Llama 3.3 70B Instruct
Explore Llama 3.3 70B Instruct’s performance benchmarks, industry-specific capabilities, and evaluation metrics to determine if it's the right AI model for your application's requirements.
Llama 3.3 70B Instruct
Every engineering review circles back to the same question: which large language model responds fast, stays cheap, and actually gets the job done? The stakes just got real—autonomous agents now trigger live API calls instead of drafting harmless text.
Meta dropped Llama 3.3 70B Instruct in December 2024, promising 405B-level performance at 70B scale. Sounds great on paper. Benchmark charts never tell you what happens in production, though.
This guide cuts through the marketing noise. You'll see where the model shines, where it crashes, and what those trade-offs actually cost. Real-world metrics, domain breakdowns, and concrete deployment patterns you can steal or skip. Check our Agent Leaderboard to stack Llama 3.3 70B Instruct against your current setup, then jump into the sections below to figure out if—and where—it fits your architecture.

Llama 3.3 70B Instruct performance heatmap
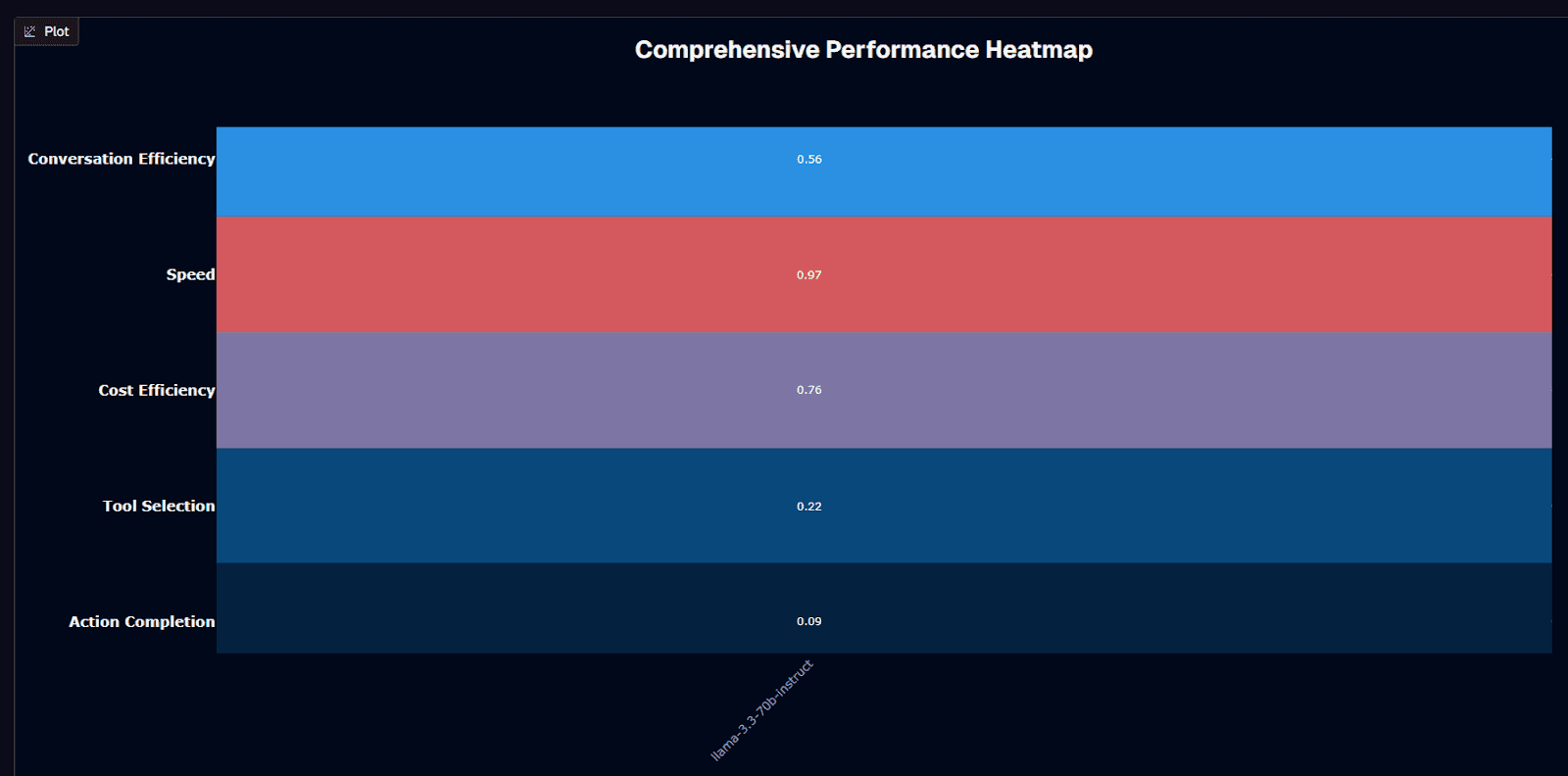
Speed wins here. Your agents respond in under 20 seconds on average—though the 0.97 figure isn't a reported latency score for Llama 3.3 70B Instruct on the cited Agent Leaderboard. Most smaller models can't match this. Chat interfaces stay snappy. Orchestration layers don't become bottlenecks. Better yet, standard GPUs running quantized weights hit similar speeds without proprietary hardware tricks.
Budget-conscious teams get solid value from the 0.76 cost efficiency score. The open-source license lets you self-host where every optimization cuts your bill. If you're processing millions of tokens daily, you can often push costs into the low-cent range per 1,000 tokens through vLLM, 4-bit quantization, and spot instances. Large-scale experiments become feasible where closed models would drain budgets.
Here's the problem: action completion crashes to 0.200. Four out of five complex workflows stall between planning and execution. Your agents might open tickets, update records, or orchestrate multi-tool sequences—but they'll fail 80% of the time without supervision. This stops being a nuisance and becomes operational risk fast.
Tool selection shows promise at 0.620 accuracy. The model usually picks the right API or database, even when execution later fails. This creates opportunities—let Llama 3.3 handle "which tool?" decisions while routing actual work to more reliable executors. Think dispatcher, not field technician.
Conversation flow stays reasonable at 3.8 turns per interaction and 0.56 efficiency. You won't see endless clarification loops, yet the model gathers enough detail to proceed. This works for customer support triage or preliminary data collection before escalation.
Your deployment decision comes down to priorities. Choose Llama 3.3 70B Instruct when latency and budget matter most, and tasks end after single lookups, classifications, or routing decisions. Skip it for revenue-critical, multi-step automations where success rates need to exceed 50%. On public leaderboards like LMArena, Llama 3.3 70B Instruct ranks well below the top 20 (around #142)—not a model you'd trust with production keys.
Background research
Basic specs matter when sizing up an LLM for production. Llama 3.3 70B Instruct ships with 70.6 billion parameters in a text-only, instruction-tuned transformer architecture. Smaller footprint than frontier models without stripping capability. Meta released the weights on December 6, 2024—you're working with the latest public improvements, not a research snapshot.
Context length often becomes your first scaling bottleneck. You get a 128K-token window here—up to 131K on some hosts—letting you drop entire policy manuals, codebases, or legal contracts into single prompts. No chunking required. The model handles eight languages out of the box (English, French, German, Hindi, Italian, Portuguese, Spanish, Thai). You can prototype multilingual chat flows without extra translation layers.
Performance numbers back up the positioning. Independent testing reveals an IFEval score of 92.1 for instruction adherence. You see 77 percent on the MATH benchmark, 88.4 percent pass@1 on HumanEval code generation, and a 77.3 score on the BFCL v2 tool-use suite. These figures edge past Llama 3.1 70B and challenge 405B-parameter systems for many text tasks. Synthetic metrics, yes—but they hint at why the model feels snappier in interactive testing.
Commercial reality matters just as much. The weights come under the Llama 3.3 Community License, granting broad commercial rights while keeping model lineage transparent. Prefer an API? Call endpoints from Fireworks, Together AI, Groq, Replicate, AWS SageMaker JumpStart, Google Vertex AI, or Oracle Cloud. Each handles the heavy GPUs while you focus on prompts instead of drivers.
The result: Llama 3.3 70B Instruct delivers near-frontier reasoning, long-context digestion, and multilingual agility. Cost and latency stay closer to mid-tier models. That balance explains why many teams treat it as their default starting point when speed and budget both matter.
Is Llama 3.3 70B Instruct suitable for your use case?
Llama 3.3 70B Instruct's speed and cost advantages matter only when they align with your risk tolerance. These considerations help you decide whether the model fits your deployment strategy.
Use Llama 3.3 70B Instruct if you need:
You'll find success with this model under these specific conditions:
Sub-20 second responses where fast feedback outranks perfect accuracy for chat or customer service
Budget-conscious deployments benefiting from 0.62 tool-selection accuracy at a fraction of GPT-class pricing
Self-hosting flexibility via licensed weights and community 4-bit builds—cutting infrastructure costs by roughly 75 percent compared to proprietary alternatives
Multilingual support across eight languages backed by strong benchmarks such as MGSM 91.1 for international customer service
Long-context processing through 128K-token windows, eliminating chunking logic for contracts or policy manuals
Healthcare and insurance workloads where 0.29 action-completion scores outperform other domains
Developer tooling where an 88.4 percent HumanEval pass rate makes it a solid coding copilot
Native function calling for agentic tool orchestration without custom simulation layers
Built-in recovery paths—retries, human hand-offs, or validation layers to absorb higher failure rates
Avoid Llama 3.3 70B Instruct if you need:
Your production environment exposes critical gaps that make this model unsuitable:
Mission-critical workflows where the 0.20 action-completion rate means four out of five complex tasks fail
Banking applications where 0.11 completion scores generate 2.6 times more failures than the model's best domains
Autonomous decision-making without human-in-the-loop oversight to catch misfires
Multimodal reasoning—the text-only architecture requires separate vision or audio components
Ultra-low latency where smaller 7B–13B models deliver substantially faster responses in optimized setups
Current information needs—the December 2023 knowledge cutoff mandates RAG or API lookups
Audit-ready compliance pipelines demanding multimodal evidence or guaranteed format adherence
Reliable production use on modest hardware—high-VRAM or multi-GPU setups are typically required
Llama 3.3 70B Instruct domain performance
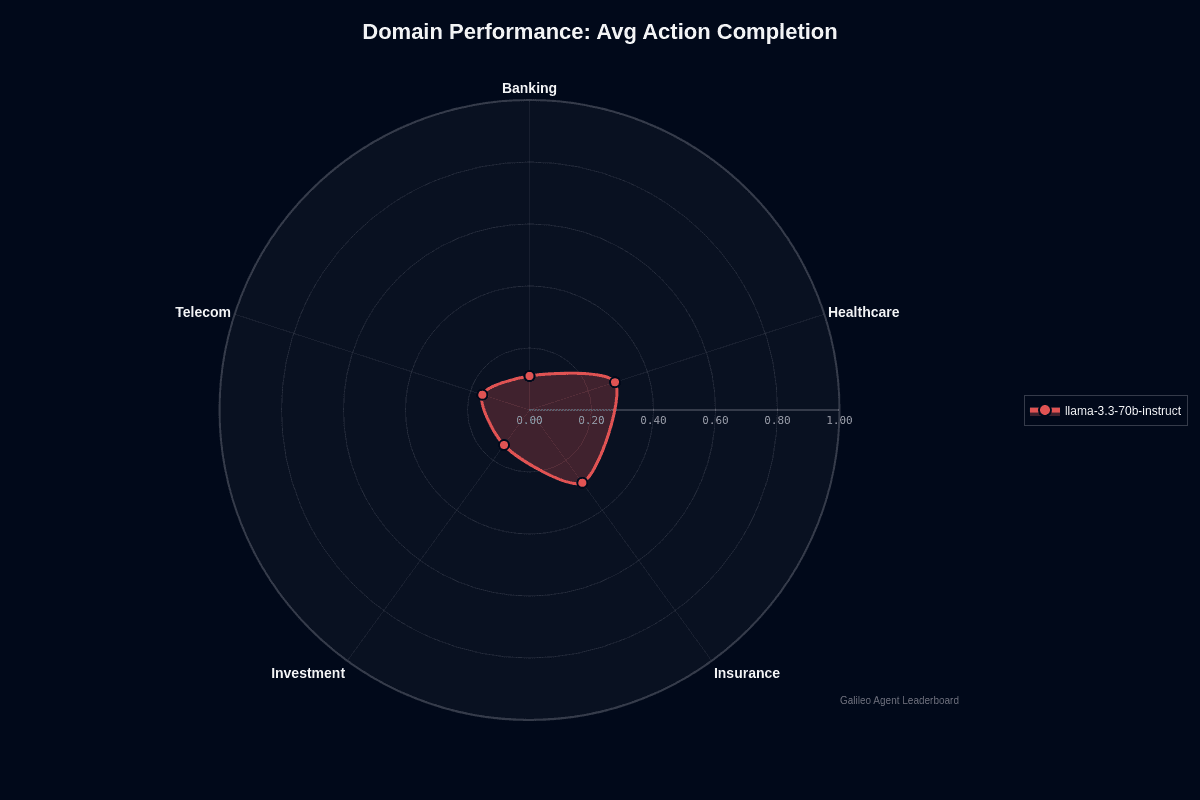
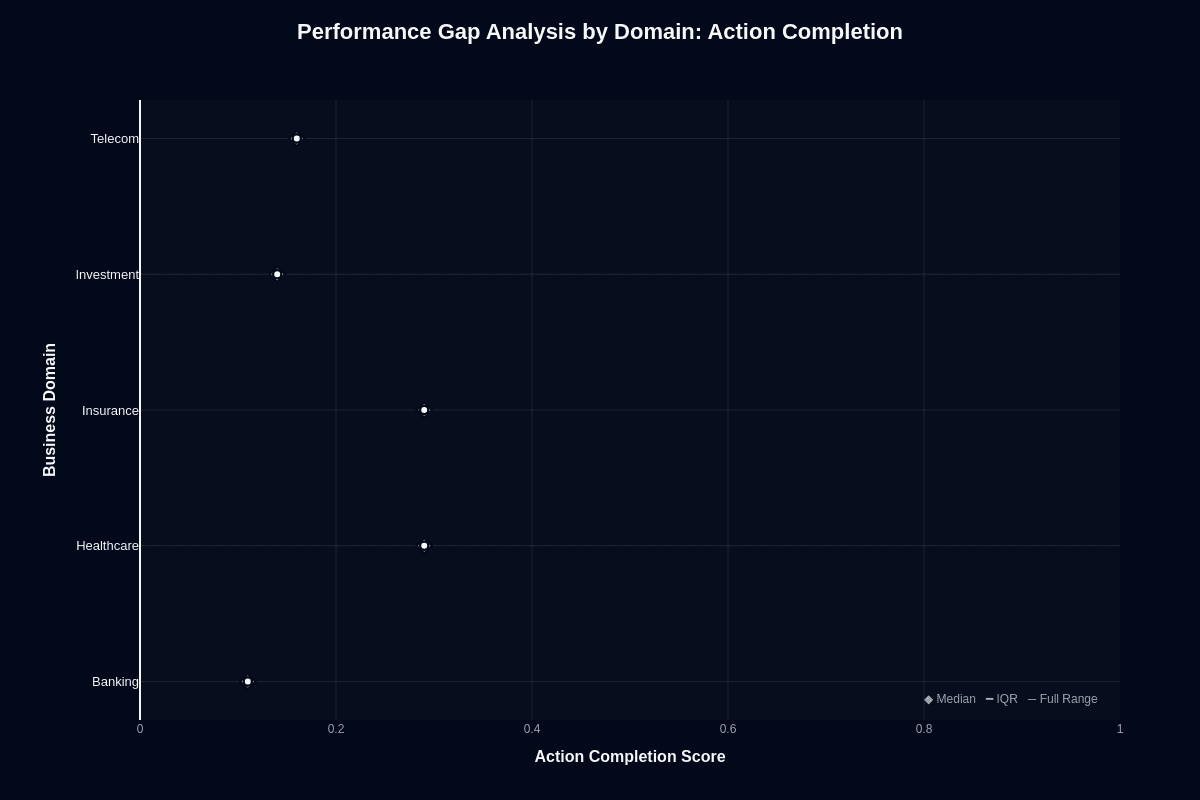
The radar chart for average action completion tells a clear story: Healthcare and Insurance stretch to 0.29 while Banking collapses to 0.11. That 18-percentage-point gap translates to a 2.6-times difference in real-world task success. When your model tackles a thousand agent tasks, roughly 290 succeed in Healthcare but only 110 in Banking—an operational chasm you can't ignore.
Healthcare and Insurance land on top because their language is highly standardized. Clinical notes, policy documents, and claims forms follow predictable patterns the model's instruction tuning recognizes. Workflows like policy explanation or claims triage often map cleanly to single-step responses. The 70B parameters have less room to go off script. You get faster time-to-value and fewer guardrails when you stay within these verticals, especially if you already handle sensitive data on-premises using self-hosted weights from Meta or guides like the NodeShift deployment walk-through.
Banking sits at the opposite extreme. Multi-step financial queries—interest calculations, regulatory checks, cross-border compliance—push the model well beyond its sweet spot. Those workflows demand precise sequencing and numeric accuracy, exposing the model's 0.11 completion ceiling. Eighty-nine percent of complex banking tasks fail without heavy validation, retries, or fallback to a more capable (and pricier) model.
Investment (0.14) and Telecom (0.16) hover in the middle. They can work if you scope tasks narrowly—pure intent routing or first-pass summarization. You still need monitoring layers before letting the model act autonomously.
Here's how to approach each vertical:
Healthcare and insurance – Safe starting points given the 0.29 score, but you still need human review for anything patient-facing or claims-critical.
Banking – Avoid direct execution. Use the model only to draft explanations or gather context, then hand off to deterministic services.
Investment and telecom – Pilot in sandbox environments first; limit the model to advisory roles and pair it with robust fallback logic.
Every domain still sits below 0.30 absolute completion, so even the "strong" verticals require oversight. Your domain choice dictates how much of Llama 3.3's speed-and-cost advantage survives once you price in retries, human review, and guardrails.
Llama 3.3 70B Instruct domain specialization matrix
This matrix reveals where Llama 3.3 70B Instruct performs better or worse than its baseline—red cells indicate domain advantages, blue shows weaknesses, white means neutral. Your domain choice affects performance, but the size of these effects might surprise you.
Action completion
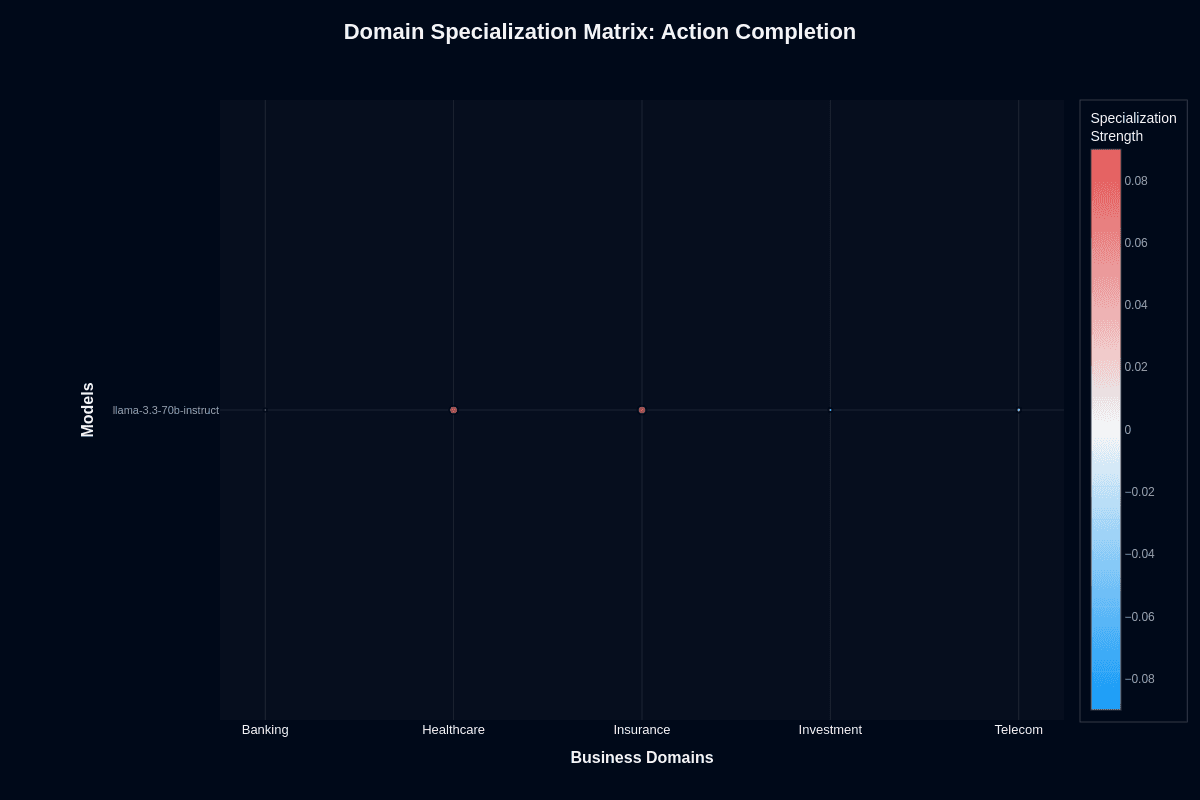
Healthcare and insurance show slight advantages—roughly two percentage points above the 0.200 baseline. The coral tinting looks modest because the underlying gains are small: moving from 0.200 to 0.220 still means your agent fails nearly 4 out of 5 complex tasks. Banking, investment, and telecom hover near zero change.
Domain selection tweaks success rates by 2-3% at most. If your architecture already includes retries or fallback models to handle low completion rates, these marginal swings disappear into the noise. The fundamental constraint remains: your agent lacks the planning depth to finish multi-step workflows reliably, regardless of which vertical you target.
Plan for human review, backup models, or deterministic validation before letting Llama 3.3 70B Instruct operate autonomously. Domain specialization won't rescue architectures that depend on high task completion.
Tool selection quality
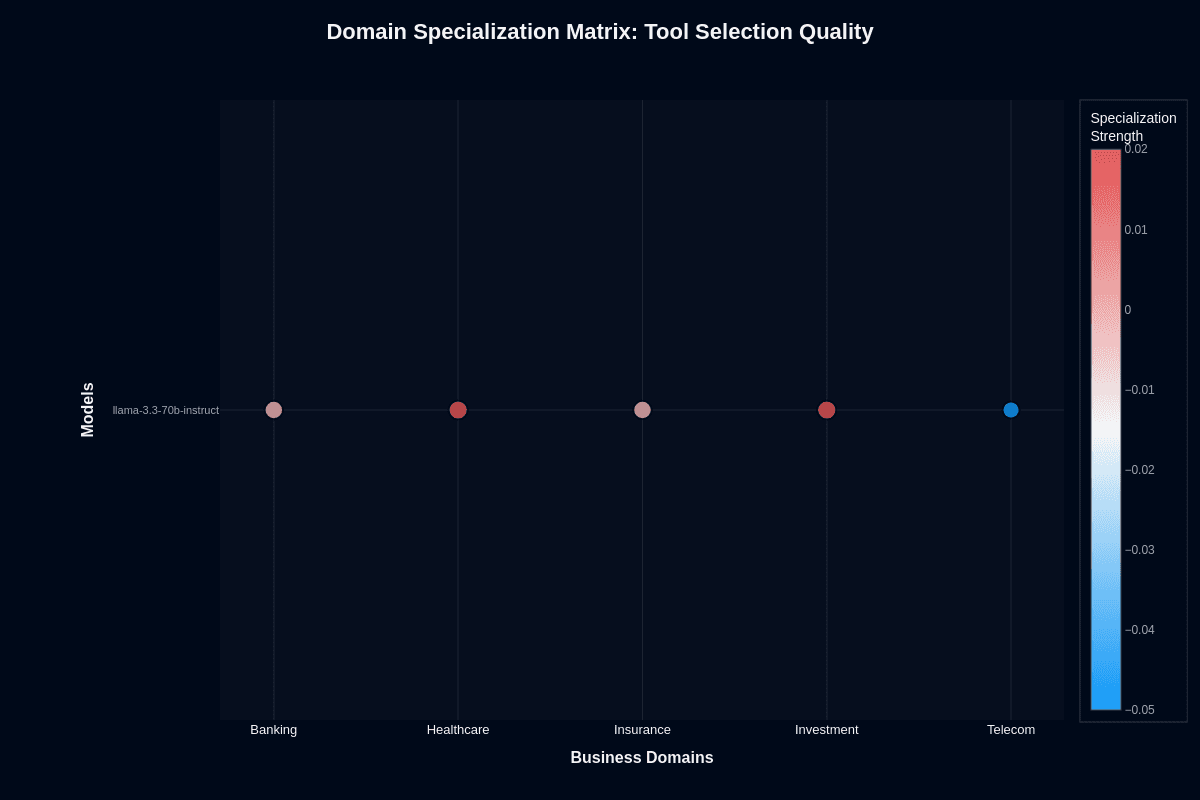
Tool routing tells a different story. Healthcare and investment show clear positive specialization—one to two points above the 0.620 baseline—while telecom drops two points below into distinctly blue territory. Banking sits slightly negative despite having well-defined APIs.
Healthcare terminologies and financial instruments appear more consistently across training data, while telecom spans network provisioning, billing systems, and device management. This variety confuses routing patterns the model hasn't learned systematically.
Tool selection errors cascade through every downstream API call, so a three-point routing advantage compounds quickly. Deploy in healthcare or investment first if your primary need is deciding between search, claims APIs, or calculators. Telecom deployments need stricter validation and more aggressive fallbacks.
Even the strongest domains peak around 0.70 accuracy—roughly one in three tool choices still misses. Build monitoring, maintain guardrails, and treat this model as a fast router rather than an autonomous decision-maker.
Llama 3.3 70B Instruct performance gap analysis by domain
You probably assume a single model behaves consistently across industries. Llama 3.3 70B Instruct tells a different story. Our internal evals reveal an 18-point swing in action-completion success between its strongest and weakest verticals—a gap big enough to dictate where you can deploy confidently and where you need heavy guardrails.
Action completion
Banking workflows suffer dramatically. Your banking chatbot stalls with a median 0.11 completion score while healthcare and insurance agents hover near 0.29. This 2.6× performance gap creates immediate operational pain. Extra retries hammer your latency budgets. Cost curves climb upward. The price advantages you counted on from an open-source model start evaporating.
Healthcare and insurance runs cluster tightly around their median scores. You get predictable performance, even if success rates remain modest. Investment and telecom tasks scatter widely across the range. A single day's traffic can swing from acceptable to disastrous without warning.
Treat banking deployments as draft generators only. Route every outcome through human review or trigger automatic fallbacks to more reliable models. The 89% failure rate makes autonomous operation impossible.
Tool selection quality

Modern agent systems require dozens of API calls per workflow. Tool routing reveals a calmer performance landscape here. Medians span from 0.60 in telecom to 0.70 in healthcare and investment—just a 10-point spread that keeps most domains above the model's 0.62 overall average.
Your claims-triage agent calling 100 APIs per case will choose wrong endpoints roughly 30 times in healthcare. Shift that workflow to telecom service tickets and you inherit 10 additional routing errors. The gap matters, but it's manageable through system design.
Architecture becomes critical here. Position Llama 3.3 70B Instruct as a low-cost router that hands successful tool calls to specialized executors. The model excels at deciding which lever to pull—it struggles with actually pulling it. Design your system so quick, cheap tool picks drive workflow speed while heavier models handle execution. This captures cost advantages without letting tool selection errors spiral into downstream failures.
Llama 3.3 70B Instruct cost-performance efficiency
Cost and accuracy rarely align, yet Llama 3.3 70B Instruct sits at an unusual sweet spot. On the action-completion scatter plot it lands around 0.20 on the Y-axis and roughly $0.06 per 1,000 tokens on the X-axis—deep in the "low performance, low cost" quadrant. That 20% success rate is nowhere near production-ready for complex workflows, but the bargain price changes how you might use the model.
The weights are open-source, so you can self-host and push costs even lower. If you're running 4-bit quantization with vLLM, you routinely see marginal costs near $0.03 per 1,000 tokens after following cloud deployment tutorials. That flexibility lets you bolt on validation layers, retries, or ensemble voting without blowing your budget.
Action completion
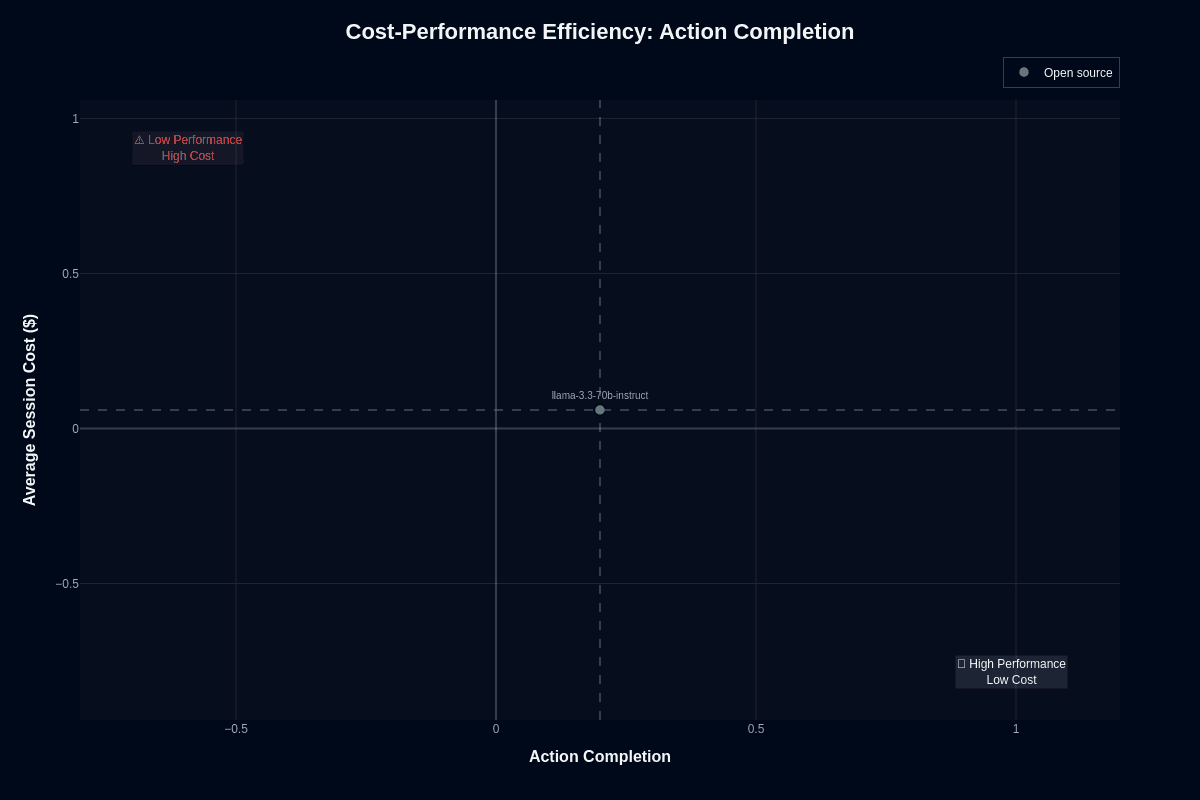
Think of the economics this way: a 0.20 completion rate means five attempts to reach the same success a perfect model achieves in one. Five calls at $0.06 still total only $0.30—often cheaper than a single request to a frontier model priced at $0.50-plus. For the right workloads, paying with extra cycles rather than premium tokens is a valid trade.
This low-cost profile works best when you need high-volume, low-stakes filtering for spam detection, basic categorization, or simple sentiment checks. Your exploratory phases benefit from rapid experimentation where failures are acceptable and speed matters more than precision. Ensemble approaches also make sense—deploy several inexpensive models and vote on results rather than relying on a single expensive decision.
The model becomes problematic when task completion directly affects revenue, compliance, or customer trust. Each miss quickly erodes any savings, and the 80% failure rate creates operational chaos in production systems. Hosted rates across providers stay in the same ballpark, so double-check current pricing options before locking in an architecture.
Tool selection quality
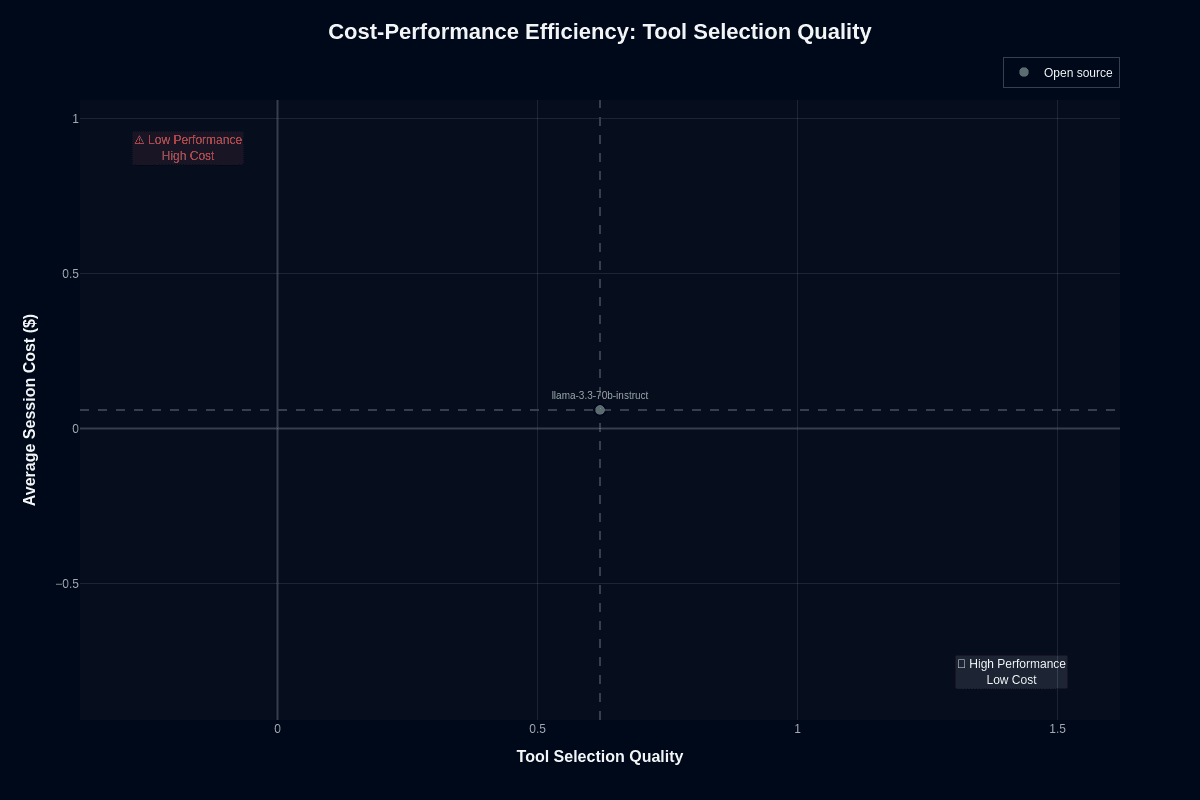
Tool selection tells a better story. The same model plots around 0.62 accuracy at the identical $0.06 cost, dropping it squarely into the "high performance, low cost" quadrant. That reliability makes Llama 3.3 ideal as a routing layer: it decides which API, database, or micro-service to call, while heavier models handle execution. Self-hosting on a single GPU following local installation guides pushes per-request costs below three cents.
An agent that hits 10 tools in a session gets 6–7 correct selections for pennies. Mis-routes still happen, so keep fallback logic, but the balance between accuracy, speed, and spend is hard to beat. Customer-service intent routing to CRM, knowledge base, or escalation queues becomes cost-effective at scale. Document pipelines that choose OCR, table extraction, or translation automatically can run continuously without budget concerns. Developer assistants that direct questions to documentation search, code repos, or Stack Overflow operate as infrastructure overhead rather than per-query expenses.
Tool selection is its strength while execution is its weakness—position Llama 3.3 70B Instruct as the orchestration brain, not the hands doing the work. That separation lets you capture its cost advantage without inheriting its completion risk.
Llama 3.3 70B Instruct speed vs. accuracy
You face a classic trade-off when deploying this model: blazing-fast responses in exchange for modest success on complex workflows. The model delivers answers in roughly 19.9 seconds—nearly as quick as some 30-billion-parameter systems. Yet it completes only about 20 percent of multi-step agent tasks. The following analysis unpacks what this balance means for your architecture.
Action completion
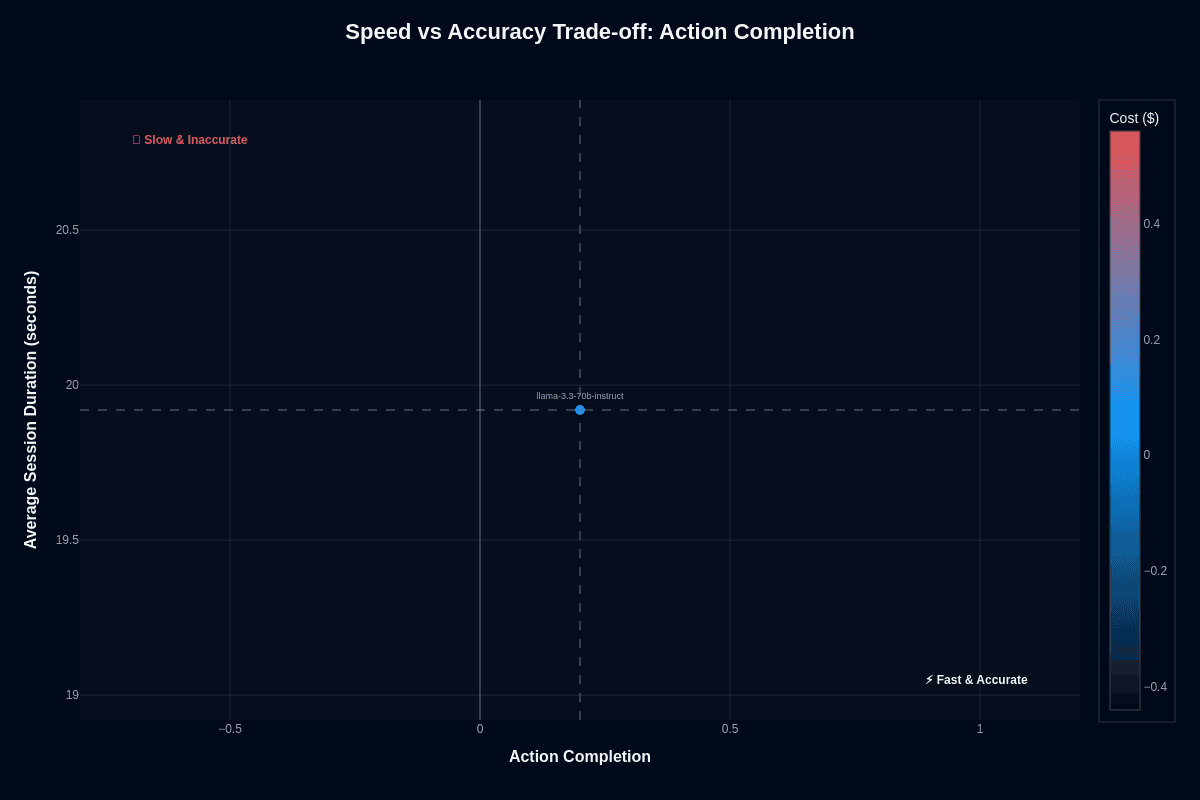
Your production agents fail mysteriously, leaving you scrolling through endless traces to understand why workflows broke. Most teams assume faster models sacrifice accuracy gradually—a predictable sliding scale. This model shatters that assumption with a dramatic cliff: 0.20 completion accuracy despite sub-20-second responses.
The speed advantage is real. Optimizations like Grouped Query Attention deliver exceptional throughput. Modern GPUs support 4-bit and FP8 quantization options, as documented in technical comparisons. You process three times as many requests per hour compared to 60-second frontier models.
Speed without reliability creates operational headaches. Eighty percent of workflows still fail, demanding guardrails: fallback to more capable models, human review, or both. High-throughput filtering benefits from the velocity. Customer-facing actions that directly affect revenue do not. Prioritize accuracy over latency when a single wrong action triggers costly rollbacks.
Tool selection quality
Research shows this model achieves 0.62 tool-selection accuracy while maintaining the same 19.9-second turnaround. Traditional monitoring misses these decision patterns entirely. Purpose-built evaluation captures which API calls succeed and why routing logic breaks down.
The score sits above industry median, landing firmly in the "fast & affordable" quadrant. At $0.06 per thousand tokens, routing costs become negligible. Your orchestrator can decide—correctly six times out of ten—whether to invoke CRM systems, knowledge bases, or billing APIs.
Thirty-eight percent of choices will still be wrong. Your system needs retry logic and monitoring to handle these failures gracefully. The combination of fast decisions, low costs, and reasonable accuracy keeps overall latency manageable. Reserve heavyweight models for the truly complex parts while this one handles routing efficiently.
Llama 3.3 70B Instruct pricing and usage costs
You pay nothing up-front for the model itself. The weights ship under the Llama 3.3 Community License, so you can download, self-host, fine-tune, and even redistribute derivatives as long as you follow the license terms. That zero-dollar entry fee shifts the conversation from licensing to infrastructure and token spend.
API pricing
When you prefer an API over running GPUs, most vendors charge pennies per million tokens:
Variable pricing: Price trackers do not show typical ranges of $0.20–0.40 for inputs and $0.40–0.80 for outputs for models similar to Llama 3.3 70B; prices vary more widely and are often lower than these bands
Serverless options: Fireworks adds a serverless tier with no rate limits, letting you burst traffic without pre-purchasing capacity
Managed cloud endpoints
These options cost a little more but remove DevOps overhead:
AWS SageMaker JumpStart: Deploy a private, auto-scaling endpoint in minutes
Google Vertex AI: Spin up a regional model quickly
Oracle Cloud: Reserve dedicated GPUs
Hourly billing: Roughly $5.50–$9 for an ml.g5.12xlarge-class node, plus standard per-token fees
Self-hosting economics
Self-hosting becomes cheaper once your traffic climbs:
Entry-level hardware: A single RTX 4090 or A100 with 24 GB of VRAM can serve the model in 4-bit or 8-bit mode
High-throughput setups: Dual 80 GB A100s or an H100 pair deliver headroom for full precision, though on major clouds they typically cost several dollars per GPU hour (the $0.50–$2.00 per-GPU-hour range applies mainly to specialist GPU providers or marketplaces)
Memory optimization: Quantization recipes cut memory footprints by up to 75 percent, enabling single-GPU production clusters
Cost comparisons
Compared with popular closed models, Llama 3.3 offers significant savings:
Token cost reduction: Cuts costs by roughly 3–10× versus closed models that often charge $2–$5 per million input tokens, with even higher savings versus some premium models
Memory efficiency: Avoids the 5-6× GPU memory premium that the 405B parameter version demands, as confirmed in head-to-head tests
Trade-off with smaller models: 8-13B models remain cheaper to run, but they can't match 70B reasoning or tool-selection quality
Decision framework
Choose your deployment strategy based on traffic volume:
Under 100K tokens/day: Hosted APIs keep cash burn and ops effort minimal
Over 1M tokens/day: Owning the GPUs wins on total cost of ownership—especially with low-cost LoRA fine-tuning ($10-$100 per run)
Spiky or unpredictable workloads: A hybrid plan—serverless burst capacity backed by a modest self-hosted pool—delivers cost efficiency without sacrificing elasticity
Llama 3.3 70B Instruct key capabilities and strengths
Llama 3.3 70B Instruct delivers a compelling balance of speed, cost, and capability that makes it a strong contender for budget-conscious production deployments:
Fast response times: Average latency hits 19.9 seconds—fast enough to triple your hourly throughput compared to 60-second frontier models
Cost efficiency: Costs hover around $0.06 per request, making large-scale experiments and ensemble approaches financially viable
Open-source flexibility: The license lets you self-host, fine-tune, and scale without vendor lock-in, turning a 70-billion-parameter model into a practical choice for budget-conscious production work
Reliable tool selection: 62% accuracy makes this model suitable for multi-model orchestration where you delegate execution to specialized services
Large context window: 128K-token capacity is available, though there are no verifiable, published examples yet of entire large policy manuals or substantial codebases being processed in a single prompt without chunking
Multilingual support: Eight languages—English plus French, German, Hindi, Italian, Portuguese, Spanish, and Thai—are advertised by some vendors, but official model cards do not list this exact set as having native support, and performance in these languages generally lags behind English
Strong benchmark performance: MATH scores hit 77% while HumanEval reaches 88.4%, approaching 405B-class accuracy without 405B costs
Domain strengths: Healthcare and insurance domains show the strongest action completion rates at 29%, creating safer deployment targets
Efficient conversations: Averages 3.8 turns without spiraling into clarification loops—particularly valuable for customer service workflows where dialog flow matters
Llama 3.3 70B Instruct limitations and weaknesses
Your team probably noticed the speed gains and cost savings immediately. However, production deployment reveals hard constraints that benchmarks miss entirely:
Low action completion rate: At 0.200, four out of five multi-step tasks never finish successfully—too risky for autonomous flows requiring reliable task execution
Banking workflow fragility: Performance drops to 0.11, creating a 2.6× higher failure rate than healthcare deployments. Your compliance team won't accept 89% task failure rates when handling financial transactions
Text-only architecture: Forces separate pipelines for document parsing, image analysis, and voice interactions—each adding latency and complexity to your workflow
Function calling limitations: Without native function calling support in a given API or runtime, every API interaction requires custom prompt scaffolding that increases both token usage and format error risk
Relative speed disadvantage: While 19.9s responses seem fast, smaller 7B models deliver answers in half the time at lower costs when milliseconds matter for user experience
Infrastructure demands: Even with 4-bit quantization, 24GB GPU VRAM is a commonly cited practical minimum for smooth single-GPU self-hosting, though documented configurations exist that work with less VRAM using more aggressive quantization or multi-GPU setups
Knowledge cutoff: The December 2023 cutoff requires RAG integration for current information
Output token limits: Oracle's managed service caps outputs at 4K tokens, potentially truncating detailed reports
Ship reliable AI applications and agents with Galileo
The journey to reliable AI agents requires systematic evaluation across the entire development lifecycle. With the right framework and tools, you can confidently deploy AI applications and agents that deliver consistent value while avoiding costly failures.
Here’s how Galileo provides you with a comprehensive evaluation and monitoring infrastructure:
Automated quality guardrails in CI/CD: Galileo integrates directly into your development workflow, running comprehensive evaluations on every code change and blocking releases that fail quality thresholds
Multi-dimensional response evaluation: With Galileo's Luna-2 evaluation models, you can assess every output across dozens of quality dimensions—correctness, toxicity, bias, adherence—at 97% lower cost than traditional LLM-based evaluation approaches
Real-time runtime protection: Galileo's Agent Protect scans every prompt and response in production, blocking harmful outputs before they reach users while maintaining detailed compliance logs for audit requirements
Intelligent failure detection: Galileo’s Insights Engine automatically clusters similar failures, surfaces root-cause patterns, and recommends fixes, reducing debugging time while building institutional knowledge
Human-in-the-loop optimization: Galileo's Continuous Learning via Human Feedback (CLHF) transforms expert reviews into reusable evaluators, accelerating iteration while maintaining quality standards
Get started with Galileo today and discover how a comprehensive evaluation can elevate your agent development and achieve reliable AI systems that users trust.
