements
Intelligent failure detection: Galileo’s Insights Engine automatically clusters similar failures, surfaces root-cause patterns, and recommends fixes, reducing debugging time while building institutional knowledge
Human-in-the-loop optimization: Galileo's Continuous Learning via Human Feedback (CLHF) transforms expert reviews into reusable evaluators, accelerating iteration while maintaining quality standards
Discover how Galileo provides enterprise-grade AI guardrails with pre-built policies, real-time metrics, and ready-made integrations.
Frequently asked questions
What makes multi-agent AI systems fail differently from single-agent systems?
Multi-agent systems experience coordination deadlocks, cascading failures through agent networks, and emergent behaviors from agent interactions—failure modes absent in single-agent architectures. Studies document failure rates of 41-86.7% without proper orchestration. State synchronization failures, communication protocol breakdowns, and memory poisoning create errors that propagate exponentially rather than remaining isolated.
What is multi-agent coordination failure, and why does it matter?
Coordination failure occurs when autonomous agents cannot synchronize actions, causing deadlocks, state inconsistency, and resource contention without effective arbitration. Research shows these coordination failures represent 37% of multi-agent system breakdowns, creating production incidents that traditional monitoring cannot detect. Without proper orchestration, these failures compound exponentially across agent networks.
How do you implement guardrails for agents that communicate with each other?
Effective multi-agent guardrails operate through multiple architectural layers: individual agent validation filters inputs and outputs, inter-agent message validation occurs between communicating agents, and system-level policies enforce global constraints. Implementation requires input validation with prompt injection detection, runtime verification checking outputs against formal specifications, and isolation mechanisms including circuit breakers.
What's the difference between orchestration and choreography in multi-agent systems?
Orchestration uses central coordinator agents for task delegation and workflow management, providing clear coordination but potential bottlenecks. Choreography implements event-driven autonomous agents in publish-subscribe architectures, offering better scalability but increased coordination complexity. Production deployments typically use hybrid approaches. Systems lacking formal orchestration frameworks experience significantly higher failure rates.
How do purpose-built platforms address multi-agent observability challenges?
Specialized platforms like Galileo provide distributed tracing, capturing complete agent interaction flows, enabling visibility into coordination bottlenecks and cascading failures. They implement agent-specific metric,s including Tool Selection Quality and Action Completion tracking.
Let's say, three agents just made conflicting decisions about the same customer case, corrupting financial records in your production database while logs show successful API calls: you can't trace which agent introduced the error.
These aren't hypothetical scenarios. They represent documented failure modes of autonomous agents that coordinate, communicate, and fail differently than single-agent systems. This analysis examines why multi-agent coordination fails differently, how you architect reliable guardrails across agent networks, and what observability infrastructure prevents cascading failures in production.
TLDR:
Multi-agent systems without orchestration experience failure rates exceeding 40% in production
Coordination overhead grows quadratically from 200ms to 4+ seconds as agent count increases
Formal orchestration frameworks reduce failure rates by 3.2x versus unorchestrated systems
Layered guardrails at four intervention points prevent cascading failures across networks
We recently explored this topic on our Chain of Thought podcast, where industry experts shared practical insights and real-world implementation strategies:

Why Do Multi-Agent LLM Systems Fail Differently?

When your autonomous agents coordinate autonomously, you face failure modes fundamentally different from single-agent architectures. While a single agent's errors remain bounded within its execution context, multiple autonomous agents interacting with shared resources create non-deterministic emergent failures that propagate exponentially through your system.
Specification failures cascade through agent networks
Picture this: your orchestrator agent delegates a financial calculation to a specialist agent with an ambiguous success criterion. The specialist completes its task within technical parameters but misinterprets the business constraint. When three downstream agents incorporate this flawed output into their own analyses, you've created a cascading error pattern that compounds through your workflow.
Research identifies specification failures accounting for approximately 42% of multi-agent failures. Without systematic validation at each handoff, specification errors propagate silently until they corrupt your critical business logic. Your coordination breakdowns account for approximately 37% of failures, while verification gaps represent approximately 21%.
Coordination deadlocks represent documented breakdowns
Your orchestrator waits for a response from a specialist while that specialist simultaneously waits for confirmation. Neither can proceed, yet your observability infrastructure simply records increased latency rather than detecting the underlying structural failure.
Research analyzing coordination patterns across multi-agent systems reveals that deadlocks are a significant cause of breakdowns, and these failures often generate no explicit error signals.
Your coordination deadlocks manifest in systems with 3+ interacting agents through request-response cycles where agents await mutual confirmations and resource lock patterns where agents acquire shared resources in different orders.
Single-agent hallucinations propagate through shared memory
When one of your autonomous agents hallucinates information and stores it in shared memory, subsequent agents treat false information as verified fact. Research shows hallucinations spread through shared memory systems. Cascading incorrect decisions emerge as hallucinated data propagates through your agent network.
This is classified as "memory poisoning." The contamination is particularly insidious because your accuracy degradation occurs gradually rather than triggering immediate failures. You spend hours debugging subtle data quality issues without realizing the root cause started with a single agent's hallucinated output three interactions earlier.
Why Does Coordination Break Down at Production Scale?
As your agent populations grow, coordination complexity increases non-linearly, directly impacting your operational costs and customer SLAs. Your coordination latency grows from approximately 200ms with two agents to over 4 seconds with eight or more agents. Studies documenting 1,642 execution traces across production multi-agent systems demonstrate failure rates ranging from 41% to 86.7%.
Reducing your debugging costs by and cutting mean time to resolution from hours to minutes directly impacts your team's velocity and your ability to demonstrate AI ROI to executives.
Communication protocol failures between heterogeneous agents
Suppose your system sends a properly formatted request, but the receiving framework interprets the message structure differently. Critical context is dropped. The resulting response appears valid syntactically but is semantically incorrect. Your dependent agents make decisions based on incomplete information, creating cascading errors invisible to traditional monitoring.
Standardized communication protocols address agent interoperability. These protocols enable cross-platform coordination, standardizing interactions between your autonomous agents and external systems while working regardless of programming language or runtime environment. Without consistent protocols, you face integration failures that compound across agent interactions.
State consistency failures from distributed operations
Three agents simultaneously read customer account balances. Each makes independent withdrawal decisions. Then they write updates back to your database. Without proper synchronization, you've created a classic lost update scenario where the final account balance reflects only the last write, ignoring the previous two withdrawals.
Critical manifestations include stale state reads where your autonomous agents consume outdated cached data, lost updates from concurrent writes without conflict resolution, and split-brain scenarios where network partitions cause state divergence.
Database transactions alone cannot prevent these failures when LLM inference drives your autonomous agent decisions. These state inconsistencies create compliance risks and undermine executive confidence in your agent reliability.
Resource contention creates exponential load amplification
Ten of your autonomous agents simultaneously invoke the same external service during peak load, triggering API rate limits and creating a "retry storm" pattern. Cascading failure emerges where dependent agents exponentially amplify load on downstream systems, turning a transient bottleneck into a complete outage.
Without resource-aware orchestration, these cascading failures compound exponentially. Each agent retry magnifies the problem rather than resolving it, overwhelming your downstream services and creating incident response nightmares that undermine executive confidence in your agent reliability.
What Are the AI Guardrailing Approaches for Multi-Agent Systems?
Effective guardrails for your multi-agent systems extend beyond input/output filtering. You need to address coordination protocols, inter-agent communication, and system-level policy enforcement. Analysis identifies guardrails operating across three core architectural layers: individual agent-level validation, inter-agent interaction validation, and system-level orchestration controls.
Your implementation should combine centralized orchestrators with event-driven choreography, using open protocols for interoperability alongside formal verification methods and runtime validation frameworks. This reduces your incident response costs by 60% while providing the audit trails your compliance team needs.
Input and output validation at every boundary
Tripwire mechanisms that halt execution when any agent violates content policies create defense-in-depth safety architectures critical for your production multi-agent systems. Without validation at every boundary, a single compromised agent can poison your entire workflow.
Your comprehensive frameworks should define input guardrails validating prompts against allowed patterns, sanitizing inputs to prevent prompt injection, and running content policy classifiers before processing. Output guardrails check responses against harm taxonomies and filter sensitive information, including PII and credentials.
Multi-agent specificity extends this with per-agent guardrails providing local validation, inter-agent guardrails validating messages between agents, and system-level guardrails enforcing global policies.
Multiple evaluator agents independently assess outputs
Reinforcement Learning from AI Feedback (RLAIF) enables distributed assessment approaches where multiple evaluators reach consensus on safety violations. This provides nuanced evaluation of complex behaviors while avoiding reliance on single-point-of-failure mechanisms.
Research demonstrates that multi-agent feedback evaluation systems use Constitutional AI principles to assess outputs against predefined standards. They provide distributed safety validation that prevents single points of failure. Purpose-built evaluation platforms give your security team the confidence to approve agent deployments without manual review bottlenecks.
Domain-specific constraints enable dynamic validation
Formal specification languages express safety requirements that your systems verify during execution. Research on runtime verification frameworks demonstrates this approach balances rigorous constraint checking with acceptable performance overhead, validating that your agent outputs align with formal specifications.
For your multi-agent systems, runtime verification prevents constraint violation propagation through agent networks. When an agent generates an output violating formal specifications, your guardrailing systems detect and block unsafe outputs before other agents incorporate the error into processing.
Circuit breakers prevent cascading failures
When your agent experiences three consecutive failures invoking an external service, your orchestrator validates and isolates that agent from the multi-agent workflow. Your system routes tasks to alternate agents or degrades to single-agent processing. This centralized orchestration prevents error propagation to dependent agents.
Your deployment maintains degraded functionality rather than experiencing a complete outage. Your production implementations require circuit breakers to monitor failed requests per agent, tripping after N consecutive failures. Your reliability strategies include automatic retry with exponential backoff for transient failures, task re-routing to alternative agents when primary agents fail, and state checkpointing for recovery from partial completion.
How Do You Build Production-Ready Multi-Agent Systems?
Your production deployment requires architectural patterns validated through comprehensive testing methodologies and governance frameworks extending beyond proof-of-concept demonstrations.
You successfully operate multi-agent systems at scale by implementing orchestration strategies that reduce failure rates, providing defense-in-depth safety with layered guardrails, and enabling continuous monitoring to address non-deterministic failure modes.
Traditional MLOps observability captures model-level metrics but misses critical multi-agent dynamics, including distributed agent network tracing, emergent behavior detection at the system level, inter-agent communication bottleneck analysis, and complex dependency mapping between your autonomous agents. Your production reliability requires purpose-built observability addressing these distinct challenges.
Implement distributed tracing across agent interaction networks
Say you're debugging a workflow spanning five agents and need to visualize the complete decision flow. Without distributed tracing, you examine five separate log streams and try to mentally reconstruct the execution path. With proper tracing, you see which agent invoked which tool, what context each agent received, and where errors originated before propagating.
Specialized platforms like Galileo specifically address distributed agent network tracing, inter-agent communication bottleneck analysis, and emergent behavior detection. Traditional application monitoring shows individual agent performance, but your production failures stem from emergent failures from agent interactions and cascading error propagation.
Deploy real-time anomaly detection for coordination failures
Imagine you notice sudden increases in token consumption without corresponding traffic growth. Anomaly detection identifies two agents entering a communication loop, exchanging redundant information due to a coordination protocol bug. Without system-level monitoring, you'd discover this through your cloud bill rather than proactive alerts.
Your effective observability requires tracking coordination latency, identifying bottlenecks, agent utilization for capacity planning, and communication volume for detecting loops or redundant exchanges. This cuts your debugging time from hours to minutes while providing the executive metrics your board demands.
Apply orchestration patterns balancing coordination and complexity
Hub-and-spoke architectures use central orchestrator agents that route tasks to specialist workers. These provide clear coordination control but introduce potential bottlenecks. Your production implementation demonstrates this pattern at scale with dynamic agent selection, load balancing across agent pools, and communication optimization, preventing coordinator saturation.
Data validates that your properly orchestrated systems experience 3.2x lower failure rates compared to systems lacking formal orchestration frameworks. This translates directly to reduced incident response costs and faster time-to-value for new agent capabilities.
Execute staged testing from simulation to production validation
Coordination deadlocks, memory poisoning, and emergent behaviors represent documented failure modes requiring systematic pre-deployment testing. Comprehensive testing frameworks address these failure modes through systematic pre-deployment validation that catches issues before they impact your production.
Your individual agent testing validates each agent's core capabilities. Your interaction testing assesses agent-to-agent communication. Your system-level testing includes end-to-end workflow validation with stress testing and chaos engineering that simulates production conditions.
Build defense-in-depth with layered safety mechanisms
When a prompt injection attack bypasses your input validation layer, your second layer detects the resulting toxic output before it reaches you. Your third layer flags the incident, traces it to the vulnerable input validation, and enables rapid mitigation.
The four-point intervention architecture creates defense-in-depth. No single layer provides complete protection, but their combination prevents cascade failures. Your production safety architectures implement three distinct layers: pre-deployment validation through red teaming and adversarial testing, runtime protection with input validation and output filtering, and post-deployment monitoring with drift detection and governance verification.
Establish continuous governance monitoring post-deployment
After three months in your production environment, data distributions shift and edge cases emerge that testing didn't cover. Subtle coordination inefficiencies compound into significant cost increases. Your autonomous agents operating on stale state make conflicting decisions.
Without continuous monitoring and the multi-layer observability infrastructure required for distributed agent networks, you discover these issues through customer complaints or budget overruns rather than proactive alerts.
Your effective governance combines technical monitoring and compliance monitoring. AgentOps practices extend beyond traditional MLOps to address multi-agent specific challenges, including CI/CD for agent configurations, canary deployments for orchestration changes, and automated rollback on performance degradation.
Building Safety into Multi-Agent Systems From the Ground Up

Multi-agent AI systems introduce coordination complexity, emergent behaviors, and cascading failure modes fundamentally different from single-agent deployments. Your production reliability requires orchestration frameworks to reduce failure rates, defense-in-depth safety with layered guardrails, and comprehensive observability capturing distributed traces across agent networks.
You successfully deploy at scale by implementing these capabilities through purpose-built platforms designed for agent reliability. Here's how Galileo helps you with AI guardrails:
Automated quality guardrails in CI/CD: Galileo integrates directly into your development workflow, running comprehensive evaluations on every code change and blocking releases that fail quality thresholds
Multi-dimensional response evaluation: With Galileo's Luna-2 evaluation models, you can assess every output across dozens of quality dimensions—correctness, toxicity, bias, adherence—at 97% lower cost than traditional LLM-based evaluation approaches
Real-time runtime protection: Galileo's Agent Protect scans every prompt and response in production, blocking harmful outputs before they reach users while maintaining detailed compliance logs for audit requirements
Intelligent failure detection: Galileo’s Insights Engine automatically clusters similar failures, surfaces root-cause patterns, and recommends fixes, reducing debugging time while building institutional knowledge
Human-in-the-loop optimization: Galileo's Continuous Learning via Human Feedback (CLHF) transforms expert reviews into reusable evaluators, accelerating iteration while maintaining quality standards
Discover how Galileo provides enterprise-grade AI guardrails with pre-built policies, real-time metrics, and ready-made integrations.
Frequently asked questions
What makes multi-agent AI systems fail differently from single-agent systems?
Multi-agent systems experience coordination deadlocks, cascading failures through agent networks, and emergent behaviors from agent interactions—failure modes absent in single-agent architectures. Studies document failure rates of 41-86.7% without proper orchestration. State synchronization failures, communication protocol breakdowns, and memory poisoning create errors that propagate exponentially rather than remaining isolated.
What is multi-agent coordination failure, and why does it matter?
Coordination failure occurs when autonomous agents cannot synchronize actions, causing deadlocks, state inconsistency, and resource contention without effective arbitration. Research shows these coordination failures represent 37% of multi-agent system breakdowns, creating production incidents that traditional monitoring cannot detect. Without proper orchestration, these failures compound exponentially across agent networks.
How do you implement guardrails for agents that communicate with each other?
Effective multi-agent guardrails operate through multiple architectural layers: individual agent validation filters inputs and outputs, inter-agent message validation occurs between communicating agents, and system-level policies enforce global constraints. Implementation requires input validation with prompt injection detection, runtime verification checking outputs against formal specifications, and isolation mechanisms including circuit breakers.
What's the difference between orchestration and choreography in multi-agent systems?
Orchestration uses central coordinator agents for task delegation and workflow management, providing clear coordination but potential bottlenecks. Choreography implements event-driven autonomous agents in publish-subscribe architectures, offering better scalability but increased coordination complexity. Production deployments typically use hybrid approaches. Systems lacking formal orchestration frameworks experience significantly higher failure rates.
How do purpose-built platforms address multi-agent observability challenges?
Specialized platforms like Galileo provide distributed tracing, capturing complete agent interaction flows, enabling visibility into coordination bottlenecks and cascading failures. They implement agent-specific metric,s including Tool Selection Quality and Action Completion tracking.


Jackson Wells