Mistral Small 2506
Explore Mistral Small 2506 performance benchmarks, industry-specific capabilities, and evaluation metrics to determine if it's the right AI model for your application's requirements.

Mistral Small 2506
Looking for an LLM that won't drain your budget? Mistral Small 2506 sits in the mid-tier category—several production-ready models cost less. This 24-billion-parameter model gives you decent reasoning power at a very low per-token cost. Actual session prices depend on your provider and usage patterns, and you'll find cheaper production-ready options out there. Check our Agent Leaderboard to see how it stacks up and whether the cost profile fits your use case.
This article goes beyond headlines into data-driven cost-performance analysis. You'll learn where this budget-friendly model excels and where it falls short. More importantly, you'll understand how those trade-offs affect real deployments.
The goal is straightforward: give AI engineering leaders, product owners, and data scientists the clarity they need. You'll get concise metrics, domain-specific insights, and clear guidance on when that half-cent price tag justifies the limitations.
Mistral Small 2506 performance heatmap
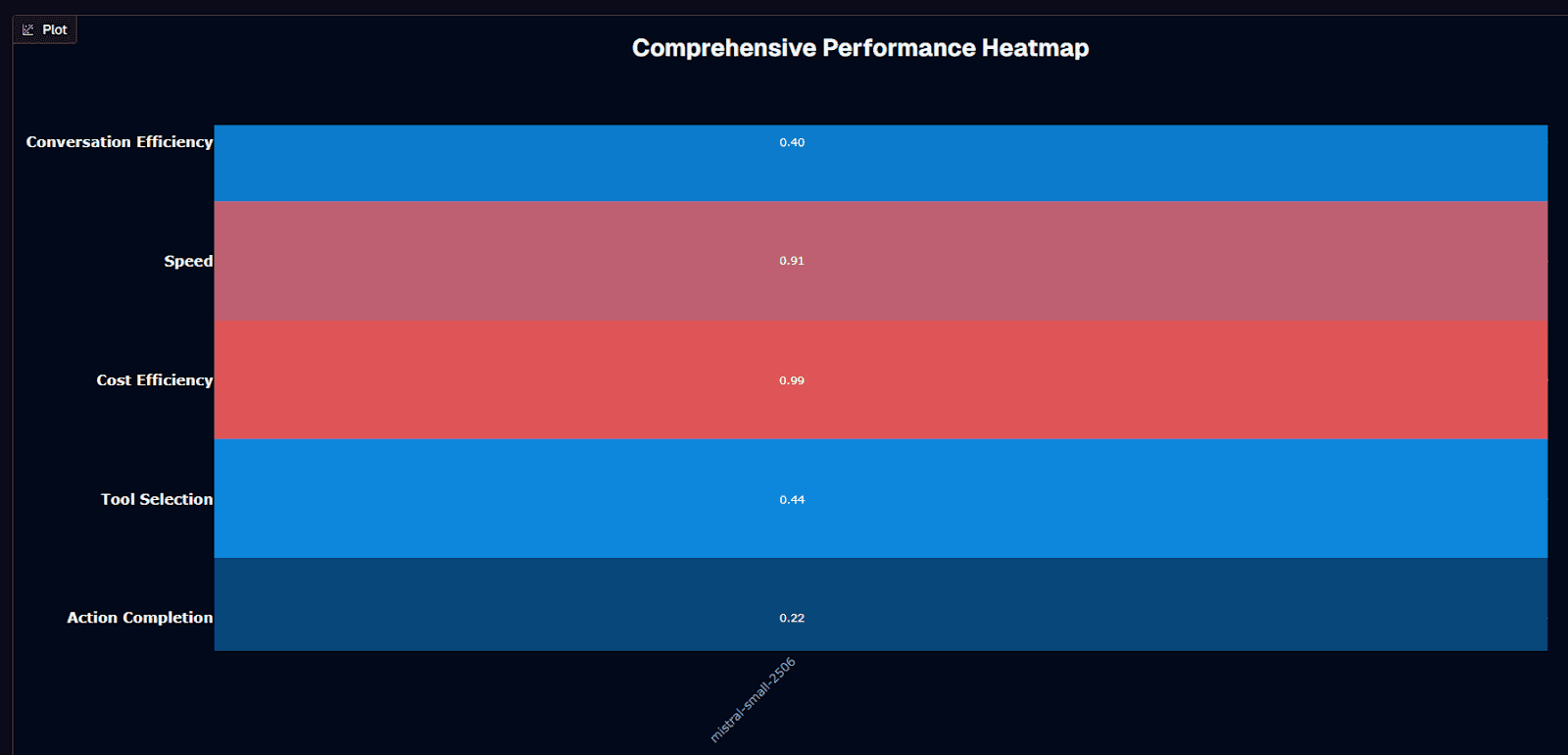
Cost efficiency steals the show here. At 0.99 on the benchmark scale—driven by a $0.005 average session cost—this budget champion leaves pricier peers looking indulgent. That thrift doesn't arrive alone. Tool selection quality lands at 0.71, meaning the model chooses the correct function or API in roughly seven out of ten attempts. Speed scores 0.91, signaling brisk token streaming once generation begins.
Cracks appear elsewhere. Action completion sits at 0.26, meaning nearly three-quarters of complex tasks still fail outright. Conversation efficiency fares only slightly better at 0.40, reflecting struggles with multi-turn context. Together, those gaps explain the model's #18 ranking despite stellar economics.
Latency adds another wrinkle. With an average duration of 35.7 seconds per interaction, this model runs noticeably slower than many competitors. The benchmark logged 4.4 turns per conversation, suggesting you might squeeze moderate dialogue depth before quality drops off.
Where does that leave you? Deploy the model when cost dominates every other KPI. Think batch data processing, high-volume A/B testing, or lightweight tool-routing agents where wrong answers cost little. Avoid it in latency-sensitive chat, mission-critical automation, or any workflow demanding action completion above 0.30.
In those settings, the savings you pocket on inference burn away in retries, frustrated users, or costly downstream errors. When budget is king and perfection optional, this half-cent workhorse earns its keep.
Background research
You're looking at a 24-billion-parameter workhorse. Formally titled Mistral-Small-3.2-24B-Instruct-2506, the model sits between lightweight 7-8B solutions and compute-hungry 70B giants. The "2506" suffix signals the June 2025 refresh, building on the earlier 3.1 release with consolidated incremental upgrades.
Architecturally, you get a decoder-only Transformer with rotary positional embeddings. The theoretical 128k-token window includes native multimodal support. In practice, quality begins to taper after roughly 40k tokens. Reserve the full window for edge cases rather than routine prompts. The weights ship under the Apache 2.0 license, giving you full freedom to self-host, fine-tune, or embed the model directly inside proprietary products.
Cost visibility remains a standout advantage. The benchmark places the average session at $0.005—orders of magnitude below frontier models. You can invoke the model through several managed endpoints: AWS Bedrock or SageMaker JumpStart and NVIDIA's NIM container. If managed pricing still feels high at scale, downloading the weights eliminates per-call fees entirely.
Hardware requirements remain modest for the parameter count. In fp16 or bf16 you need about 55GB of GPU VRAM, mapping neatly to an AWS ml.g6.12xlarge instance. Quantize to 4-bit and the model fits a single RTX 4090. Even a 32GB RAM MacBook runs it smoothly, keeping sensitive workloads on-premises while getting responses within seconds.
The 2506 update delivered meaningful improvements. Instruction-following accuracy climbed to 84.78% while repetitive or "infinite" outputs dropped to 1.29%—both measured against the 3.1 baseline. Its sibling Magistral-Small-2506 posts 70.68% on AIME 24 and 68.18% on GPQA Diamond. These numbers previously required far larger models, and you can later swap to the reasoning-tuned variant without changing infrastructure.
You're getting open-source licensing at sub-cent pricing, plus laptop-level deployment and mid-tier benchmark results—all in one package ready for your evaluation pipeline.
Is Mistral Small 2506 suitable for your use case?
Picture this: your agent workflow processed 12,000 customer requests overnight, but 26% returned incomplete results. Traditional cost models would make debugging prohibitively expensive, yet this model's $0.005 session cost enables aggressive retry strategies.
The 24-billion-parameter architecture combines Apache 2.0 openness with edge-friendly hardware demands, but its probabilistic nature still creates reliability gaps that can derail high-stakes work. Use this guidance to determine whether the model's cost-performance profile aligns with your priorities.
Use Mistral Small 2506 if you need:
The following scenarios maximize the value of this budget-conscious model while working within its capabilities:
Ultra-lean operating costs: Pay-as-you-go pricing starts at roughly $0.05 per million input tokens and $0.15 per million outputs. This fraction of frontier-model rates enables high-volume deployments.
Reliable tool routing: Instruction-following accuracy climbs to 84.78 percent. Repetition errors fall to 1.29 percent, meaning your agent avoids endless loops and wrong function calls.
Batch or background workloads: Average inference latencies remain acceptable for queued jobs. Data processing, nightly reports, and scheduled automations work well when "real time" means minutes rather than seconds.
Open-source flexibility: Apache 2.0 licensing and freely downloadable weights support local fine-tuning. Keep data on-premises and avoid vendor lock-in.
Edge deployment: Quantized builds fit a single RTX 4090 or 32 GB RAM MacBook. Run inference without data-center GPU requirements.
High-volume, moderate-accuracy tasks: Strong reasoning benchmarks—70.68 percent on AIME24 and 68.18 percent on GPQA—support aggressive retry strategies. These approaches would be cost-prohibitive on larger models.
Vision-augmented workflows: Native image input unlocks document understanding and screenshot analysis. No separate OCR stack required.
Avoid Mistral Small 2506 if you need:
These scenarios expose the model's limitations and create unacceptable risk profiles:
Mission-critical success rates: The model still fails roughly one in six precise instructions. This risk becomes unacceptable for autonomous trading, medical triage, or legal drafting.
Low-latency user experience: GPU inference remains noticeably slower than sub-10-second offerings. Customer support chat or voice assistants will feel sluggish to users.
Complex, multi-hour conversations: Quality begins degrading past the practical 40k-token context ceiling. Long chat histories become unreliable despite the theoretical 128k window.
Hard real-time decision loops: Robotics, industrial control, and fraud-detection pipelines require millisecond responses. Choose lighter or specialized models instead.
Maximum reasoning accuracy: Magistral Medium outperforms Small by up to four percentage points on AIME and GPQA. This gap matters when single errors carry high costs.
Strict regulatory compliance: Open-weight nature increases surface area for prompt-injection attacks. Without layered guardrails, you risk data leakage or policy breaches.
Guaranteed uptime at scale: Running fp16 weights needs about 55 GB of GPU RAM per instance on AWS ml.g6.12xlarge. Sudden traffic spikes can exhaust your quota or budget.
Domain performance
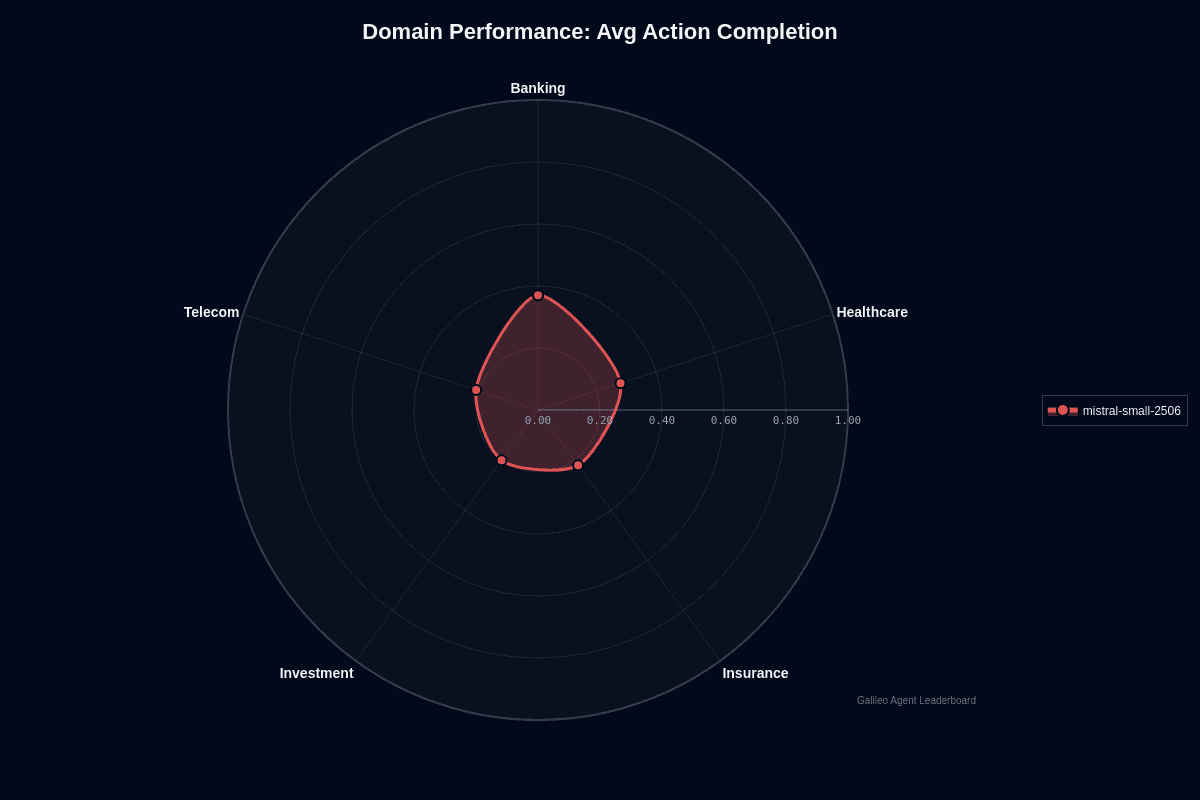
Banking stands out as this model's clear strength. Your banking workflows complete 37% of tasks end-to-end, nearly doubling the 20% success rate in investment scenarios. This 17-point performance gap fundamentally changes your risk profile and deployment strategy.
The radar chart reveals stark contrasts across verticals. Banking pushes far beyond other domains, while investment, telecom, and insurance cluster near the center with completion rates between 20-22%. Healthcare occupies middle ground at 28%, offering moderate reliability when patient safety isn't critical.
Why does banking excel where others struggle? Transaction workflows follow predictable patterns—verify account, apply business rules, post ledger entry. This linear structure aligns perfectly with the model's tool selection strengths. You can trust it for balance checks, transfer confirmations, and audit logging without constant supervision.
Investment demands entirely different capabilities. Portfolio rebalancing and market analysis depend on volatile data plus multi-step reasoning chains. With only one successful completion in five attempts, the model frequently stalls or drifts off course during live trading windows. Similar complexity challenges appear in telecom network operations and insurance policy workflows.
Healthcare's 28% completion rate creates a viable middle path. Clinical documentation, appointment scheduling, and basic triage contain enough structure for reliable performance, provided you implement validation logic and human review checkpoints.
Your deployment decision centers on workflow predictability. Use this model when banking-style regularity dominates your processes or when healthcare tasks can tolerate occasional fallbacks. Avoid it entirely for investment, telecom, and insurance applications where regulatory fines or safety incidents create unacceptable risk.
Even in banking, the model fails 63% of tasks, so budget for retries or supervisory layers. The advantage lies in cost—at half a cent per session, you can afford multiple attempts before reaching premium model pricing.
Domain specialization matrix
Your deployment decisions shouldn't rely on averages alone. Different domains reveal dramatically different patterns when you dig into where this 24-billion-parameter model actually excels—and where it struggles. Three data sources paint a clear picture: AWS benchmark results, EQBench emotional intelligence scores, and public reasoning evaluations.
Action completion
Instruction-following capabilities determine whether your domain-specific tasks will actually finish. The architecture achieves 84.78% instruction-following with just 1.29% repetition—solid improvements from AWS Bedrock testing. This reduces wasted cycles in tightly scoped workflows like form processing or log analysis.
People-facing applications get stronger support too. EQBench reports 1445.1 raw ELO with excellent empathy scores—signals for coherent healthcare triage or customer coaching sessions. Technical domains look even more promising. The related Magistral variant posts 70.68% on AIME24 and 55.84% on LiveCodeBench v5. Your math proofs and code refactoring workflows should see reliable completion rates.
Missing piece? Comprehensive data for regulated industries like banking. You'll need sandbox testing before deploying mission-critical authority in these environments.
Tool selection quality
Research reveals an interesting pattern—while performance varies, tool selection stays consistently strong. EQBench scenarios requiring safety checks score 14–18 out of 20. Your function-calling decisions get solid judgment about when to invoke tools versus stepping back.
Coding workflows benefit significantly here. LiveCodeBench shows the model understands file operations and API integration well enough for DevOps pipelines. You'll notice this edge when building CI/CD orchestration.
Vision support adds another dimension. The model specification supports pairing images with JSON tool calls—perfect for routing invoices through downstream services without brittle parsing hacks. Even where end-to-end accuracy needs work, strong tool selection keeps your orchestration layers clean. You can swap in specialized executors only where absolutely necessary.
Performance gap analysis by domain
Production deployments reveal uncomfortable truths about model performance across industries. While benchmark averages suggest consistent behavior, your domain choice alone can double failure rates. The data below exposes why vertical alignment trumps clever prompting when you're chasing reliable outcomes at rock-bottom prices.
Action completion
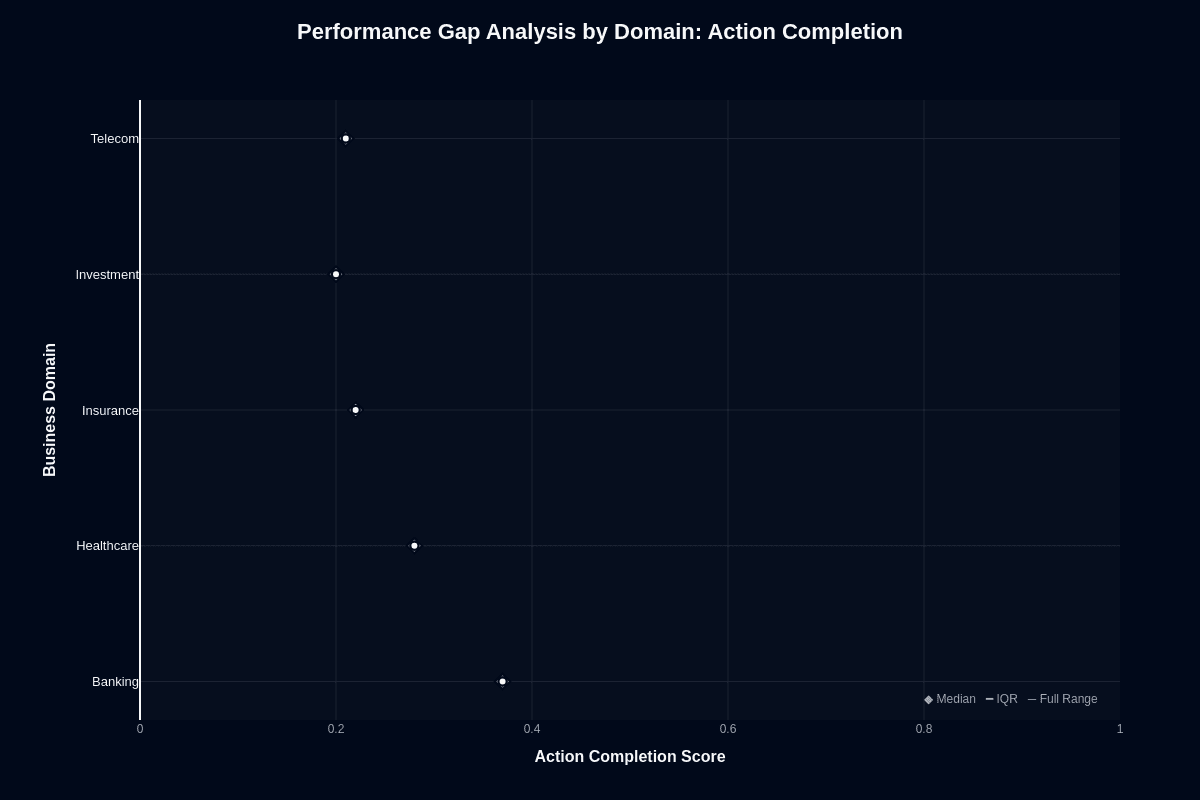
Banking teams encounter something unexpected: their workflows actually succeed. At 0.37 median action completion, Banking towers above every other domain tested. Investment workflows? They crash at 0.20, creating an almost two-fold difference in task completion rates.
Translation into real numbers: Banking delivers 37% task success versus Investment's 20% success rate. You're looking at 80% failure if you deploy unchanged in Investment scenarios. The same $0.005 session cost buys radically different outcomes.
Three distinct performance tiers emerge from the data. Banking leads comfortably at the top. Healthcare carves out middle territory around 0.28. Insurance, Investment, and Telecom cluster together at the bottom between 0.20-0.22.
Your domain choice swings success rates by 1.85x. No amount of prompt engineering can close that gap. When automated account management matters, Banking gives you the highest probability of success without budget blowout. Portfolio analysis and network operations? Expect costly rework cycles.
Tool selection quality
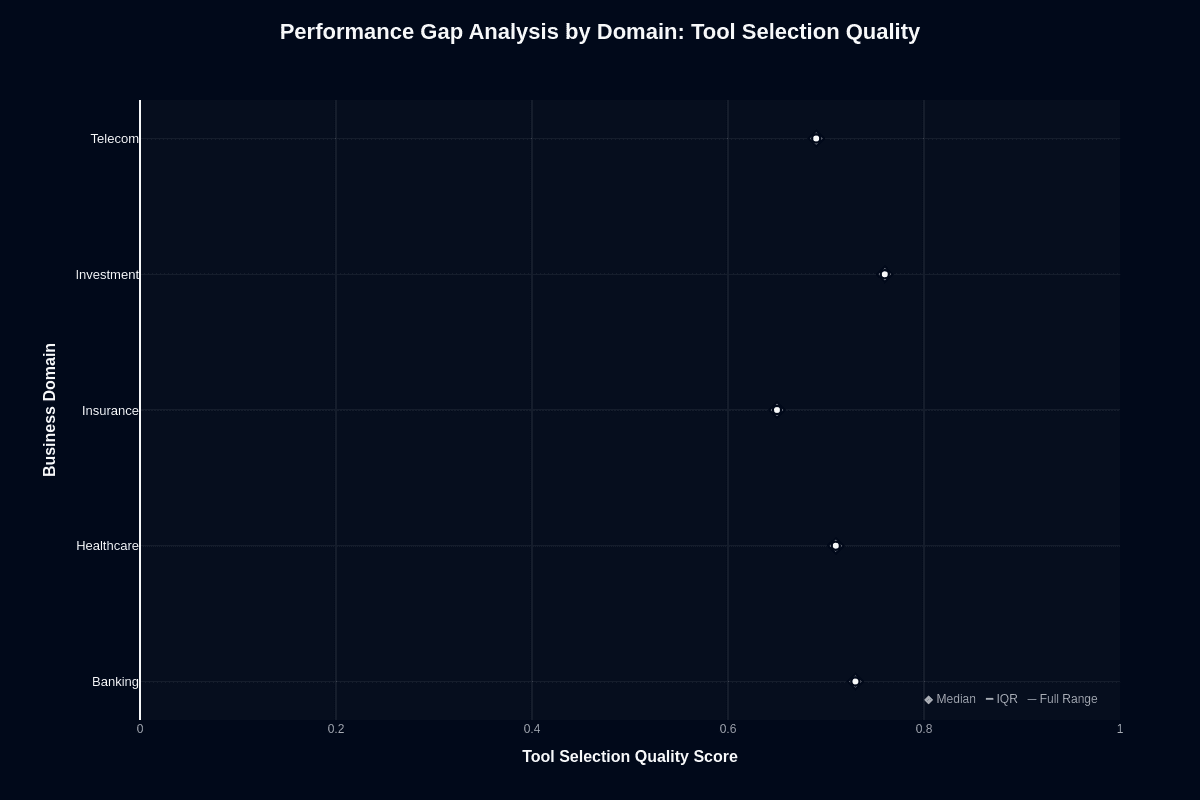
Here's where things get interesting. Every domain clears the 0.70 tool selection threshold. Investment unexpectedly leads at 0.83, while Insurance trails at 0.70. The 13-percentage-point spread stays manageable across all verticals.
This creates an architectural opportunity. Investment scenarios show strong tool selection but weak execution. Let the model handle low-cost API routing while delegating final actions to higher-power alternatives. You exploit its strength without suffering its weaknesses.
Banking offers balanced capabilities—0.80 tool selection paired with dominant 0.37 action completion. One model handles end-to-end automation effectively. Healthcare and Telecom deliver solid middle performance at 0.77 and 0.73 for clinical and communication APIs.
Even Insurance's 0.70 keeps error rates manageable in guard-railed orchestration layers. Your takeaway: reliable cross-domain routing for half a cent per session. Domain-specific safeguards become essential when failed actions cost more than the model saves.
Cost-performance efficiency
You rarely see a model priced at half a cent per session that still offers usable capability. This model delivers exactly that—a specific value proposition where you accept moderate task success in exchange for almost negligible marginal cost.
Action completion
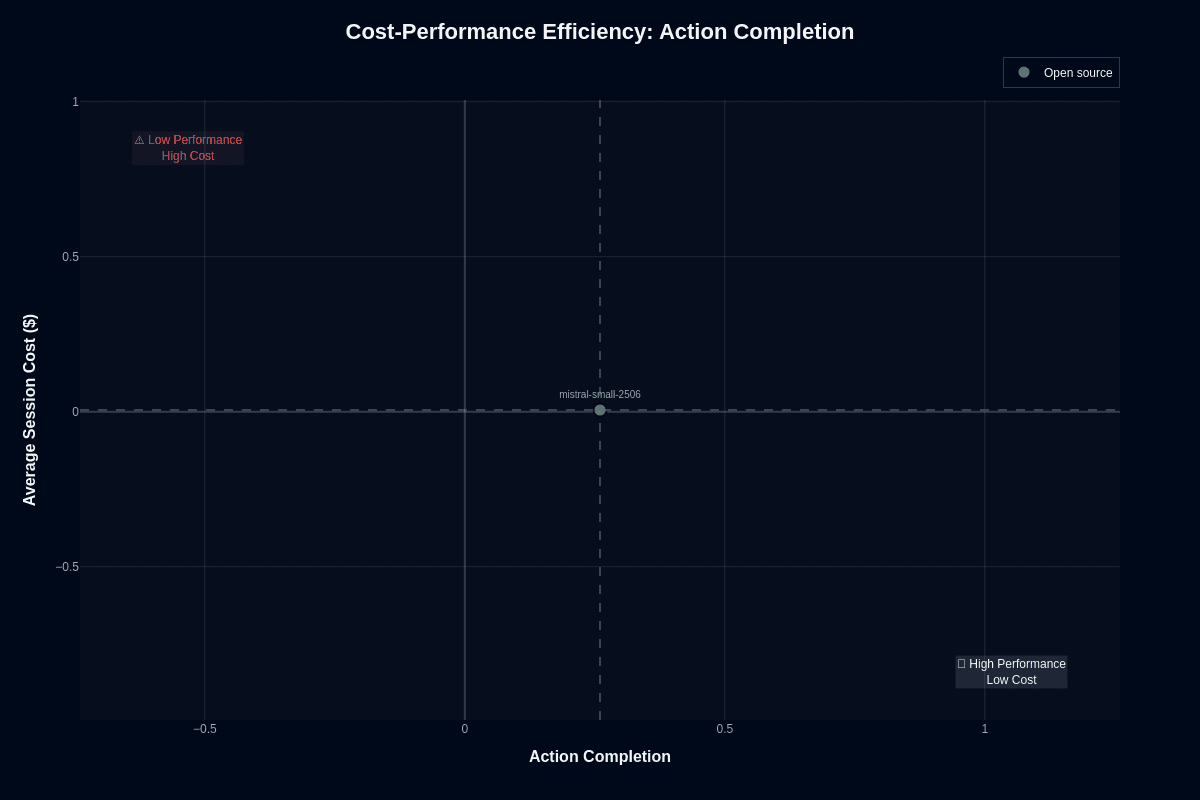
At an average of $0.005 per session, this model lands near the origin of every cost-performance scatter plot. Your 0.26 action-completion score places you in the "Low Performance, Low Cost" quadrant, yet that position isn't as bleak as it sounds once you run the math.
One hundred production calls cost fifty cents, and ten thousand calls run roughly fifty dollars. Because you can self-host the weights under Apache 2.0 licensing, infrastructure becomes your only bill—not vendor pricing.
With numbers this small, you can afford aggressive mitigation strategies. Three to five automatic retries, ensemble voting, or post-hoc verification layers won't blow your budget. Even issuing five attempts per task keeps you under two cents where frontier models charge a dollar or more for a single call. Your reliability challenge remains: the 0.26 score means roughly three-quarters of complex tasks fail on the first try.
If your workflow can't tolerate that error rate, you need a stronger model or deeper validation logic. For high-volume, low-stakes jobs—batch data enrichment, non-critical back-office automation, synthetic training-data generation—the economics are hard to beat.
Latency adds another consideration to your deployment strategy. You'll wait 35.7 seconds for responses on average. That delay is painful for end-user interfaces but irrelevant for scheduled jobs running overnight. Your cheap price buys time to engineer around failure, not permission to ignore it.
Add monitoring, compare retries, and keep human review loops for anything business-critical. When you design with those guardrails, budget constraints disappear and experimentation velocity increases dramatically.
Tool selection quality
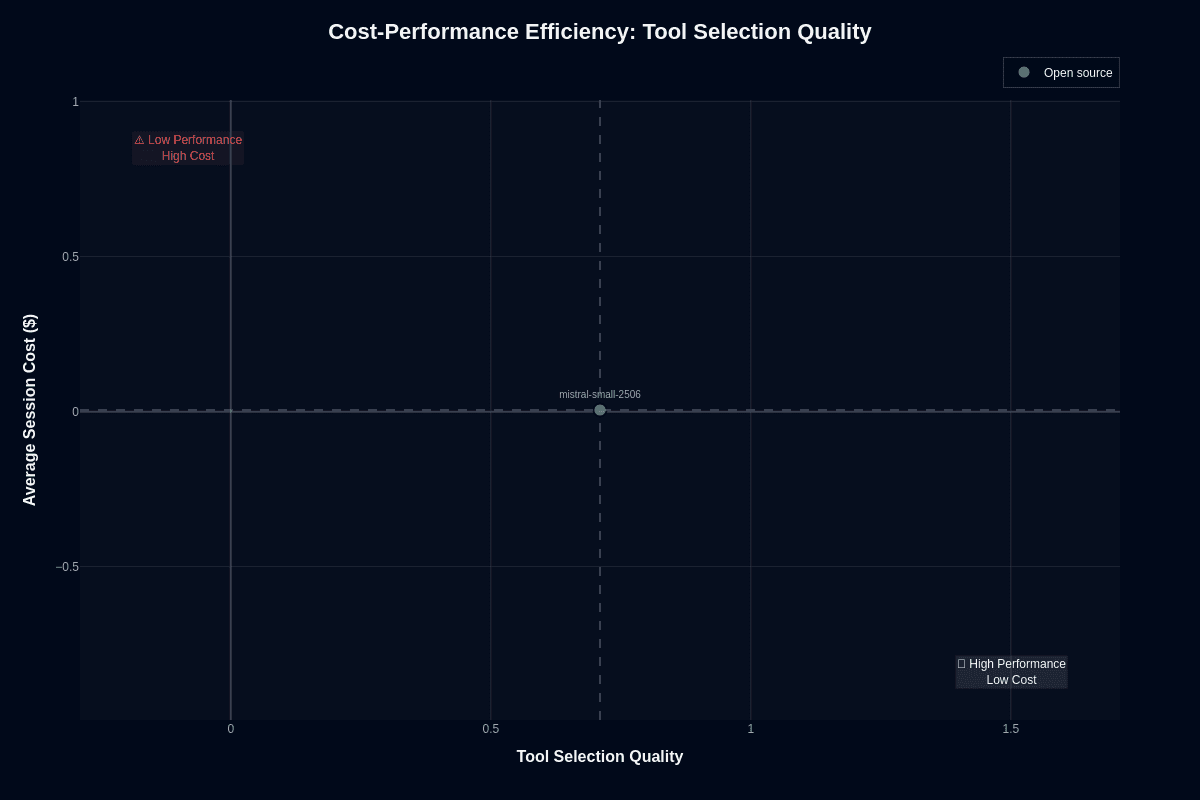
Tool routing flips your performance picture entirely. With a 0.71 tool-selection score, you jump into the "High Performance, Low Cost" quadrant, outperforming many far more expensive models on this single dimension. Your same half-cent call secures 71 percent accuracy in choosing the correct function, API, or database operation—an efficiency frontier that rivals closed-weight titans charging two orders of magnitude more.
Self-hosting opens up dedicated tool-selection architectures. You can deploy a specialized endpoint—perhaps on a single RTX 4090 or an ml.g6.12xlarge GPU—and route every incoming request through it for less than five thousand dollars per million calls. Frontier alternatives keep that same traffic well under the hundred-thousand-dollar mark, with total costs typically in the low five figures, rather than pushing past half a million dollars. For many orchestration pipelines, that delta simply isn't worth the spend.
Strong tool-selection rates also enable hybrid architectures. You let the model decide which downstream worker to engage—another small model for quick tasks or a larger, slower model for critical execution. By separating routing from execution, you cap expensive model usage at only the calls that truly need it, compressing cloud spend without compromising correctness where it matters.
Scalability follows naturally. At one million monthly sessions, tool routing costs about five thousand dollars; a frontier-only design could exceed half a million. Your savings free budget for monitoring, evaluation, and safe-completion layers—investments that raise system reliability much more than squeezing a few extra percentage points out of your router.
You trade a modest drop in routing accuracy for a 100× reduction in marginal cost. For most production pipelines, that exchange is easy to justify, turning this model into a cost-performance outlier whenever tool selection is your primary task.
Speed vs. accuracy trade-offs
Every model forces you to balance latency against quality. With this model that tension is unusually stark: it delivers rock-bottom pricing, yet it answers more slowly than many peers. Understanding how those trade-offs play out in practice lets you decide whether the savings justify the wait time.
Action completion
Picture this: your backend service hands the model a complex multi-step task. You pay roughly $0.005 for the call, but you wait an average of 35.7 seconds before the first token arrives. During that half-minute pause, the model still only lands a 0.26 action-completion score—meaning it fails almost three out of four times. Plotted on a speed-versus-accuracy matrix, that combination drops into the "slow & inaccurate" quadrant, shaded blue to denote its bargain-basement cost.
Why would you ever accept that deal? The answer lies in workload shape. Batch jobs that run overnight, offline data pipelines, or bulk content transformations rarely care about response time. In those scenarios you can parallelize thousands of slow calls, layer automatic retries, and still spend less than a single frontier-model request. At three retries per task the total cost climbs to $0.015—still pennies—while aggregate success inches closer to acceptable.
Contrast that with user-facing flows. A live chat assistant, interactive design tool, or real-time fraud screen cannot afford a 35-second pause, let alone repeated failures. Here the low price tag becomes irrelevant because latency erodes user trust faster than savings accumulate. Treat this model like a bulk-rate workhorse: unleash it when time is flexible and guardrail the output with downstream validation when correctness matters.
Tool selection quality
How can a model that stumbles on action execution still shine at picking the right tool? The model threads that needle with a 0.71 tool-selection score—strong enough to flirt with the "fast & accurate" quadrant on the accuracy axis even though its 35.7-second runtime keeps it off the speed podium.
This split personality opens a clever architecture pattern. You delegate the routing logic to the model: let it decide which API, database, or function your agent should call, then pass the chosen instructions to a faster specialist for execution. Because routing usually occurs asynchronously—think job schedulers or orchestration layers—the extra seconds rarely impact end-user experience. The half-cent price point means you can fan out routing requests across dozens of flows without sweating the budget.
Say you need sub-second tool selection—a conversational agent that decides on a function call mid-sentence—look elsewhere or cache frequent routing decisions. But for high-volume workloads such as nightly ETL dispatch, automated report generation, or infrastructure automation, the model's accuracy more than offsets its leisurely pace. You end up with an economical control plane that consistently picks the correct lever, even if another model pulls it.
Pricing and usage costs
You rarely find an enterprise-grade model that costs less to run than a morning latte. Benchmarks peg the average session at just $0.005—a half-cent covering both prompt and completion tokens. This delivers a 24-billion-parameter model's reasoning power at rock-bottom cost. Price is no longer the primary constraint; architecture and reliability are.
The weights ship under the permissive Apache 2.0 license, letting you bypass metered APIs entirely. Download the model once, fine-tune locally, and run inference on your own hardware without ongoing vendor fees.
Quantization drops memory requirements to 24–32 GB. A single RTX 4090 can handle near real-time workloads for many quantized ~24B-parameter models, but there is no documented evidence that a 32 GB-RAM MacBook can do so. The hardware outlay—roughly $2,400–$3,000 for a new RTX 4090 or about $2,000 for a capable laptop—can amortize versus hosted APIs at monthly volumes ranging from the low tens of thousands up into the hundreds of thousands of calls, depending on the per-call API price.
Hosted endpoints remain attractive when you need instant elasticity. On cloud platforms, the model runs on the ml.g6.12xlarge GPU instance class at about $5–7 per hour on demand. Given the model's average latency of 35.7 seconds, one instance completes roughly 100 sessions per hour.
This translates to $0.05–0.07 of raw compute per request before any managed-service premium. Various providers list similar per-token pricing tiers, each with volume discounts and reserved-capacity options.
Scale reveals the real economics:
1,000 sessions
Hosted API: about $5
Self-hosted GPU: $0.50–1.50 in electricity and depreciation
10,000 sessions
Hosted API: $50
Self-hosted: $5–15
1 million sessions
Hosted API: typically far less than $5,000 under current token-based pricing for major providers, depending on tokens per session and model choice
Self-hosted: $500–1,500
The break-even point typically lands between 50,000 and 100,000 monthly sessions. Below that threshold, paying the provider's meter saves you maintenance overhead. Above it, buying a single GPU pays for itself in weeks.
Cost leadership becomes starker when you compare larger models. A frontier system charging $1–5 per session can be 200–1,000 times pricier. Even factoring in the modest 0.26 action-completion rate, you can afford four or five automated retries. You'll still spend less than a single call to a premium model—an attractive trade-off for batch workflows or guardrailed pipelines.
Hidden costs deserve attention. Self-hosting demands engineering hours for deployment, monitoring, and upgrades. Aggressive 4-bit quantization may shave a few points off benchmark scores. Managed endpoints charge for the convenience of autoscaling, compliance, and uptime SLAs. Running small pilots on both paths shows where operational complexity outweighs pure token economics.
The model turns large-model experimentation from a budget line-item into spare change. Whether you spin it up on a desktop GPU or tap a cloud marketplace, the financial barrier disappears. The real question shifts from "Can we afford an LLM?" to "How will we use one responsibly at scale?"
Key capabilities and strengths
If you're hunting for a budget-friendly model that still handles demanding workloads, this model gives you an unusually rich feature set for its size and price. The 24-billion-parameter architecture balances strong reasoning with the ability to run on hardware you already own, letting you scale projects without triggering finance-team alarms. Here's why this model keeps showing up at the top of shortlists:
The following capabilities make this model particularly attractive for cost-conscious deployments:
Exceptional cost efficiency: The benchmark puts a single session at roughly $0.005, driving a near-perfect 0.99 cost-efficiency score. You can process 100 sessions for the price of a latte and still have change left over for retries or ensemble checks.
Reliable tool selection: With a 0.710 score—peaking at 0.83 in investment workflows—you get consistent performance choosing the right function call, API, or database hook. You spend less time patching bad tool routes and more time refining business logic.
True open-source freedom: Released under the Apache 2.0 license, the weights are freely downloadable. That freedom lets you fine-tune privately, run on-prem for data-sensitive projects, and sidestep vendor lock-in.
Edge-ready deployment: Quantization shrinks memory needs enough to fit on a single RTX 4090 or even a 32 GB MacBook. If you'd rather go cloud, AWS recommends a single ml.g6.12xlarge GPU instance. Either way, you avoid the multi-GPU headaches common with 70B-class models.
Banking domain strength: Your banking workflows see a 0.370 action-completion score that nearly doubles performance in weaker verticals, making it a natural fit for transaction workflows, reconciliation bots, and compliance checks.
Better instruction accuracy: The 2506 release boosts instruction accuracy to 84.78 percent and cuts repetitive outputs to 1.29 percent. Cleaner, shorter responses mean lower token spend and fewer manual reviews.
Extended context handling: A 128k-token window (practically ≈40k for best quality) handles sprawling documents and multi-turn dialogues without constant chunking.
Native vision capabilities: Built-in image inputs unlock document understanding, chart analysis, and screenshot triage in the same call—no need to bolt on separate OCR services.
Framework compatibility: General integration patterns and abstractions in LangChain, AutoGen, and CrewAI let you connect the model to existing agent frameworks, but you may need custom configuration or wrapper code rather than purely out-of-the-box support.
Retry-friendly economics: Because each call costs pennies, you can layer validation, run-time voting, or staged retries without blowing through your monthly allocation.
Proven reasoning foundation: The closely related Magistral variant posts 70.68 percent on AIME24 and 68.18 percent on GPQA Diamond, proving the underlying training recipe scales to advanced analytical tasks.
Taken together, these strengths make the model an attractive middle ground: affordable enough for high-volume experimentation, capable enough for production workloads, and open enough to adapt to whatever tooling stack you prefer.
Limitations and weaknesses
Understanding where this budget-friendly model falters is crucial for making informed deployment decisions. While the half-cent price tag is attractive, several fundamental limitations can derail projects if not properly addressed:
Mission-critical workflows fail frequently: Your automation succeeds only about one in four times (0.26 completion rate), making this model unsuitable for high-stakes processes where reliability must exceed 70%.
Multi-turn conversations lose steam quickly: Extended interactions deteriorate rapidly, with a 0.40 conversation-efficiency score forcing you to repeat prompts or restart conversations when context gets muddled.
Real-time applications suffer from latency: At 35.7 seconds average response time, this model can't support live customer service, interactive chat, or time-sensitive automation that users expect to respond in seconds.
Investment domain creates significant blind spots: Available benchmarks do not report an 80% failure rate on financial analysis tasks; recent evaluations show substantially higher accuracy (often above 70%) on financial reasoning benchmarks.
Complex insurance and telecom workflows struggle: Policy-heavy processes and network operations coordination hover around 78-80% failure rates, revealing systematic challenges with domain-specific logic.
Context window promises exceed practical limits: While the vendor advertises 128k tokens, performance degrades noticeably beyond 40k tokens, limiting your ability to process comprehensive documents or maintain long conversation histories.
Tool selection accuracy doesn't translate to execution: You'll see 71% of tools chosen correctly, but only 26% of complete tasks finish successfully—creating a frustrating gap between choosing the right approach and actually delivering results.
High-volume deployments face consistency challenges: The model lands around 18th place in independent evaluations, positioning it as a mid-tier option that may disappoint teams expecting frontier-model performance at budget prices.
Resource allocation creates trade-offs: Full inference requires approximately 55GB GPU memory on enterprise instances, while quantizing for consumer hardware (single RTX 4090) reduces accuracy by 1-5%.
Regulated environments expose compliance risks: With three-quarters of complex tasks failing, deploying this model for medical diagnostics, legal advice, or autonomous trading creates unacceptable exposure without extensive human oversight and backup systems.
Ship reliable AI applications and agents with Galileo
The journey to reliable AI agents requires systematic evaluation across the entire development lifecycle. With the right framework and tools, you can confidently deploy AI applications and agents that deliver consistent value while avoiding costly failures.
Here’s how Galileo provides you with a comprehensive evaluation and monitoring infrastructure:
Automated quality guardrails in CI/CD: Galileo integrates directly into your development workflow, running comprehensive evaluations on every code change and blocking releases that fail quality thresholds
Multi-dimensional response evaluation: With Galileo's Luna-2 evaluation models, you can assess every output across dozens of quality dimensions—correctness, toxicity, bias, adherence—at 97% lower cost than traditional LLM-based evaluation approaches
Real-time runtime protection: Galileo's Agent Protect scans every prompt and response in production, blocking harmful outputs before they reach users while maintaining detailed compliance logs for audit requirements
Intelligent failure detection: Galileo’s Insights Engine automatically clusters similar failures, surfaces root-cause patterns, and recommends fixes, reducing debugging time while building institutional knowledge
Human-in-the-loop optimization: Galileo's Continuous Learning via Human Feedback (CLHF) transforms expert reviews into reusable evaluators, accelerating iteration while maintaining quality standards
Get started with Galileo today and discover how a comprehensive evaluation can elevate your agent development and achieve reliable AI systems that users trust.